* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BreastNext: A 17-Gene Hereditary Breast Cancer Test
Survey
Document related concepts
DNA paternity testing wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
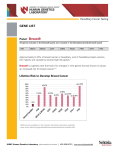
BreastNext: A 17-Gene Hereditary Breast Cancer Test white paper november 2014 key point logistics BreastNext is a multi-gene test that analyzes 17 breast cancer susceptibility genes: ATM, BARD1, BRCA1, BRCA2, BRIP1, CDH1, CHEK2, MRE11A, MUTYH, NF1, NBN, PALB2, PTEN, RAD50, RAD51C, RAD51D, and TP53. Many patients undergoing BRCA1 and BRCA2 testing for a history of breast cancer have no mutation identified. Multi-gene testing increases the likelihood of identifying an explanatory gene mutation that may clarify the patient’s future cancer risk(s) and target medical management. •Blood or saliva samples accepted (6-10cc blood; 2 Oragene saliva kits) • Insurance verification is performed either before or after a sample is sent to the lab, per the clinician’s request. Patient notified prior to test initiation if out-of-pocket cost is expected to be greater than $100 •Ambry is contracted with the majority of health plans, Medicaid plans, and Medicare • AmbryPort 2.0 provides an easy way to order testing and receive reports through a HIPAA compliant, secure online portal • 2-4 week TAT potential indications for breastnext testing •Early-onset breast cancer (diagnosed ≤ 45, particularly if diagnosed ≤ 35) •Bilateral or multiple primary breast cancers • Male breast cancer at any age • Breast and ovarian cancer in the same woman • Three or more cases* of breast, ovarian, and/or pancreatic cancer •Multiple close family members* with breast and other cancers * on the same side of the family technology • Next generation sequencing (NGS) with Sanger confirmation of all reported alterations, including variants of unknown significance (VUS) • Custom targeted microarray (aCGH) for detection of deletions/duplications penetrance vs. prevalence of brcaplus and breastnext genes penetrance vs. prevalence of brcaplus and breastnext genes fanconi anemia/brca1/2 pathway DNA Double-Strand Break dna doublestrand break BRCAplus mre11 rad50 nbn atm tp53 Cell Cycle Checkpoint and/or Cell Death * chek2 bard1 brca1 brip1 palb2 brca2 pten rad51 xrcc3 rad51c rad51d * Low penetrance SNP’s have been identified in these breast cancer susceptibility genes which do not influence clinical management and are thus not included in Ambry’s test. rad51b xrcc2 dna repair DNA Repair breastnext experience as of october 2014 Mutation Identification In Over 7000 Recent BreastNext Tests BreastNext Mutation Distribution for Over 500 non-BRCA1/2 Positive Cases * RAD51D RAD51C CDH1 MUTYH biallelic MRE11A PTEN NBN Negative MUTYH Carrier BARD1 BRIP1 VUS Positive 68.32% TP53 RAD50 CHEK2 NF1* 1.73% PALB2 21.52% ATM 8.43% Many patients undergoing BreastNext previously underwent BRCA1 and BRCA2 genetic testing. As 5-10% of patients are identified to have a mutation on BRCA1 and BRCA2 testing, it is expected that the overall detection rate of BreastNext would be 13-18% in BRCA1/2-naive patients. rationale for considering breastnext •Higher probability of detecting an explanatory gene mutation than single gene testing •Concurrent testing reduces the likelihood of patients being lost to follow-up •Many patients have personal and family histories that are suggestive of mutations in multiple BreastNext genes * Interesting Finding: 40% of NF1 mutations identified through multi-gene panels were in patients who did not meet clinical criteria1 Summerour et al (2014, October) NF1 Mutations Detected on Multi-Gene Cancer Panel Testing in Probands with Atypical Phenotypes, Poster presented at the 33rd annual meeting of the National Society of Genetic Counselors, New Orleans, LA 1 CANCER IN FAMILY POTENTIALLY CAUSATIVE GENES Breast & Pancreatic BRCA1, BRCA2, PALB2, ATM Breast & Colon TP53, CHEK2, PTEN Breast & Ovarian RCA1, BRCA2, BARD1, BRIP1, RAD51C, B RAD51D, TP53 case example Relevant History 40 80 50 90 94 Pancreas 87 95 borderline ovarian tumor - 70 65 Lung •Patient was diagnosed with breast cancer at 58 •There is a family history of multiple cancers including pancreatic, ovarian, and breast •Clinician ordered BreastNext given the history being suggestive of multiple gene mutations including BRCA1, BRCA2, PALB2, and ATM Result • PALB2 pathogenic mutation identified Cancer Risks With a PALB2 Mutation 2 55 Esoph 68 Breast - 58 Bilateral Mastectomy 70 75 Melanoma - 44 64 60 Pancreas - 60 71 Breast - 59 •Risk of breast cancer is 35% by age 70 (ranging from 33-58% depending on family history)2 •Elevated risk for pancreatic cancer •Possibly elevated risk for ovarian cancer Implications 33 •Patient already had bilateral mastectomy •Pancreatic cancer screening can be offered •Other cancer risks (such as ovarian) may be increased •Family members may have genetic testing for the familial mutation to better assess their cancer risk(s) 2 50339.1465_v3 15 Argonaut, Aliso Viejo, CA 92656 Antoniou AC et al. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014 Aug;371(6):497-506 Toll Free 866 262 7943 Fax 949 900 5501 ambrygen.com