* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Medieval Ages
Migration Period wikipedia , lookup
Early Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Late Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Christianity in the 9th century wikipedia , lookup
Carolingian Empire wikipedia , lookup
History of Christianity during the Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
High Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
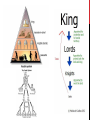
THE RISE OF MEDIEVAL EUROPE WORLD HISTORY I. The Rise of Medieval Europe A. Germans adopt Christianity 1. Clovis united the Franks and converted to Christianity 2. Charles Martel – defeats the Muslims at Tours in 732 B. Charlemagne (Charles the Great)- son of Pepin the Short 1. Used royal agents to keep tabs on counts (governors) 2. Doubled the size of his kingdom – a.k.a. Frankish Empire a. Germany, France, & Northern Spain & Northern Italy 3. Defended the Pope against Roman nobles a. Pope Leo crowns Charlemagne the Roman Emperor 1. sets a precedent – church officials superior to rulers (?) 4. Died in 814 A.D. a. Louis the Pious’ (son of Charlemagne) sons fought one another for control b. Treaty of Verdun divides the empire between the sons 1. France - Charles the Bald 2. Germany – Louis the German 3. Lothair – North Sea to Italy Louis the German Charles the Bald No hair & lots of hair Get it? Lothair C. The Vikings - raiders from Scandinavia a. used long, deckless, one sail ships with long oars 1. were ocean worthy and shallow enough for river travel b. became known for surprise attacks and speedy retreats 1. would plunder, steal, and burn c. motivated by adventure, riches, and an overpopulated homeland 2. Were ferocious fighters and showed no mercy 3. Were explorers and settlers a. North Atlantic - Greenland, Iceland, & North America b. Europe – England, Normandy (NW France), Ukraine, & Russia 4. Effects of Viking raids on Europe a. isolated European communities b. severely weakened the central authority of monarchs c. trade decline led to economic collapse d. nobles and local officials take over local defense Leif Ericson D. Feudalism – political relationship between nobles 1. Emerges in the A.D. 900s as a result of Viking (& others) raids - Arabs & Magyars (Hungarians) too 2. Highly decentralized form of government a. alliances of mutual protection between monarchs & nobles b. land given to nobles in exchange for loyalty & military aid 1. raised armies & dispensed justice c. peasants farmed the land 3. Fiefs – estates with peasants 4. Vassal – a noble who served a lord of a next higher rank a. most important obligation was military service (knights served) b. also served in the lord’s court, provided food & lodging, contributed funds, and paid ransom 5. Castles built for defense – every noble a. built of stone on a hill w/moat, keep, hall, dungeon, & bailey E. The Manorial System – economic system of agricultural production 1. Peasants worked the land in exchange for the lord’s protection 2. Manor – estate that produced everything its residents needed 3. Serfs – peasants bound to the land 4. Provided a stable and secure way of life 5. Agricultural production increased with the three field system and the mold board plow F. Catholic Church – dominant spiritual influence of western Europe 1. Pope – became the strongest political leader in western Europe a. claimed spiritual authority over all Christians 2. Administered sacraments - baptism, penance, Eucharist (communion), confirmation, matrimony, anointing of the sick, and holy orders 3. Monasteries/monks & convents/nuns a. took vows of poverty, chastity, and obedience b. provided schools, hospitals, food, & guest houses 4. Catholicism spread to England, northern Germany, Ireland 5. Nobles influence church policies through appointments (investiture) 6. Call for church reform because of scandal and corruption a. drunkenness, feasting, & dancing among the clergy b. heresy increased – conversion and excommunication used c. Simony & priests marrying and raising families 7. Inquisition (mainly in Spain)– for seeking and punishing heretics a. confess or be punished (imprisonment, loss of property, or execution) G. Jews – lived peacefully with Christians until 1000s 1. Anti-Semitism develops a. seen as outsiders and as a threat b. blamed for plagues, famines, and other social problems c. blamed for Jesus’ death & resented for not converting to Christianity d. forced to wear badges and live in separate communities e. could not own land & practice certain trades 1. became peddlers, merchants, or money lenders f. some are expelled and settle in southern and eastern Europe H. England – native Celts defeated by Germanic Angles 1. Alfred the Great unites Anglo-Saxon kingdoms & defeats Vikings 2. Norman Conquest (1066) a. William the Conqueror wins at Battle of Hastings 3. Magna Carta (1215) – King John signs a. placed clear limits on royal power b. consent of Great Council (Parliament) needed to tax I. France – strong monarchy develops 1. Capetian dynasty, Philip Augustus, Louis IX, & Philip IV J. Holy Roman Empire (Germany & Northern Italy) 1. King Otto I crowned Holy Roman Emperor by Pope John XII (962) 2. Problems a. wars - powerful German lords prevent a strong unified state b. disputes between Holy Roman emperors & Catholic Popes 3. Neither “holy,” nor “Roman,” nor an “empire” K. Crusades 1. First Crusade – called by Pope Urban II which captured Jerusalem 2. Second Crusade – called by St. Bernard of Clairvaux that was a dismal failure 3. Third Crusade – led by King Richard the Lionhearted to recapture the city of Jerusalem from Islamic forces led by Saladin; failed in attempt 4. Fourth Crusade – Crusaders attack and sack Constantinople 5. Motivated by reunification of Christendom, desire for land, adventure, riches, religious fervor, feudalism, chivalry, and forgiveness of sins 6. Impact: increase in trade, cultural diffusion, Byzantine Empire weakened, legacy of bitterness/hatred, decline of feudalism, lessened power of pope