* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Disruption to Ecosystems
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Conservation psychology wikipedia , lookup
Introduced species wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem services wikipedia , lookup
River ecosystem wikipedia , lookup
Conservation agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Conservation biology wikipedia , lookup
Ecological resilience wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Lake ecosystem wikipedia , lookup
Habitat destruction wikipedia , lookup
Overexploitation wikipedia , lookup
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
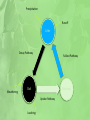
Disruption to Ecosystems Energy And Nutrients • Energy and nutrient flows are fundamental to an ecosystem functioning properly • Nutrient Cycle – the feedback of minerals from decomposed organic material back into plants • Energy Flows – the flow of energy through the system e.g. food chain or food web Energy Flows • Primary producers at level 1 convert sunlight into energy via photosynthesis. • Energy is lost through each respiration at each stage • The amount of biomass at each level also decreases. • Any change to this cycle can put the ecosystem under threat. Nutrient Flows • The circulation of chemical elements from the environment to organism and back to the environment again. • Nutrients are stored as either soil, litter or Biomass • This is easily affected as it is an OPEN SYSTEM and nutrients can be added physically or by human elements. Precipitation Runoff Litter Decay Pathway Weathering Fallout Pathway Soil Biomass Uptake Pathway Leaching Movement of Species • As we have traversed the world species have been moved both knowingly and unknowingly • They can pose a threat to the native ecosystem • Along with that many species become invasive along with other problems Alien Species share several features • Enhanced survival rates • Lack native predator • Not as susceptible to disease This means that they are often very difficult to control Look at the sheets about other alien species! VIDEO: Cane Toads: An Unnatural History • Why Is This Important? • The reason behind the introduction of cane toads to Australia was well intended but the results were unimagined. This is a good example of the fallibility of scientists and what can happen when an exotic species invades an ecosystem. A Natural Balance? Natural systems operate a dynamic equilibrium – a moving, changing balance. Weather events or disasters can alter the balance, but the system gradually adjusts either to new conditions or revert to previous situation. With the coming of humans and their domination of so much of the natural world this balance has been drastically altered and, in many cases, so quickly that ecosystems have not been able to adapt. How can humans influence the nutrient flow? • Deforestation • Over harvesting • Soil degradation • Fertilisation Case Study: Giant Kelp, California • Giant kelp is a type of seaweed which supports a wide range of species of the coast of California • It acts as a breeding ground and nursery for many fish • One herbivore of the giant kelp is the sea urchin, which could destroy the habitat • The sea otter is the predator responsible for keeping the urchin at bay • BUT the sea otter was hunted by humans during the 19th and early 20th Century • The whole ecosystem collapsed • The sea otter is known as a keystone species Food chain in the kelp forest, California What factors threaten biodiversity? An unsustainably high rate of human population growth and natural resource consumption Inequality in ownership, management and flows of benefits which threatens the lives of the poorest people Concentration of agriculture, forestry and fishing on a narrowing spectrum of products Legal and institutional systems that promote unsustainable exploitation at the expense of more sustainable strategies Lack of knowledge and understanding in the management and conservation of biodiversity What are the global factors? What does this diagram tell you about the global factors? Demonstrate: Using the factors create a mind map to show what impact they have. Climate change Deforestation Global threats to biodiversity What are the local factors to affect biodiversity? Fire – used to be used all over Europe and North America to clear forests for settlements. This is now used regularly in the rainforest to clear land for cattle ‘slash and burn’. Causing huge loss of biodiversity. Habitat Change – developing natural habitats for agriculture or urban growth…eventually leads to loss of biodiversity Recreational use – often occurs where ecosystems are vulnerable and plants are fragile e.g. sand dune system.