* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Multiple Choice Reproduction Review Name: Core: ___ Date
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
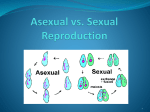
Multiple Choice Reproduction Review A. B. C. D. A. B. C. D. A. B. C. D. A. B. C. D. A. B. C. D. Name: __________________________ ___1. Asexual reproduction involves only one parent and results in offspring that are very different from the parent. two parents and results in offspring that are identical to one parent. two parents and results in offspring that are different from both parents. only one parent and results in offspring that are identical to the parent. ___2. Offspring that are produced through sexual reproduction are usually similar, but never identical, to their parents. This is because all of the offspring's genes only come from one parent or the other. genes are not transferred between parents and offspring during sexual reproduction. genes mutate during every occurrence of sexual reproduction. half of the offspring's genes come from one parent while the other half comes from the other parent. ___3. Which is an advantage of sexual reproduction over asexual reproduction? Sexual reproduction produces more diversity. Sexual reproduction produces more offspring. Sexual reproduction is quicker and less complex. Sexual reproduction never produces genetic defects. ___4. Mammals reproduce through a process called sexual reproduction. During this process, which involves two parents, a female egg cell and a male sperm cell each develop separately into an offspring that is different from both parents. a female egg cell and a male sperm cell each develop separately into an offspring that is identical to its parent. a female egg cell combines with a male sperm cell to make an offspring that is identical to one of the parents. a female egg cell combines with a male sperm cell to make an offspring that is different from both parents. ___5. Each organism's sex cells contain _______ of the organism's genetic information. half 2 copies none all Core: ___ Date: _____ A. B. C. D. ___6. In sexual reproduction, sex cells from each parent combine to form a new offspring. These sex cells are called ________. diploids zygotes genes gametes A. B. C. D. ___7. The process of cell division that creates sex cells in sexually reproducing organisms is called mitosis. translation. meiosis. replication. ___8. What process of cellular division results in two daughter cells that are genetically identical to each other and to the parent cell? A. diffusion C. respiration B. meiosis D. mitosis ___9. When a cell undergoes mitosis, what is the result? A. four genetically different cells B. four cells created from the combination of two parent cells C. two cells, each containing half of the parent cells' genetic information D. two genetically identical cells A. B. C. D. ___10. Which of the following are threadlike linear strands of DNA and proteins that carry the genes and functions in the transmission of hereditary information for living organisms? chromosomes cells mutations chlorophyll A. B. C. D. ___11. What gets passed from one cell to another in sexual reproduction? chromosomes pairs of DNA bases individual bases of DNA individual genes ___12. A _______ is a segment of DNA that contains a single unit of information. A. molecule C. atom B. gene D. fossil ___13. A rabbit is carrying a dominant allele for brown hair (B) and a recessive allele for white hair (b). What is the rabbit's phenotype? A. white hair B. BB C. Bb D. brown hair A. B. C. D. ___14. An organism's _______ describes its genetic composition. An organism's _______ describes its appearance or observable characteristics. species; heredity phenotype; genotype heredity; species genotype; phenotype A. B. C. D. ___15. Organisms typically have more than one form of each gene. If one form can mask the appearance of another form, that form is considered _______ the other form. worse than dominant over better than recessive to ___16. between a tall pea plant and a short pea plant shown below, what is the probability that the resulting offspring will be tall? T t t ? ? t ? ? A. B. C. D. 50% 100% 25% 75% ___18. In a certain breed of cats, having black hair is the result of two dominant alleles for hair color (HH). The heterozygous genotype (Hh) produces a cat that has black and white spots. Having two recessive (hh) genes results in a white-haired cat. The Punnett square below shows the results of a cross between which two cats? H H H HH HH h Hh Hh A. B. C. D. a spotted cat and a white cat a black cat and a spotted cat two spotted cats two black cats ___19. Examine the pedigree below. Look at the pedigree chart above. The squares are the male members of the family, and the circles are the female members of the family. Squares or circles that are all black are nearsighted members. Squares or circles that are all white have normal vision. Squares or circles that are part black are family members who carry the gene for nearsightedness but are not nearsighted. A. B. C. D. How many individuals in Generation II of the family have the gene for nearsightedness? 2 3 5 6 ___17. In pea plants, the allele for tallness (T) is dominant to the allele for shortness (t). In the cross A. B. C. D. If night blindness is a recessive trait, what should the phenotype of the couple's fourth child be? The child will develop night blindness later in life. The child could be night blind or have normal vision. The child will have normal vision. The child will be night blind. ___20. A farmer chooses the plants that produce the sweetest tomatoes to pollinate one another over many generations. Eventually all of the offspring of his plants produce only sweeter tomatoes. A. B. C. D. What process did the farmer use to produce his new and sweeter variety of tomatoes? random breeding domesticated reproduction asexual reproduction selective breeding