* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Early Heart Attack Care - Southern Ohio Medical Center
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
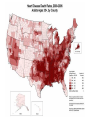
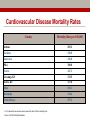
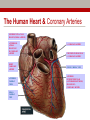
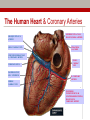
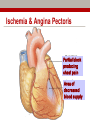
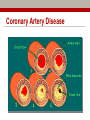
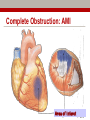
Early Heart Attack Care Heart attacks have beginnings For Questions, call Amy Fraulini, MSN, RN Director of Critical Care and Heart Services (740)356-8305 [email protected] Heart Attack: A community problem… with a community solution Cardiovascular Disease Mortality Rates County Mortality Rate per 100,000 Adams 283.2 Jackson 328.0 Lawrence 346.8 Pike 300.0 Scioto 401.2 Greenup, KY 332.5 Lewis, KY 327.8 Ohio 303.1 Kentucky 324.4 United States 279.2 BLUE indicates those counties which exceed the state of Ohio’s mortality rate Source: US CDC Mortality Database Course Outline 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Anatomy and Physiology 101: Your Heart Who’s at risk for heart disease? A Heart Attack in Progress Concepts of Early Heart Attack Care Recognition and Intervention Delay and Denial You: The Early Heart Attack Caregiver Part 1 Anatomy & Physiology 101: Your Heart The Human Heart • Location – Middle of the chest • Size – That of a fist • Purpose – Pumps blood throughout the body • Weight – 7 - 12 ounces • Capacity – Pumps 1,800 gallons of blood & beats over 100,000 times daily The Human Heart & Coronary Arteries SUPERIOR VENA CAVAL BRANCH (NODAL ARTERY) ANTERIOR R. ATRIAL BRANCH OF R. CORONARY ARTERY L. CORONARY ARTERY CIRCUMFLEX BRANCH OF L. CORONARY ARTERY RIGHT CORONARY ARTERY GREAT CARDIAC VEIN ANTERIOR CARDIAC VEINS ANTERIOR INTERVENTRICULAR (ANTERIOR DESCENDING) BRANCH OF L. CORONARY ARTERY SMALL CARDIAC VEIN The Human Heart & Coronary Arteries OBLIQUE VEIN OF L. ATRIUM GREAT CARDIAC VEIN SUPERIOR VENA CAVAL BRANCH (NODAL ARTERY) SINOATRIAL (S-A) NODE CIRCUMFLEX BRANCH OF L. CORONARY ARTERY CORONARY SINUS POSTERIOR VEIN OF L. VENTRICLE SMALL CARDIAC VEIN R. CORONARY ARTERY MIDDLE CARDIAC VEIN POSTERIOR INTERVENTRICULAR (POSTERIOR DESCENDING) BRANCH OF R. CORONARY ARTERY The Human Heart: Electric Pump Who’s at risk for Heart Disease? • Some persons are more likely than others to have a heart attack because of their “risk factors” • There are – Factors you can control – Factors you cannot control Risk factors we can control: • • • • • • Smoking High blood pressure High blood cholesterol Overweight and obesity Physical inactivity Diabetes Risk factors we cannot control: • Pre-existing coronary heart disease, including a heart attack, prior angioplasy, bypass surgery, or angina • Age • Family history of heart disease – A father or brother diagnosed before age 55 – A mother or sister diagnosed before age 65 Part 3 A Heart Attack in Progress Heart Attack Facts • #1 Killer of Adults BOTH Men and Women • 1.1 million Americans suffer a heart attack each year • 460,000 of those heart attacks are fatal • Hundreds of thousands survive but are left with a damaged heart Some different presentations of heart attack • Sudden, severe pain that stops you in your tracks. • Gradual increasing pain with damage occurring over a period of hours. • Very early presentation with mild symptoms over hours or days. Ischemia & Angina Pectoris Partial block producing chest pain Area of decreased blood supply Coronary Artery Disease Complete Obstruction: AMI Area of Infarct Part 4 Concepts of Early Heart Attack Care Are all heart attacks created equal? Progress: Heart Attack Treatment • Prehospital Cardiac Care • Thrombolytic Therapy (clot busters) • Angioplasty (preferred treatment with optimal outcomes) • Decrease in time to treatment saved heart muscle improvement in quality of life Too Little Progress: Heart Attack Recognition • Most heart attack patients do not benefit from optimal medical advances……………WHY? Delay • in recognizing and responding to the early warning signs of a heart attack Why Early Heart Attack Care? • Early Care: Recognize & Respond – often mild symptoms, usually normal activity • Late Care: Obvious Emergency & Respond – incapacitating pain, diminished activity • Too Late Care: Critical Emergency & Respond – unconscious, CPR, defibrillation, probable death • 85% of the heart damage takes place within the first two hours. Part 5 Recognition & Intervention Early Symptoms of a Heart Attack • Non-Specific Heart Attack Symptoms: • Specific Heart Attack Symptoms – weakness/fatigue – chest discomfort – clammy/sweating – chest pressure – nausea/indigestion – dizziness/nervousness – shortness of breath – neck/back/jaw pain – feeling of doom – elbow pain – chest ache – chest burning – chest fullness Part 6 Delay & Denial Why do we delay? Denial and Procrastination = Our Heart’s Enemy! It’s nothing really serious “I’ll just rest a bit” I’m too busy right now “I don’t have time to be sick” I don’t want to be a problem “If it turns out to be nothing, I’ll be embarrassed by the fuss made.” Paramedics BEWARE! First responders can easily be swayed by patient rationalizations and denials It’s probably heartburn or indigestion “I’ll take something for it” I’m strong! “Just walk it off, grin and bear it” I’m healthy “I have no serious medical problems…I exercise.” I’ll just wait it out “Everything will be OK.” Part 7 YOU: The Early Heart Attack Caregiver Who is the Caregiver? • • • • • • • Spouse Children Parent Co-worker Friend Exercise Partner Anyone who cares about you! What to ask and look for • Do you have any chest discomfort? • Is it tightness, pressure, pain in the center of your chest? • Is the discomfort also in your arms or jaw or neck or throat or back? • Are you sick to your stomach? • Is the person sweaty or clammy? • What were you doing when the symptoms started? • Do the symptoms go away with rest? • Are you having any shortness of breath? Listen to your Heart and be a Winner • Be aware of pressure, not necessarily pain, in your chest. • Be aware if it increases with activity and subsides with rest. • Don’t try to rationalize it away. Be honest with yourself and others. • Call 9-1-1 or have someone drive you to the nearest emergency room. • Don’t go to your doctors office or wait for an appointment. • Recognize the subtle danger signs and act on them before damage occurs. Remember to Call 9-1-1 WHY? • EMS can begin treatment immediately-even before arrival at the hospital • The heart may stop beating during a heart attack. EMS have the equipment needed to start the heart again • Heart attack patients have emergency needs that can be met by the EMS….such as oxygen, heart medications, and pain relief treatments • EMS are linked to the hospital and doctors to give them needed resources during this critical time Any questions? www.somc.org Safety Quality Service Relationships Performance