* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch. 22 2012
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
Objections to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Hindu views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
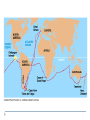
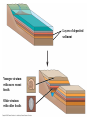
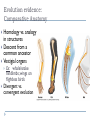
Chapter 22 Descent with Modification: A Darwinian View of Life Evolution Evolution (per evidence): Natural selection (as mechanism): change over time of the genetic composition of populations populations of organisms can change over the generations if individuals having certain heritable traits leave more offspring than others (differential reproductive success) Evolutionary adaptations: a prevalence of inherited characteristics that enhance organisms’ survival and reproduction November 24, 1859 Descent with Modification, I 5 observations: 1- Exponential fertility (cue romantic music) 2- Stable population size (cue funeral dirge) 3- Limited resources (no cue for you) 4- Individuals vary (which cue to choose…) 5- Heritable variation (you have your mom’s cue) Descent with Modification, II 3 Inferences: 1- Struggle for existence 2- Non-random survival 3- Natural selection (differential success in reproduction) Evolution evidence: Biogeography Geographical distribution of species Examples: Islands vs. Mainland Australia Continents Evolution evidence: The Fossil Record Succession of forms over time Transitional links Vertebrate descent Fig. 22-3 Layers of deposited sediment Younger stratum with more recent fossils Older stratum with older fossils Evolution evidence: Comparative Anatomy Homology vs. analogy in structures Descent from a common ancestor Vestigial organs Ex: whale/snake hindlimbs; wings on flightless birds Divergent vs. convergent evolution Evolution evidence: Comparative Embryology Pharyngeal pouches, ‘tails’ as embryos Evolution evidence: Molecular Biology Similarities in DNA, proteins, genes, and gene products Common genetic code You should now be able to: 1. 2. 3. 4. Describe the contributions to evolutionary theory made by Linnaeus, Cuvier, Lyell, Lamarck, Malthus, and Wallace Describe Lamarck’s theories, and explain why they have been rejected Explain what Darwin meant by “descent with modification” List and explain Darwin’s four observations and two inferences Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings 5. 6. Explain why an individual organism cannot evolve Describe at least four lines of evidence for evolution by natural selection Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings