* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 23 Pronoun Usage
Lithuanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Norse morphology wikipedia , lookup
Relative clause wikipedia , lookup
American Sign Language grammar wikipedia , lookup
Udmurt grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Irish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Preposition and postposition wikipedia , lookup
English clause syntax wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
Nominative determinism wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Arabic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Georgian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Russian declension wikipedia , lookup
Grammatical case wikipedia , lookup
Icelandic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Turkish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Romanian nouns wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
English grammar wikipedia , lookup
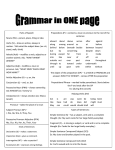
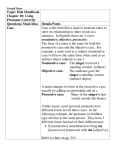
Chapter 23 Pronoun Usage Mr. Brasher Case • Definition- form of a noun or a pronoun that indicates its use in a sentence; 3 cases are nominative, objective, and possessive. 3 Cases • Nominative- subject or predicate nominative – Example: The old car would not start. (car is the subject of the sentence) • Objective- Direct Object, Indirect Object, Object of a Preposition, Object of a Verbal (examples: running the mile; planning the surprise attack) – Example: We could not start the old car. (car is the direct object) • Possessive- To show ownership – Example: The old car’s battery needed to be replaced. (form changes in this form by adding an apostrophe s) • Note box about personal pronouns and the different forms in all 3 cases. The nominative case • Use nominative case when a pronoun is used as the subject of a verb or as a predicate nominative. • Appositive- noun or noun phrase that renamed another noun right beside it. The Objective Case • Use the objective case when a pronoun is used as the object of any verb, preposition, or verbal. • Participle- verbal (based on a verb and therefore expresses action or a state of being) that is used as an adjective and most often ends in –ing or – ed. – Example: Racing her, he crashed into an antique car. • Gerund- verbal that ends in –ing and functions as a noun. – Example: Dad likes helping me with my homework. • Infinitive- verbal consisting of the word to plus a verb functioning as a noun, adjective, or adverb. – Example: To tell them clearly, he had to shout. Note about preposition between • Incorrect: This matter is between you and I. • Correct: This matter is between you and me. The Possessive Case • Used to show possession before nouns and before gerunds. – Noun Example- My report on the Roaring Twenties is almost done. – Gerund Example- Your asking questions made me focus. – Use certain possessive pronouns by themselves to indicate possession; example- The move is hers, not his. – Note about spelling on page 550 Homework • Page 551 exercise 8-10 23.2 Special Problems with Pronouns Case Pronoun Use in sentence Nominative Who, whoever Subject or predicate nominative Objective Whom, whomever Direct Object, Object of a verbal, or object of a preposition Possessive Whose, whosever To show ownership Nominative Case: Who and Whoever • Use who or whoever for the subject of a verb. Nominative Case: Who or Whoever • Use who or whoever for a predicate nominative. The Objective Case: Whom and Whomever • Use whom or whomever for the direct object of a verb or object of a verbal. The Objective Case: Whom and Whomever • Use whom or whomever for the object of a preposition. Use pronouns correctly in Elliptical Clauses • In an elliptical clause, some words are omitted because they are understood; these clauses are often used to draw comparisons. • In elliptical clauses beginning with than or as, use the form of the pronoun that you would use if the clause were fully stated. Use pronouns correctly in Elliptical Clauses • If omitted words come after the pronoun, use a nominative pronoun because it is the subject of the omitted verb. If omitted words come before the pronoun, use an objective pronoun. • Always follow these steps when choosing a pronoun in an elliptical clause: – Consider choices of pronouns: nominative or objective. – Mentally complete the elliptical clause. – Base your choice on what you find. Homework • Page 559 exercise 18-20 • Exercise 18 do as directions say • Exercise 19- write down word that completes sentence and tell me how it is used. (Subject, possessive, direct object, object of preposition, etc.) • Exercise 20- write down word that completes sentence correctly.