* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch.11-14 Byzantine
Medieval Inquisition wikipedia , lookup
Early Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Late Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
High Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Christianity in the 13th century wikipedia , lookup
Christianity in the 9th century wikipedia , lookup
History of Christianity during the Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
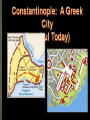
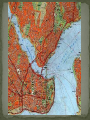
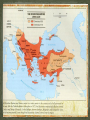
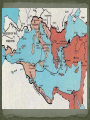
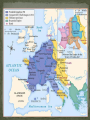
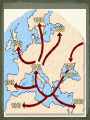
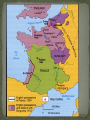
Strategic City-on a peninsula, Constantinople overlooked the Bosporus, the narrow strait between the Sea of Marmara and the Black Sea. Water protected the city from the Germanic invaders. The strait made it perfect for trade. Mediterranean Sea Balkan Peninsula Russia Black Sea Caucasus Mountains The Roman empire divided in A.D. 395. The eastern half became known as Byzantine Empire. Constantinople is the perfect location between Europe and Asia. Constantinople is the capital of the “Eastern Rome”. Strong imperial leadership Strategic location of its capital. Successful military conquest. Strong ties to church Emperor Justinian – Ruled the Byzantine Empire at its height in A.D. 527. Justinian tried to restore the old Roman Empire ( it was very expensive) Theodora- wife, empress was very intelligent. She helped to shape his polices. She built homes for poor and helped the status of women. Emperor Justinian Justinian’s Code Corpus Juris Civilis: 1. Digest 2. Code 3. Institutes Corpus of Civil Law- Justinian reformed the Roman Laws and appointed a commission to organize and classify the laws. Later the Justinian Code became the basis for most European legal system. Justinian’s Empire at its Peak Justinian was plagued by attacks by the Persians and the Germanic invaders. (Ostrogoths in Italy and Spain, Visigoth is Southern Spain and the Lombard in Northern Italy.) Emperor Justinian chose two Greek mathematicians to design. Combines Greek balance and proportion with Roman engineering skills. The Church is a vast rectangle and in the center is a huge dome. The dome seems to look like it is floating in the heavens. Byzantine Emperors appointed Church officials and used the wealth of the Church for government purpose. Justinian tried to unify the Church under one Christian faith, this led to persecution of the Jews and non- Greek Christians. Clergy- Church people, priest, ministers etc… Laity- Church goers, people that go to church. Conflicts over use of Icons- Some argued that the Bible prohibits such images and others said they were symbols of God’s presence in human affairs. Emperor Leo- (A.D. 726) Believed icons encouraged superstitions and the worship of idols. His supporters became known as Iconoclast or image breakers. The word icon is Greek for “image”. In Byzantine art the image on an icon is of a holy person. Refusal to help Pope with military protection against the Germanic Lombard’s in Italy. The Pope then turned to the Franks, Germanic Catholic people in Western Europe. The Pope gave Charlemagne, the leader of the Franks, the title of emperor. Schism - Separation 1054 A.D. doctrinal, political, and geographical differences finally led to a schism. Split of the Christian church: Roman Catholicism and Eastern Orthodox. Carolinian Miniscule Curia Clovis Pope Urban II Battle of Tours Battle of Hastings Viking Henry II William the Conquer Chivalry Cardinals Charlemagne Serfs Magna Carta Fiefs Heresy Feudalism Inquisition Excommunication Interdict Saldein vassals Middle Ages (Between Dark Ages and Renaissance) Germanic invasions destroyed the Roman Empire by A.D. 476 Dark Age- trade declined, money was no longer used, law and order did not exist, education almost disappeared. ( Transition between ancient and modern times.) Franks- Clovis was king of the Franks who settled in France and Western Germany. Clovis was the first Frankish ruler to accept Catholicism. Louis Frankish rulers divided the kingdom among their heirs until the political power had passed from the kings to the government officials known as mayor of the palace. Charles Martel- Mayor of the Palace in A.D. 714, he had defeated the Muslims and gained much respect. Battle of Tours Pepin the Short- son of Charles Martel became King of the Franks in A.D. 752. The pope anointed Pepin and had the Church’s blessing. Pepin forced the Lombard's out of Rome. He then gave the pope a piece of land in central Italy. Papal States Charlemagne- son of Pepin the Short became king in A.D. 768. Charlemagne is one of Europe’s greatest