* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 6- p3 heart
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
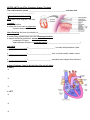
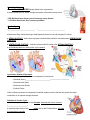
NOTES: UNIT 6 part 3-The Circulatory System: The Heart The cardiovascular system _________________________________________ to tissues and ______________________________. STRUCTURE OF THE HEART Size: about 14 cm long and 9 cm wide Location: ● 2/3 left of midline ● below 2nd rib and rests on diaphragm *Location allows for CPR Heart Covering: the heart is enclosed in a ______________________________________________; protects against ______________________ ● loosely fitting superficial part of the sac: fibrous pericardium ● deep to the fibrous pericardium: serous pericardium *composed of 2 layers *space between the layers = pericardial cavity (____________________________________) Heart Wall ● ____________________ = _____________________________; in contact with pericardium (older people= infiltrated with FAT) ● ____________________ = _________________________; thick, muscular (mainly cardiac muscle tissue!) ● ____________________ = _________________________; has elastic and collagen fibers (lines the heart chambers) 4 Heart Chambers: (heart is divided into right and left sides) ● RIGHT: ● LEFT: Heart Valves: designed to prevent backflow of blood! ATRIOVENTRICULAR VALVES: -________________________: separates R atrium from R ventricle -________________________ (a.k.a. _______________________): separates L atrium from L ventricle ● Structure of AV valves: -CHORDAE TENDINAE: _________________________________________________ Label me! _____________________________ -PAPILLARY MUSCLES: _________________________________________________ __________________ attach to the chordae tendinae *serve to anchor flaps in their closed position so pressure doesn’t blow them into atria like an umbrella on a windy day SEMILUNAR VALVES: -________________________________: separates R ventricle from pulmonary arteries -__________________________: separates L ventricle from aorta *ventricle contraction forces these valves open until contraction is over; blood flow backwards closes valves Path of Blood Through the Heart: ● Blood _____________________________________ enters the ______________ SIDE through the vena cava and is then pumped into pulmonary circulation (_________________________________________) ● After blood is ________________________ in the lungs, it returns to the __________ SIDE through the pulmonary veins and is then pumped into ______________________ circulation via the aorta (_________________________) Path of Blood Flow Through the Heart •Right side –Blood enters the right atrium through the superior and inferior vena cava right atrioventricular (tricuspid) valve right ventricle pulmonary semilunar valve pulmonary artery lungs •Left Side –Blood returns from the lungs through the pulmonary veins left atrium left atrioventricular (bicuspid, mitral) valve left ventricle aortic semilunar valve aorta Heart Blood Supply: ● the CORONARY ARTERIES supply blood to the myocardium ● blood returns to the R atrium through the cardiac veins and coronary sinus **500,000 Americans die per year of coronary artery disease **3.5 million Americans have coronary problems Cardiac Cycle: *______________________________ *______________________________ ●Ventricular filling: blood returning to heart passively flows into atria & the open AV valves ● ATRIAL SYSTOLE: atria contract (propels residual blood) while the ventricles relax (VENTRICULAR DIASTOLE) ● VENTRICULAR SYSTOLE: ventricles contract while the atria relax (ATRIAL DIASTOLE) ● all chambers relax for a brief period; cycle repeats! Conduction System of the Heart •The conduction system of the heart is composed of 4 structures –Sinoatrial Node (___________________________) –Atrioventricular Node –Atrioventricular Bundle –Purkinje Fibers •Each of these structures is composed of modified cardiac muscle cells that only permit the rapid conduction of an impulse through the heart Initiation of Cardiac Cycle: ● electrical impulses originate in the SA node: stimulate the atria to contract (_____________________) ● impulses pass slowly to the _____ node, then to the Purkinje fibers: stimulate the ventricles to contract ELECTROCARDIOGRAM (ECG/EKG): ● records the electrical changes in the myocardium during a cardiac cycle ● the pattern has several characteristic waves: 1) P wave: depolarization wave from SA through atria atria contract 2) QRS complex: ventricular depolarization; precedes ventricle contraction ventricles contract 3) T wave: ventricular repolarization diastole Regulation of Cardiac Cycle: ● heartbeat is affected by: -