* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Funded in part by a grant from the City`s Special Program through
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Marine habitats wikipedia , lookup
Southern Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Arctic Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Indian Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on oceans wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem of the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre wikipedia , lookup
Pacific Ocean wikipedia , lookup
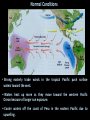
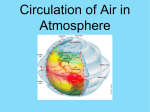
Funded in part by a grant from the City’s Special Program through the Houston Arts Alliance. Factors that Influence Climate • Solar radiation received at a particular latitude • Air mass influence • Location of global high and low pressure zones • Heat exchange from ocean currents • Pattern of prevailing winds • Distribution of mountain barriers • Altitude • Distribution of land and sea Climate Cycles that Influence Global Weather Patterns El Niño La Niña Drought Monsoon Normal Conditions • Strong easterly trade winds in the tropical Pacific push surface waters toward the west. • Waters heat up more as they move toward the western Pacific Ocean because of longer sun exposure. • Cooler waters off the coast of Peru in the eastern Pacific due to upwelling. El Niño Conditions • Weaker easterly trade winds in the central and eastern Pacific Ocean. • This causes the normal upwelling of the cold water from below the surface to stop and the warm surface water to remain. Effects of El Niño Winter temperatures are warmer than normal in the North Central States and cooler than normal in the Southeast and the Southwest. Increase in the rainfall across the southern United States from Texas to Florida. La Niña Conditions • Stronger than normal easterly trade winds in the central and eastern Pacific Ocean. • This causes more upwelling off the western coast of South America resulting in cooler than normal surface water across the eastern equatorial Pacific Ocean. Effects of La Niña Drier and warmer than normal conditions across much of the southern United States. Wetter than normal conditions across the Pacific Northwest. Drought A period of abnormally dry weather sufficiently prolonged for the lack of water to cause serious hydrologic imbalance in the affected area. Causes serious problems such as crop damage and/or water supply shortages. Monsoon A period of seasonal winds; strongest on the southern and eastern sides of Asia. For more information, visit the INTERACTIVE CLIMATE ZONE EXHIBIT at The Weather Museum Funded in part by a grant from the City’s Initiative Program through the Houston Arts Alliance.