monarchs. He started the Carolingian dynasty. He doubled the Frankish kingdom and reinstated law and education of the Old Roman days. Pope Leo III – Charlemagne defended him against the Roman nobles. To thank him, the pope, crowned Charlemagne the New Holy Roman Emperor. Counts- local officials who Charlemagne depended on…..Missi Dominici to spy on the counts. Education for boys and girls Carolingian miniscule-form of writing Raised armies for the emperor Charlemagne’s three grandsons fought for control of empire and finally agreed in the Treaty of Verdun to divide the Carolingian lands. Charlemagne’s empire was divided between his grandchildren. Louis the German Charles the BaldFrance Lothair- Italy Raided Ireland to Russia. Norsemen, Northmen or Vikings Scandinavia (Norway, Sweden, & Denmark) Eric the Red Leif EricksonNewfoundland Norwegians settled in Greenland an Iceland and North America. Danes settled in England and established Normandy in northwestern France. The Swedes settled in present-day Ukraine and Russia. Normandy-Northern France Europeans finally worked out a way to defend themselves. Castles Europeans learned to respond quickly. Vikings converted to Christianity. Europe’s climate got warmer. Feudalism – political system Manorialism- economic system Fiefs- Estates with peasants given to the cavalry of Charles Martel in return for their service. Mutual alliances between monarchs and nobles. It was based on giving land to nobles in exchange for loyalty and military aid. Castles were built to protect the lord and his land. Origins in early Byzantine Empire Muslim conquerors of Spain built similar structures. Spread to France in the 1100’s and were used as private fortresses and homes. Purpose was for military security Castles were dark and dingy and not very “warm” and were made of thick stone walls. Life of Nobility was not luxurious. (Lords, Ladies, and Knights) In the feudal system investiture was the ceremonial transfer of a fief by an overlord to a vassal. The lord invested the vassal with a fiefdom, by giving a symbol of the land or office conveyed in return for an oath of fealty. Knights- train for knighthood at age 7 by becoming a page or assistant. Squire at age 15 a boy had to prove himself worthy to be a knight. Chivalry was the code for knights to be brave in battle, fight fairly, and treat noblewoman in a courteous manner. Tournaments- Mock battles between knights. Vassals-A person who held land from a feudal lord and received protection in return for homage and allegiance. Manorialism- System of agricultural production among lords and peasants. The Manor would include the lord’s manor house, pastures, fields, forest, and a village for the peasants to live in. Peasants worked in return for food, shelter, and protection. Serfs- most peasants were: they were bound to the manor and could not leave without permission. They were not slaves, they could not be sold. Improvements of farming: heavier plow and dividing plots of land into three instead of two fields and they left one field unplanted. The role of women changed. Eleanor of Aquitaine Limited home or convent It was in marriage that a woman had the greatest power/ independence Medieval society was a hierarchy based on leaders from the top to bottom. Each medieval person’s duties were based on his/her position in life. People did not question their standing in life. King Lords Knights Priests Merchant serfs Fairs- served as centers of trade in Medieval Europe Attracted merchants form all over the Western Europe. Held four times a year: winter, Easter, midsummer, and October. Uniformity- goal of the Medieval church to unify Western Europe Center of most people’s lives during the Medieval Ages was the Catholic Church. It became the religious support, spiritual guidance, education, medical care and charity of the people. The Church taught that all people were sinners and they depended on God’s grace or favor through the Sacraments or church rituals. These seven sacraments are still taught through the Catholic Church. Baptism, penance, Eucharist, confirmation, matrimony, anointing of the sick, and holy orders. Latin was the language of the Church and few people understood it. Priests were uneducated and the people could not read or write, people learned about the Christian faith from the statues and painting on the walls of the churches. Secular clergy- Latin for “ in the world”; pope, bishops, and priests Regular clergy- included monks and nuns who lived apart from society. Benedict- A.D. 529 a Roman official founded a monastery in Monte Cassino in Italy. Model for other monasteries and drew up a list of rules for monks. Monks- life of poverty, chastity, and obedience to the Abbot. Nuns – same vows as monks only direction of the Abbess. Monks and