* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Magnetism - Miss Toole
Magnetosphere of Jupiter wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Magnetosphere of Saturn wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic storm wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Edward Sabine wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic stripe card wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Magnetometer wikipedia , lookup
Giant magnetoresistance wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic nanoparticles wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Earth's magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotactic bacteria wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Superconducting magnet wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
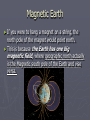
Drill: 10/26/10 ►What is an electromagnet? Why is it a useful tool? Magnetism Magnets magnet is any material that attracts iron or materials that contain iron. ►A ► Magnetic Force- the force of attraction or repulsion generated by moving or spinning electric charges (in the magnet) Magnetic Field ► The region around a magnet in which magnetic forces can act Magnetic Poles ► One of two points, such as the end of the magnet, that have opposing magnetic qualities. ► Opposites ► North Attract and Like Poles Repel. and South Magnetic Earth ► If you were to hang a magnet on a string, the north pole of the magnet would point north. ► This is because the Earth has one big magnetic field, where geographic north actually is the Magnetic south pole of the Earth and vise versa. Atoms and Domains ► Everything is made of atoms, in a magnet groups of atoms are in tiny areas called domains. ► The north and south poles of magnets line up and make a magnetic field. ► This means that even if you cut a magnet into pieces, each piece will have a north and south pole. Magnetizing ► When a magnet’s domain move because of another strong magnetic field, dropping or temperature it can become de-magnetized. ► Objects made of cobalt, iron or nickel can be magnetized by lining up its domains. Kinds of Magnets ► Ferromagnets- cobalt. ► Temporary made of iron, nickel or Magnets- magnetized objects ► Electromagnets- made by an electric current around an iron core. Electromagnetism ► The interaction between electricity and magnetism. ► Solenoid- a coil of wire that produces a magnetic field when carrying a current. ► Electromagnets are made from a solenoid around an iron core.













![magnetism review - Home [www.petoskeyschools.org]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002621376_1-b85f20a3b377b451b69ac14d495d952c-150x150.png)






