* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Role of cardiac CT in coronary artery diseases
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiothoracic surgery wikipedia , lookup
Echocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
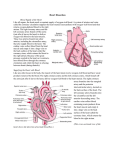
Role of cardiac CT in coronary artery diseases Dr. Ahmed Refaey MBBCh, MS, FRCR Format of the lecture • • • • Normal anatomy of coronary arteries MSCT coronary angio Clinical application of CTA Illustrated cases Coronary arteries anatomy LCA “ left coronary artery “ • Normally arises from the left sinus of Valsalva • Courses posterior to the right ventricular outflow tract (RVOT), and bifurcates into the left anterior descending (LAD), and the left circumflex (LCX) branches. Right Coronary Artery (RCA) • Normally arises from the right coronary sinus (CS) and courses in the right AV groove toward the crux of the heart Diagnosis Of CAD • Clinical Presentation • ECG • Echocardiography • Stress Test • Thallium Study • Coronary cathetrization • Multislice Coronary CT Scan Methods of imaging of coronary arteries • Coronary catheterization • Multislice cardiac CT Coronary catheterization CORONARY CATHETERIZATION Advantages • High resolution • Option for intervention Disadvantages • X-ray exposure • Hospitalization • Invasive complications Figure 21.8d Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings Multislice CT coronary angiography What is Coronary CTA? • Coronary CTA is a non-invasive minimal risk procedure to directly visualize the coronary arteries through administration of IV contrast • It allows visualization of the coronary arteries similar to a cardiac catheterization with additional information about the WALL of the artery and composition of plaque (calcified or non-calcified) Clinical application of CTA • Diagnosis of CAD * intermediate liklihood of disease * after equivocal/discordant stress imaging * coronary anomalies * before vascular surgury * nonischemic vs ischemic cardiomyopathy * acute chest pain * bypass graft patency / location Patient Preparation • No Caffeine for 12 hours prior to exam • Everyone gets Beta-Blockers (Verapamil can be substituted) Goal Heart Rate • < 60 bpm makes us happy Contraindications • • • • • • Atrial Fibrillation Tachycardia Beta Blockade Contraindication Heart Block Renal Failure (Creat>1.5) Contrast Allergy The Examination Computed Tomography (CT) X-ray tube and detector rotate around the patient, transversal slices are constructed following each rotation by computer Spiral multislice CT continuous scanning instead separated slices • Entire heart imaged in 5-15 seconds • CT images that are used come from mid to end diastole due to relative motion free period CT Angiography Timing CT-Angio Advantage Excellent for Coronary vessel, bypass vessels, LV wall thickness and function, cardiac anatomy and pericardium assessment Coronary Vessel Analysis Maximum Intensity Projection Soft Plaque in Proximal LAD Curved Planar Image 3-D Volume Rendered Image Effective Radiation Doses for Various Tests • • • • • • • • • Bone Density CXR: Mammogram: CT of the head: CT colonoscopy CT of the abdomen: Stress Gated Myocardial Perfusion Scan SPECT: CT chest: MSCT angiogram: • Coronary angiography: • CT chest/abd/pelvis: • Dose allowed for radiological personnel: 0.01 mSv 0.02 mSv 0.7 mSv 2 mSv 5 mSv 10 mSv 10-11 mSv 13 mSv 15 mSv 30mSv 35 mSv 20 mSv/year CLINICAL APPLICATION OF CARDIAC CT ANGIO 1. 2. 3. 4. Examine plaque components Evaluate coronary vessels Evaluate stent patency Assess cardiac function Examine plaque components Plaque Characterization • Calcified vs. Soft • Plaque composition rather than the degree of lumen stenosis determines the risk of plaque rupture. • Vulnerable or “high-risk” plaques have thin fibrous cap with extracellular lipid core. • Not visible by catheterization, but is being explored with CT angio. • Plaques initially grow extrinsic and bulge adventitia, then grow into the lumen resulting in stenosis Coronary Artery Plaque: approximate amounts of lipid rich, fibrotic and calcified plaque Fibrotic & Calcified 20% 66% Fibroti c 33% Lipid Rich The “Tip of the Atherosclerotic 80% Iceberg” What does coronary calcification mean? • Calcium score correlates extremely well with coronary event risk • If multi-vessel CAC, then risk increases • Zero calcification suggests a very low probability of obstructive disease Curved MPR reformatted image of Right Coronary Calcium Scoring “ Agatston score” • The Calcium Scale The calcium scale is a linear scale with 4 calcium score categories: 0 1–99 100–400 >400 none mild moderate severe *Calcium score correlates directly with risk of events and likelihood of obstructive CAD* Agatston-90 Examples of Coronary Artery Scans NO CALCIFICATION MODERATE SIGNIFICANT CALCIFICATION CALCIFICATION Images courtesy of HeartScan San Frasco Coronary Artery Calcium Scans – – – – – Task: Detect Calcium in Coronary Artery 130 kVp 625 mA .1 sec 3 mm Coronary Artery Calcium Scans Coronary Artery Calcium Scans Coronary Artery Calcium Scans Coronary Artery Calcium Scans Coronary Artery Calcium Scans Coronary Artery Calcium Scans Coronary Artery Calcium Scans Coronary Artery Calcium Scans Coronary Artery Calcium Scans Calcification in LAD Calcification in RCA EVALUATING CORONARY VESSELS It can look even better than a conventional angiogram Left Main Coronary Artery Left Main, LAD, & Circumflex LAD Circumflex Obtuse Marginal Diagonal Branch off LAD Diagonal Branch Right Coronary Artery Acute Marginal Right Coronary Artery Sinoatrial Right Coronary Artery Evaluate stent patency LAD Stent from Top to Bottom (1 mm) LAD Stent from Front to Back (1 mm) Cardiac function • Recent studies show good correlation between function parameters derived from MDCT and levocardiography. • DETERMINING EJECTION FRACTION FUTURE OF CARDIAC CT • One-stop shopping— ( cardiac function, coronary artery evaluation, plaque analysis, calcium quantification.) • Non-invasive Illustrated cases High-resolution Imaging 1 LAD 1 2 3 4 2 3 RCA LM 4 DSCT LCx LM Significant stenosis of the left anterior descending artery Soft Plaque Visualization stent in LAD,LCx & RCA I Aortic Coarctation Visualized Fröhlich, G et al. Circulation. 2005;112:e81. Pericardial Calcification Multi-Slice CT Scanning Superior to MRI Hoffmann et al. Circulation 108 (7): 48e Figure IG1 Mild CAD, and… Pulmonary Emboli Teaching Points • Cardiac Cath: Lumen only-no wall information. Evaluate stenosis. Cannot characterize plaque. Better delineates small vessels • What is needed is a non-invasive, minimal-risk, outpatient procedure to detect early signs of CAD Coronary CTA- Strengths • Noninvasive. • Can measure HU of plaques and characterize them as fatty, atheroma, fibrosis, calcium. • Can evaluate status of bypass grafts. • Can determine stent patency. • Evaluates portions of mediastinum and lungs. Coronary CTA- Weaknesses • Cannot accurately measure stenosis with heavy, calcified plaque burden. • Occlusions can be missed by brisk collateral flow. What do I do with this information? • Reports will be classified in one of four categories of severity: Normal Mild Plaque with No stenosis Moderate Plaque with mild/Mod stenosis Severe Plaque and stenosis: Cardiac Cath