* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name Date Ch 19 reading guide – Biology in Focus (Adapted from
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
Objections to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Jewish views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education in the United States wikipedia , lookup
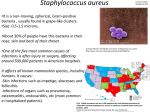
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Vestigiality wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
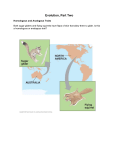
Name _______________________________ Date __________________ Ch 19 reading guide – Biology in Focus (Adapted from Fred and Theresa Holtzclaw’s reading guides) Concept 19.1 The Darwinian revolution challenged the traditional view of a young Earth inhabited by unchanging species. 1. How did each of the following sources view the origin of species? a. Aristotle b. The Old Testament c. Carolus Linnaeus d. Georges Cuvier e. James Hutton f. Charles Lyell 2. Jean-Baptiste de Lamarck proposed a mechanism for how life changes over time. Explain the two principles of his mechanism. a. use and disuse b. inheritance of acquired characteristics 3. Although Lamarck’s mechanism of evolution does not explain the changes in species over time, his thinking has been influential. What is considered to be the great importance of the ideas? Concept 19.2 Descent with modification by natural selection explains the adaptations of organisms and the unity and diversity of life. 4. What are adaptations? Give two examples. 5. Explain the process of natural selection. 6. Summarize Darwin’s observations that drive changes in species over time. Observation 1. Variations in traits exist. Cite an Example 2. These variations (traits) are heritable. 3. Species overproduce. 4. There is competition for resources; not all offspring survive. 7. To demonstrate your understanding of this section, complete the following sentences. These are extremely important! _____________________ do not evolve. __________________________ evolve. Concept 19.3 Evolution is supported by an overwhelming amount of scientific evidence. 8. Examine figure 19.14 and explain how the study of soapberry bugs by Scott Carroll et al demonstrated observable evolutionary change. 9. Explain how Staphylococcus aureus evolved into MRSA, methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus. 10. Do antibiotics cause bacteria to become resistant? Explain your response. 11. Make a list of four evidences for evolution from this section. Evidence for Evolution 12. What is meant by each of the following terms? Give an example of each. Term Homologous structures Example Vestigial structures Analogous structures 13. How do homologous structures give evidence for evolution? 14. Organisms that are only distantly related can resemble each other. Explain convergent evolution and describe how analogous structures can arise. 15. Give two examples of convergent evolution. 16. How does the fossil record give evidence for evolution? 17. Looking at Figure 19.20 – explain how cetaceans (whales) are closely related to hippopotamuses. 18. What is biogeography? How is it affected by continental drift and the presence of endemic species? Scientific Skills Exercise – p. 378 – answers questions 2-4 2. 3. 4.