* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cellular Respiration
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
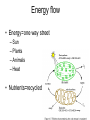
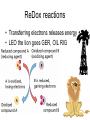
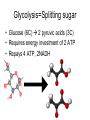
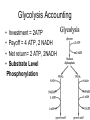
Cellular Respiration Life is Work Energy flow • Energy=one way street – Sun – Plants – Animals – Heat • Nutrients=recycled Catabolic pathways • Complex molecules=more free energy • Simple molecules = less free energy • Spontaneous, exergonic reaction – Organic compounds+O2 CO2 +H2O+Energy • Combustion • Cellular Respiration ReDox reactions • Transferring electrons releases energy • LEO the lion goes GER, OIL RIG • Na + CL Na+ + Cl• Oxidized? Reduced? • CH4 + 2O2 CO2 +2H2O + Energy – Carbon loses control of electrons, oxygen gains control of electrons – Electrons moving toward electronegative atoms are losing potential energy Oxidation of Glucose • C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy Sugar is oxidized, oxygen is reduced – Electrons associated with hydrogen are a good source of energy as they fall to oxygen • Carbohydrates • Fats • Glucose will burn in air • Enzymes lower activation energy Electron Transport Chain • Releasing all energy is inefficient • Step-wise degradation harvests more energy • Electrons are first passed to NAD+, then through the electron transport chain, then to oxygen NAD+ • Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide • Electron acceptor • Dehydrogenase enzyme removes 2 hydrogens (2 H+, 2 electrons) form sugar • Gives 2 electrons, 1 H+ to NAD+ NADH Electron Transport Chain • Electrons are delivered to ETC by NADH • ETC breaks the fall of electrons to oxygen • Each step/transfer releases a portion of the potential energy in electrons Each protein is more electronegative than the one above it Electrons move downhill towards oxygen Food NADH ETC Oxygen Stages of Cellular Respiration • Glycolysis • Citric Acid Cycle/ Kreb’s Cycle • Oxidative Phosphorylation Glycolysis=Splitting sugar • Glucose (6C) 2 pyruvic acids (3C) • Requires energy investment of 2 ATP • Repays 4 ATP, 2NADH Energy Investment Phase • Enzyme transfers 2 phosphates to glucose – Enzyme that transfers second phosphate is allosterically regulated by ATP (shuts down glycolysis when there is enough ATP in cell) • 2 Glyceraldehyde -3- phosphate Energy Payoff Phase • G-3-P is oxidized by NAD+ • Energy released by this step is used to attach a phosphate from cytosol • Phosphate groups are relocated to ADP by Enzymes (4 ATP formed) • Results in 2 pyruvic acid (pyruvate) Glycolysis Accounting • Investment = 2ATP • Payoff = 4 ATP, 2 NADH • Net return= 2 ATP, 2NADH • Substrate Level Phosphorylation