* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
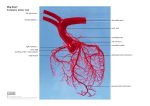
Download The arterial blood supply of the heart is provided by
Survey
Document related concepts
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Drug-eluting stent wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
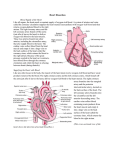
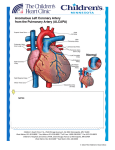
• circumflex branch of the left coronary artery The arterial blood supply of the heart is provided by the right and left coronary arteries, which arise from the ascending aorta immediately above the aortic valve. The coronary arteries and their major branches are distributed over the surface of the heart, lying within subepicardial connective tissue. The right coronary artery arises from the anterior aortic sinus of the ascending aorta and runs forward between the pulmonary trunk and the right auricle. This artery gives rise to an important branch immediately after leaving the ascending aorta. This is the anterior right atrial branch, which gives rise to the important sinoatrial nodal artery. This artery supplies the SA node or pacemaker of the heart. The right coronary artery continues in the coronary sulcus, giving off a marginal branch, which supplies the right ventricle. Finally, the right coronary artery gives rise to the posterior interventricular branch (posterior descending artery), which supplies both ventricles, and then anastomoses with the circumflex artery from the left coronary artery. The left coronary artery, which is usually larger than the right coronary artery, arises from the left posterior aortic sinus of the ascending aorta and passes forward between the pulmonary trunk and the left auricle. It supplies the major part of the heart, including the greater part of the left atrium, left ventricle, and ventricular septum. It then enters the atrioventricular groove and divides into an anterior interventricular branch (descending branch) and a circumflex branch. Important: (1) Coronary arteries receive the majority of their blood flow during ventricular relaxation, or diastole, when the left ventricle is filling with blood (2) The anterior interventricular artery is the one most often involved in coronary occlusions and is often the one that is bypassed in bypass cardiac surgery.