* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Initial practice problems. + + - O O O 2m 5m What is the net force on
History of subatomic physics wikipedia , lookup
Noether's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Spherical wave transformation wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
Aristotelian physics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Field (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
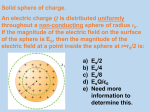
Initial practice problems. + O + O O 2m 5m What is the net force on each charge? Each unit charge is 1.602E-19C What is the initial acceleration of each charge? (Me = 9.1E-31kg, Mp = 1.67E-27kg) What happens to each acceleration after the initial instance? O X 2m + O O 7m What is the net force on each charge? Each unit charge is 1.602E-19C What happens to each acceleration after the initial instance? What is the Electric field strength at X? 1998E1. The small sphere A in the diagram above has a charge of 120 C. The large sphere B1 is a thin shell of nonconducting material with a net charge that is uniformly distributed over its surface. Sphere B 1 has a mass of 0.025 kg, a radius of 0.05 m, and is suspended from an uncharged, nonconducting thread. Sphere B1 is in equilibrium when the thread makes an angle = 20° with the vertical. The centers of the spheres are at the same vertical height and are a horizontal distance of 1.5 m apart, as shown. a. Calculate the charge on sphere B1. b. Suppose that sphere B1 is replaced by a second suspended sphere B2 that has the same mass, radius, and charge, but that is conducting. Equilibrium is again established when sphere A is 1.5 m from sphere B2 and their centers are at the same vertical height. State whether the equilibrium angle 2 will be less than, equal to, or greater than 20°. Justify your answer. 1989E1. A negative charge - Q is uniformly distributed throughout the spherical volume of radius R shown above. A positive point charge + Q is at the center of the sphere. Determine each of the following in terms of the quantities given and fundamental constants. a. The electric field E outside the sphere at a distance r > R from the center b. The electric potential V outside the sphere at a distance r > R from the center c. The electric field inside the sphere at a distance r < R from the center d. The electric potential inside the sphere at a distance r < R from the center The long, solid inner (insulating) core of the above object has a charge of +Q. The outer shell has a charge of -2Q. a) b) c) d) What are the volume & linear charge densities of the inner core? Using Gauss Law, find the E field at any point r < a. Using Gauss Law, find the E field at any point a < r < b. Using Gauss Law, find the E field at any point r > b. A charged plate has a charge density of = 1.5 µC/m2. A small particle with a charge of 0.05 µC is placed 1m from the plate. What work is required to move this charge halfway to the plate? Let’s now move the particle VERY far away, so that the charged plate now appears to be a point charge. What work is required to move the small particle from 0.5m to infinity?