* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 3 * Chapter 3 Biochemistry
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Biosequestration wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
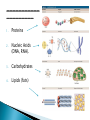
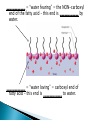
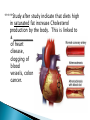
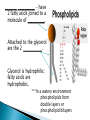
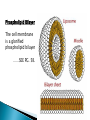
Water – is a _______________ (different ends of the molecule are oppositely charged). - This causes an attraction between water molecules and leads to the “sticky” nature of water. - Also allows water to _________________________ ________________(sugar, salt, protein). - Many dissolved (dissociated) ions are found in aqueous solutions in living things. ____________________– forms between water molecules (positive H end links to negative oxygen end). Causes water to have its “sticky” nature. - Hydrogen bonds are _________________, but they play a role in many molecules. ____________ – attractive force between particles of the ______ kind. Ex.) Water bulging from the brim of a full glass. ____________ – attractive force between __________ substances. Ex.) Attraction between water and straw or meniscus in a graduated cylinder. ____________ – Adhesion/Cohesion working together to move liquids in narrow tubes, upward against the force of gravity. This is known as capillary action. _________________ ___________________________________. Organic Compounds – made within living systems. A key feature is the presence of ____________ in organic compounds. ____________(Covalent Bonding) – carbon only has 4 e-’s in its outer shell…..it would like to have 8. Therefore, carbon will easily form covalent bonds to fill its shell. - - Carbon ___________________________________ ________________________________________. See page 52, figure 3-5 NOTE – carbon will form double or triple bonds, if needed, to fill its outer shell. _______________________– clusters of atoms that influence the properties of molecules they are a part of. Ex.) -OH (hydroxyl group) – if this is attached to an organic compound, it will form an alcohol. ____________ – smaller subunits that can join to form larger carbon compounds. ____________ – many monomers linked together. ____________ – very large molecule (polymer). Ex.) DNA _______________________– the linking together of monomers to form a polymer – water is removed (condensed) from this reaction. Ex.) ________ + ________ → _______ + ________ - See figure 3-8, page 54 ____________ – Exact reverse of the Condensation reaction above. Water is added to cause the breakdown of a polymer……See figure 3-9, page 54. ________________________ - energy currency for cells. Energy is stored between the bonds of the 3 phosphate groups in . All cell reactions are powered by energy stored in ATP. Ex.) A-P-P-P + water → A-P-P + P + Energy ______________________ __________________ 1. 2. Proteins Nucleic Acids (DNA, RNA). 3. Carbohydrates 4. Lipids (fats) _______________________ – made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen…….hydrogen and oxygen are always in a 2 to 1 ratio. **There are 3 classes of Carbs. 1. 2. 3. _______saccharides ______sacharides _____saccharidessugars 1. - Monosaccharides – _________ ______________ (monomers) Most common monosaccharides: a. Glucose - main energy source for cells. b. Fructose – fruit sugar c. Galactose – milk sugar *The above 3 monosaccharides are ISOMERS – they have the same molecular makeup, but are in slightly different forms. 2. Dissacharides – ____________ – 2 monosaccharides joined together by a condensation reaction. a. Sucrose (table sugar) = glucose + fructose b. Lactose (milk sugar) = glucose + galactose c. Maltose (malt sugar) = glucose + glucose 3. Polysaccharides – ________ monosaccharides joined together (polymer or macromolecules). a. Starch – plants make it, we use for food. b. Cellulose – plant cell walls….we cannot digest (fiber)……also wood, cotton fibers, etc. Proteins – organic compounds made mainly of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. _______________– monomer building blocks of proteins. (20 different kinds). See page 194. Structure of Amino Acids – consist of a carbon atom bonded to 4 other functional groups: a. ________________ b. __________________(-COOH) c. ________________(-NH₂) – note NH₃ = ammonia d. _____________– different in all 20 amino acids. NOTE – as R – group changes, this gives proteins different shapes and properties. See page 56. ____________– condensation reaction that joins amino acids together. See page 57. ____________ – 2 amino acids linked by a peptide bond. ____________ – Many amino acids (can be 100’s) linked together by peptide bonds. ____________ = 1 or more polypeptides – often they bend and fold on one another to take on different 3D shapes and properties. Protein Shapes – influenced by conditions such as Temperature, pH, etc. Ex.) Egg Albumin → Heat → Egg White Enzymes – most are proteins. 1,000’s act as ____________ ____________ - help many reactions take place. Ex.) Lactase is an enzyme that helps us digest Lactose (milk sugar). If a person lacks this enzyme, they are lactose intolerant and get sick when they consume dairy products. Enzyme reactions depend on a physical fit between the enzyme and the substrate (the reactant being catalyzed) ___________________________– explains how enzymes work. Enzymes are very specific for the reactions they work in. See page 57 in book. Lipids (fats, oils, waxes) – ____________________ _____ ____ ____________ ________ _______ . They have a higher ratio of carbon/hydrogen : oxygen than carbohydrates. -Lipids store more energy than Carbs (9 calories/gram vs. 4 calories/gram in Carbs) ____________– make up most lipids. - They are long straight carbon chains + a carboxyl group (-COOH) at one end -Fatty acids have both polar and non-polar ends and 12 to 28 carbons in their chains. See page 58. ____________ = “water fearing” = the NON-carboxyl end of the fatty acid – this end is ____________ by water. ____________ = “water loving” = carboxyl end of fatty acid – this end is ____________ to water. ____________ – ______ ____________ ______ of dietary fat. = Glycerol + 3 fatty acids. -glycerol never changes, BUT there are many different types of fatty aids (some are saturated and some are unsaturated). ***If you change the fatty acids that are attached to the glycerol, you change the type of fat you get. That is – you get either saturated or unsaturated fats…..THIS MAKES A BIG DIFFERENCE FOR HEALTHY FOOD CHOICES!!!!!!!!! ____________– carbons in the fatty acid are bonded to 4 atoms….. ____________ are required to make the carbon e- shell complete. The carbons are “saturated with atoms”. Tend to be solid at room temperature. Exs.) lard, crisco, butter, fat in meats ____________– carbon atoms have to form double or triple bonds between themselves to fill their outer e- shell. Tend to be liquid at room temperature. Exs.) Plants oils such as – corn oil, olive oil, canola oil, peanut oil, etc. *****Study after study indicate that diets high in saturated fat increase Cholesterol production by the body. This is linked to a __________ of heart disease, clogging of blood vessels, colon cancer. _______ __________ – have 2 fatty acids joined to a molecule of __________. Attached to the glycerol are the 2 ___________. - Glycerol is hydrophilic; fatty acids are hydrophobic. ***In a watery environment phospholipids form double layers or phospholipid bilayers Phospholipid Bilayer The cell membrane is a glorified phospholipid bilayer ……SEE PG. 58. _________ – is highly waterproof found in places like the wax coating on leaves and earwax. Steroids – lipids made of _________________ ____________ . Exs.) many animal hormones, testosterone, cholesterol, synthetic steroids. ____________– store hereditary information – also known as the genetic code. Exs.) DNA, RNA. ____________ – monomer building blocks of nucleic acids. Made up of a sugar + phosphate + nitrogen base. See page 59. DNA = _____ _________________ (Deoxyribose is the sugar). Contains the master set of instructions to direct the cell’s activities. RNA – ________ _______________ (Ribose is the sugar). Stores the information needed for making proteins.