Nuns preserved ancient religious works, copied classical books by hand, illuminated manuscripts books, provided schools, hospitals, food, guest houses for travelers, and missionaries. Pretzel – creation of medieval monks to give to children as rewards for memorizing prayers. Latin for “Pretiola”, or small reward. The shape represented the folded arms of children in prayer. Church power got to strong and the Church would appoint special church positions to nobles who have helped them. Christians wanted reform!!! Cardinals-all future popes would be elected by leading bishops. Political leaders used to vote for the pope, now a group of cardinals would elect one. The Pope is elected by a gathering of cardinals call a “conclave”. They meet no later than the 20th day after the death of a pope. They vote secretly for a a 2/3 majority on a candidate. Pope Gregory VII – reform – minded people elected in 1073 Proposed the practice of Lay Investiture in which secular rulers gave the symbols of office, such as a ring to the bishops they had appointed. Pope Innocent III- stopped the spread of heresy, or the denial of basic church teaching, and threatened the heretics with excommunication, or expulsion from the church. Interdict- no religious ceremonies in that Nations. Pope Gregory VII clashed with Henry IV Banned all married priests. Banned lay investiture Henry IV called the Pope Gregory VII names. Pope Gregory VII Excommunication Henry 1077 Henry IV begged forgiveness Concordant of Worms-Church would grant a bishop His ring. Inquisition – Church set up a court in 1232 to punish heretics. Heretic is someone who goes against god. Friars- reformers of the Church, wandering preachers who followed the rules of the monastery but lived among the people and preached Christianity to them. The Jews- the most powerful source of anti- Semitism during the Middle Ages was the way the Christian doctrine was interpreted. Many Church leaders and others blamed the Jews for Jesus’ death. Guilds- skilled labor, had to be Christian. No Jews allowed. England: Alfred the Great- united the Anglo- Saxon kingdoms and defeated the Danes in 866. His kingdom became known as England. William Duke of Normandy wanted the English throne-fought against Harold Godwinson. Henry II – William’s grandson who set up the system of common law, grand jury, and a petit jury. Eleanor of Aquitaine – wife of Henry and she owned vast lands in southwestern France. Sons were Richard I ( the lionhearted) and John. Magna Carta – Balanced power in government, placed clear limits on royal power and bound the king to law. Example: the king could no longer collect taxes without the people’s consent. It also assured all freemen the right of trial by jury. John- un-liked and unpopular because he increased the taxes and punished enemies without a trial. Nobles forced him to sign the Magna Carta Parliament – Knights, burgesses (townspeople) were added to the Great Council that advised King Henry III. 1400 Parliament divided into two chambers. House of Lords – nobles and clergy House of Commons – knights and burgesses Estates- general- assembly of nobles, clergy, and townspeople but was never as powerful as the English Parliament started by Louis IX’s grandson, Philip IV. Series of military expeditions undertaken by European Christians to recover the Holy Land from the Muslims. 1050-1270 A.D. Jerusalem- Holy city for Jews, Christians, & Muslims, the city fell to the Arabs. Pope Urban II in 1096 called for a Crusade Pope goal- unite all Christians (Byzantine & Rome) Knights goal- Forgiveness sins ( glory & wealth) Merchants goal- trade ( Genoa, Piza, Venice) Caused tension among the Christians and non Christians. Crusaders massacred most of the Muslims and Jews in Jerusalem in 1099. 50 years after the First Crusade the Seljuk Turks conquered part of the Crusader states. They were not successful In 1187 he united the Muslim forces & captured Jerusalem. Third Crusades started by the rulers of Germany, France, & England. All forces of religion, feudalism, & chivalry got together. New trade Europe, Middle East, & Asia New spices, technology End of the Middle Ages New inventions. The crusades helped to speed up the changes that were already in play. Early merchants used the Barber system: The money economy replaced it. This led to the development of banking. Serfs-began to buy their freedom feudalism declined. Black Death killed Europeans from 1348-1350. 