* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 15 Evolution KL updated
Objections to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
The Expression of the Emotions in Man and Animals wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
On the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
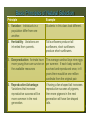
Chapter 15 Evolution 15.1 Darwin’s Theory of Natural Selection 15.2 Evidence of Evolution 15.3 Shaping Evolutionary Theory 15.1 Darwin’s Theory of Natural Selection ! Main idea: Charles Darwin developed a theory of evolution based on natural selection ! Objectives n Discuss the evidence that convinced Darwin that species could change over time. n List the four principles of natural selection. n Show how natural selection could change a population ! New Vocabulary n Selective breeding, Artificial selection, Natural selection, Evolution Developing the Theory of Natural Selection ! Charles Darwin boarded the HMS Beagle in 1831. ! Most believed the world was about 6,000 years old. ! During the ship’s five year voyage, Darwin made extensive collections of rocks, fossils, plants and animals. ! He also read Charles Lyell’s Principles of Geology – a book proposing the Earth was millions of years old. Developing the Theory of Natural Selection HMS Beagle ! In 1835, the Beagle arrived in the Galapagos Islands off the coast of South America. ! Darwin began to collect mockingbirds, finches, and other animals on the four islands. ! He noticed that the different islands seemed to have their own, slightly different varieties of animals. Developing the Theory of Natural Selection Galápagos Islands ! Almost every specimen that Darwin had collected on the islands was new to European scientists. ! Darwin suspected populations from the mainland changed after reaching the Galápagos. Developing the Theory of Natural Selection ! Darwin hypothesized that new species could appear gradually through small changes in ancestral species. ! Darwin inferred that if humans could change species by artificial selection (selective breeding), then perhaps the same process could work in nature. Developing the Theory of Natural Selection Natural Selection ! Darwin called his theory Natural Selection ! He reasoned that, given enough time, natural selection could modify a population enough to produce a new species. Basic Principles of Natural Selection Principle Example 1. Variation: Individuals in a population differ from one another. Students in this class look different. 2. Heritability: Variations are inherited from parents. Tall sunflowers produce tall sunflowers, short sunflowers produce short sunflowers. 3. Overproduction: Animals have The average cardinal lays nine eggs more young than can survive on per summer. If each baby cardinal the available resources survived and reproduced once, in 8 years there would be one million cardinals from the original pair. 4. Reproductive Advantage: Variations that increase reproductive success will be more common in the next generation. If having a fan-shaped tail increases reproductive success of pigeons, then more pigeons in the next generation will have fan-shaped tails. The Origin of Species ! Darwin published On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection in 1859. ! Today, biologists use the term evolution to define changes in groups of organisms through time. ! Darwin’s theory of natural selection is NOT the same as evolution. Natural selection is a means of explaining HOW evolution works. 15.2 Evidence of Evolution ! Main idea: Multiple lines of evidence support the theory of evolution. ! Objectives: n Describe how fossils provide evidence of evolution. n Discuss morphological evidence of evolution. n Explain how physiology and biochemistry provide evidence of evolution. ! New Vocabulary n Derived trait n Ancestral trait n Homologous structure n Vestigial structure n Analogous structure n n n n Embryo Fitness Mimicry Camouflage