* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download N - barransclass
Electrostatics wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Field (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Condensed matter physics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
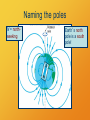
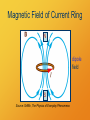
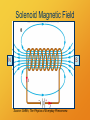
Magnetism The shadow of electricity Magnetic Force Magnets apply forces to each other. Opposite poles attract, like poles repel. CPS Question The magnitude of the force between magnetic poles A. is the same at all distances. B. becomes stronger as the poles come closer. C. becomes weaker as the poles come closer. Magnetic Field Lines Conventions as with electric field lines. direction is direction of force on a north pole strong field where lines are close together Field lines point from North to South pole. Group Work 1. What happens to a dipole magnet in a uniform magnetic field? B N S Naming the poles N = northseeking Earth’s north pole is a south pole! Current Creates Magnetism An electric current creates a magnetic field. Look, Ma! No poles! Vector Direction Conventions Left Right Up Down In Out Poll Question If a wire in front of you carries a current from left to right, what is the direction of the resulting magnetic field where you are? I A. B. C. D. E. F. Board Work An electric current creates a magnetic field whose lines circle right-handed around it. Draw lines for the magnetic field created by a ring of current. I Magnetic Field of Current Ring N dipole field S Source: Griffith, The Physics of Everyday Phenomena Solenoid Magnetic Field N S Source: Griffith, The Physics of Everyday Phenomena Electrons are Magnets! spin Electrons are Magnets! current Electrons are Magnets! magnetic field Electrons are Magnets! N S magnetic dipole Types of Magnets • Electromagnets – currents travel through conducting coils • Permanent Magnets – materials whose electrons have aligned spins or orbits Moving charges create the fields!