25% of Europeans died. Cause of the plague? The Black Plague was caused by infected rodents carrying the virus. “Grim Reaper” The first symptoms of the bubonic plague often appear within several days: headache and a general feeling of weakness, followed by aches and chills in the upper leg and groin, a white coating on the tongue rapid pulse, slurred speech, confusion, fatigue, apathy and a staggering gait. A blackish pustule usually will form at the point of the flea bite. By the third day, the lymph nodes begin to swell. The swelling will be tender, perhaps as large as an egg. The heart begins to flutter rapidly as it tries to pump blood through swollen, suffocating tissues Subcutaneous hemorrhaging occurs, causing purplish blotches on the skin. The victims nervous system begins to collapse, causing dreadful pain and bizarre neurological disorders, from which the "Dance of Death" rituals that accompanied the plague may have taken their inspiration. By the fourth or fifth day, wild anxiety and terror overtake the sufferer-and then a sense of resignation, as the skin blackens and the rictus of death settles on the body (Smithsonian, 70). Ring Around the Rosie” This nursery rhyme began about 1347 and derives from the notso-delightful Black Plague which killed over twenty-five million people in the fourteenth century. The "ring around a rosie" refers to the round, red rash that is the first symptom of the disease. The practice of carrying flowers and placing them around the infected person for protection is described in the phrase, "a pocket full of posies." "Ashes" is a corruption or imitation of the sneezing sounds made by the infected person. Finally, "we all fall down" describes the many dead resulting from the disease. Most important scholastic thinker. He claimed that reason existed in harmony with faith. Universities spread the advancement of literature and art. One of the earliest literary works was “Beowulf” Arabs- had established universities 200 years earlier than the Europeans. 1100’s traveling poet-musicians who composed poems and songs about love and the accomplishments of knights. Romance referred to the narratives written in the Vernacular. Vernacular- everyday language or speech. England and France fought a series of conflicts. Reason) The English tried to keep the French lands that they had received from the Normans. Normandy Conflict began when the England’s Edward III claimed the French crown. The English were successful at first because they had weapons of firearm and the longbow. She believe to hear voices telling her to save France. dauphin gain the French throne She is considered the First French hero. Maid of Orleans She was captured and burned to a stake. Joan heard a voices telling her to place Charles VL”s son on the throne. Dauphin- french term for crown prince Reims-Charles VII was crowned Joan was captured and burned at the stake. Gabella- tax on salt Batliffs- Knights are outdated (old school) Kings replaced knights with national armies. England monarch’s power was limited by Parliament. Conflict arose between the English nobility for control of the throne. Rose symbols of the rival families involved. House of York—white rose House of Lancaster- red rose Edward, Duke of York, became King Edward IV. At the time of his death, two brothers were given the throne. Their uncle Richard proclaimed himself King. Uncle Richard had his nephews murdered. Henry Tudor, conquered Richard, became the first Tudor King. Made up of Portugal in the west. Castile in the center. Aragon on the Mediterranean coast. Granada-in the south were in the hands of the Muslims. (moors) 1492 Both Ferdinand and Isabella kicked out the Muslims from Spain. Spain use the Spanish Inquisition to enforced Catholic teachings. Reconquista During the Middle Ages it was made up of German, Italian, and Slavs. The Hapsburgs- a family of nobles in Austria. They will become the most powerful European royal family. Pope Gregory XI returned to Rome form Avignon. Mobs of people forced the College of Cardinals to elect an Italian pope. They elected a second pope-who settled in Avignon. Two popes now led the church. 1414 another council met in Germany –forced the two popes to resign. Pope Martin V was elected the new pope. Bulls- official statement from the pope. Unam Sanctam- a pope statement that there were only two powers: Temporal-early Spiritual- heavenly Englishman Wycliffe True head of the church was Jesus Christ, not the pope. Priests should not own land or wealth. Bible only authority not the pope. Translated the New Testament in English. Hus Bohemia He argued that the Bible was the only way to seek God. He was declared a Heretic and burned at the stake. Moscow- Volga, Dnieper, and Con Rivers Ivan I “Great Prince Kremlin- Fortress or citadel Ural Mountains Boyars- princes Ivan the Terrible Henry II Normandy Richard the Lionhearted Parliament Boyars Bulls Kremlin Batliffs Ural Great Schism Henry Tudor John Hus War of the Roses Bubonic Plague Dauphin John Wycliffe Joan of Arc Estates General Ivan the Terrible King John Reconquista Magna Carta Hundred Years War Burgesses Unam Sanctam