* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Histogenesis
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Chromatophore wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
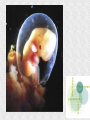
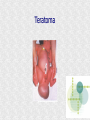
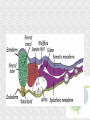
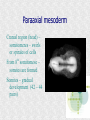
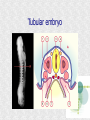
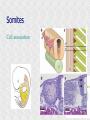
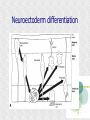
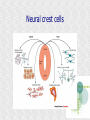
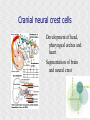
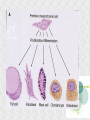
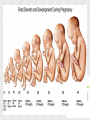
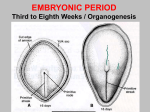
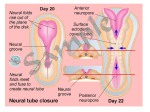
Histogenesis 149 DCT Basic morphologic processes Processes which are involved in development Proliferation Apoptosis Association – cells express intercellular junctions Migration – loss of intercellular contacts – cells express adhesive molecules for attachment to the intercellular matrix Induction → determination and differenciation Organogenesis: 3rd-8th week Formation of all organ systems: − − Cardiovascular and nervous - 3.week External genitalia – later than 8.week Changes in outer shape Most critical period Formation of 3D shape Head fold Tail fold Lateral folds Head fold - growth of brain and spinal cord – folding (septum transversum and heart are pushed ventrally) Changes in shape of intraembryonic coelomic cavity Tail fold – cloacal membrane is also pushed ventrally Lateral folds – gut closure, formation of umbilical cord Notochord Axial structure Signalization – induction of changes in ectoderm – neuroectoderm and ventral plate of neural tube, in mesoderm – somites and in endoderm = segmentation It grows to the praechordal (oropharyngeal) plate Prechordal plate – organizer in head regioninduction of prosencephalon development Development of notochord After notochord has reached oropharyngeal membrane, it grows by proliferation and migration of cells of primitive streak and node – caudal morfogenetic system After head and neck has formed, body grows by the activity of caudal morfogenetic system Primitive streak breaks down or reduces gradually Sacrococcygeal teratoma Teratoma Neurulation Primitive node and notochord – signal molecules – interaction between epithelial and mesenchymal cells Regionalization – craniocaudal gradient -segmentation of CNS (hox genes) Neural plate – restriction, determination and differenciation of ectoderm Cell proliferation – neural groove, neural folds Folds fuse – it starts in cervical region and continues to the cranial and caudal end – Cranial and caudal neuropores + Neural crest cells Neural tube segmentation Brain segmentation - 3 brain vesicules – prosencephalon, mesencephalon and rhombencephalon Segments – neuromeres Mechanism: segmental genes are expressed (hox) Segmentation of neural tube – induction - signals from notochord Mesoderm development Axial mesoderm – notochord and cranial organizer (praechordal plate) Intraembryonic mesoderm – Paraaxial mesoderm– somites Intermediate mesoderm Lateral: somatopleura, splanchnopleura and intraembryonic coelom Cardiogenic field Paraaxial mesoderm Cranial region (head) – somitomeres – swirls or spirales of cells th From 8 somitomese – somites are formed Somites – gradual development (42 – 44 pairs) Derivatives of the three germ layers Ectoderm – CNS, PNS, retina, epidermis, mammary gland, enamel Cells of neural crest -– ganglia, Schwann´s cells, melanocytes, medulla of suprarenal gland, meninx, muscle, connective tissue and cartilages/ bones of pharyngeal arches Mesoderm – connective tissue, cartilage, bone, muscle, vessels, kidney, ovary, testes, spleen, cortex of suprarenal gland, mesothelium Endoderm – digestive and respiratory system (epithelium and glands), thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, thymus, pancreas, liver, urinary bladder 4 week th Closure of rostral and caudal neuroporus (24th and 26th day) Somites (4.-12.) Pharyngeal arches are visible by 26th day Heart prominence Upper limb buds 26th- 27th day Otic pits and lens placodes Lower limb buds – by the end of week Tubular embryo 5 week th Head growth – brain and pharyngeal arches Pharyngeal arches – development of face and neck Ectodermal grooves and endodermal pouches, pharyngeal membranes Aortic arches – vessels in pharyngeal arches 6 week th Development of limbs – future fingers – digital rays are visible Development of ear: external acustic meatus (first pharyngeal groove), swelling around it fuse to form auricle Head is longer than body 7 week th Development of limbs – digits of upper limbs Umbilical herniation– intestine enters the extraembryonic coelom in the proximal region of umbilical cord. 8the week Digits also in lower limbs Tail disappears at the end of 8th week Embryo has distinct human characteristics – head constitutes almost ½ of embryo Eyes – eye lids fuse by end of 8th week External genitalia - indifferent Somitogenesis Segmentatio – stimulated from notochord (Shh) and ectoderm Various concentration of signal molecules Other signals – Wnt, Pax, BMP-4 Dermatomyotome – dermatome and myotome Sclerotome Somites Cell association Development of vertebrae Vertebrae develop from sclerotome Mesenchymal tissue from sclerotome surrounds notochord (nucleus pulposus) Vertebral body forms from the cranial and caudal halves of two succesive sclerotomes Chicken embryo Sclerotome Neural tube development Signaling from notochord and superficial ectoderm – histo-differentiation of neuroectoderm Various neuron types Neural tube – proliferating cells Neuroectoderm differentiation Neuroectoderm differentiation Germ layer – proliferating cell – future ependym Cells migrating to mantel layer – neuroblasts – neurons – enter G0 phase Other cells – glioblast – radial glia (Müller cells in retina) and glia – astrocytes and oligodendrocytes Neural crest cells Cranial neural crest cells Development of head, pharyngeal arches and heart Segmentation of brain and neural crest Mesenchyme Blood cells Endothelium Connective tissue cells – fibroblast, mast cell, adipocytes, chondrocyte, osteoblast and osteocyte,odontoblast Skeletal muscle development Cells in somite Myoblast – they can migrate and proliferate Myotubes – myoblast fuse Mature myofiber – presence of actin and myosin – fully differentiated cells Development of epidermis Simple cuboidal epithelium Periderm – 2 layers Squamous stratified epithelium Later – superficial cells start to cornified Fetal period By 9th week till birth Measurement: Biparietal distance, head circumference, body circumference, femur length Disorder – IUGR – intrauterinne growth retardation – reduction of vascular supply, placental insufficiency