* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch 25 and 26 Phylogeny and The History of Life on Earth
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
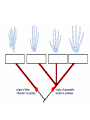
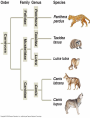
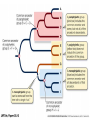
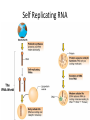
Phylogenetic Trees and The History of Life on Earth Ch 25 & 26 Phylogeny • The evolutionary history of a species or group by using: – The fossil record – Systematics (morphological and molecular (DNA) analysis) --Continues to change as we learn new info! Homologies • Morphological- comparing body forms of current and extinct organisms • Molecular- comparing DNA; the closer the sequence the more related – Some analogous structures (wings in insect compared to a bat) may have very different molecular origins. The result of convergent evolution. Evaluating Molecular Homologies • The more time that has passed, the more mutations in the DNA sequences of organisms and the less closely related they are. • This can be used as a fairly accurate “molecular clock” since the rate of some gene mutations is constant. Taxonomy • Created by C. Linnaeus • Classifying life based on similarities and differences. • Binomial nomenclature- a two part scientific name of the Genus and species taxa – Ex: Panthera leo and Panthera pardus Heirarchical Classification Phylogenetic Trees • Hypotheses about evolutionary relationships – Each branch point is a divergence from a common ancestor. Cladogram • Clade- within a tree, includes ancestor and all its descendants • Diagram that shows shared characteristics How We Think Life Arose • 1. small organic molecules form • 2. they join into larger molecules like protein and nucleic acid • 3. protobionts are membrane enclosed droplets • 4. self-replicating molecules (RNA) form Experiment • Oparin and Haldane hypothsized early conditions that Miller and Urey tested. Self Replicating RNA • Hypothesized to be the first genetic material. Fossil Record • Relative Dating- youngest on the top Radiometric Dating Create a Time Line of Earth’s History! • Needs to be to scale • Include marks for every .25 billion years • Illustrate and label the following events: Earth forms 4.6 bya Life emerges (prokaryote) 3.8bya Photosynthetic prokaryotes produce O2 2.7 bya Eukayotes appear 2.1 bya Multi cellular organisms 1.2 bya Plants, fungi, animals colonize land .5bya 5 major MASS extinctions!