* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download So…….what is natural Selection?
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Dual inheritance theory wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Inbreeding avoidance wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Selective breeding wikipedia , lookup
The Selfish Gene wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Life history theory wikipedia , lookup
Group selection wikipedia , lookup
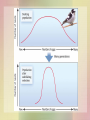
Natural Selection Garielle Wagnac Who knows? Natural Selection……… • It’s a process – Beneficial traits inherited become more common in consecutive generations • Causes evolution to occur • Happens because of adaptation YES, NATURAL SELECTION FAVORS INDIVIDUALS! BUT WHICH?!?! Reproductive Success • Likelihood of an individual contributing fertile offspring to the next generation • Traits favorable to reproductive success • Two categories of traits – Characteristics organisms better adapted – Traits associated with reproductive success Principles of Natural Selection I. Allele variation due to mutation (may alter function of protein) II. Some alleles enhance reproductive success III. Beneficial alleles more likely to survive IV. Allele frequency change through natural selection How do you measure reproductive success? FITNESS likelihood that a genotype will contribute to gene pool of next generation compared to other genotypes Mean Fitness average reproduction success of members *as mean increases, so does natural selection of organisms AA produces 5 offspring Aa produces 4 offspring aa produces 1 offspring There are 4! Directional Selection • Individuals at one extreme of phenotypic range have greater reproductive success in a particular environment • Arise from? – New allele added – Expose to change in environment Stabilizing Selection • Favors individuals with intermediate phenotypes an selects against those with extreme phenotypes • Tends to decrease genetic diversity Diversifying (Disruptive) Selection • Favors the survival of two or more different genotypes that produce different phenotypes • Likely to occur in populations that occupy heterogeneous environments Balancing Selection • Type of natural selection that maintains genetic diversity • Balanced polymorphism occurs – 2+ alleles kept in balance of each other • Can happen by……. Balancing Selection Heterozygote Advantage • Phenomenon where heterozygotes have a higher fitness than the corresponding homozygotes Negative frequencydependent selection • Fitness of a genotype decreases when its frequency becomes higher! At least, I hope so! NOW YOU KNOW EVERYTHING ABOUT NATURAL SELECTION!