* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Class Notes - December 4
Anti-gravity wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Atomic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Chien-Shiung Wu wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear physics wikipedia , lookup
Condensed matter physics wikipedia , lookup
Electrostatics wikipedia , lookup
Time in physics wikipedia , lookup
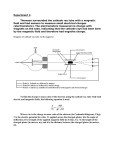
Atomic Physics.notebook December 04, 2013 Cathode Ray Tubes Cathode ray tubes consist of three main chambers: Main Chamber Acceleration Chamber The cathode rays (electrons) are first accelerated across a potential difference using electrical potential energy. The electrical potential energy is converted to kinetic energy and the electrons gain speed. Velocity Selection Chamber In a velocity selection chamber, a magnetic field and electric field are adjusted until the magnetic force and electric force are balanced for all electrons moving at a particular speed. These electrons will travel undeflected through the velocity selection chamber and enter the main chamber. Fe = Fm qV = 1/2 mv2 Nov 912:31 PM 1 Atomic Physics.notebook December 04, 2013 JJ Thomson (1897) JJ Thomson did some experimentation with a cathode ray tube that led to his discovery of the electron. It was well known before Thomson began his experiments that cathode rays could be deflected by electric and magnetic fields. From these deflections, Thomson reasoned that the cathode rays were really beams of negatively charged particles (electrons). He further reasoned that he could measure the chargetomass ratio of these electrons by passing a cathode ray through a magnetic field and measuring the radius of its path. Fm = Fc Nov 912:31 PM 2 Atomic Physics.notebook December 04, 2013 Example 1 A student performs a cathode ray tube experiment. The magnetic field strength from the coils was 0.040 T. The parallel plates were set 3.0 mm apart. In order to produce a straight cathode ray beam a 3600 V potential was applied across the plates. When the electric field is turned off, the cathode rays are bent into a curve of radius 4.26 mm by the magnetic field. What is the charge to mass ratio for the cathode ray particles? Nov 912:31 PM 3 Atomic Physics.notebook December 04, 2013 Example 2 In a modified Thomson experiment, when a hydrogen atom beam is exposed to a magnetic field of 0.0400 T and an electric field produced by 3600 V applied across parallel plates which are 3.00 mm apart, the particles go straight. When the electric field is turned off, the particles were observed to move through a radius of curvature of 7.828 m. What is the chargemass ratio for the hydrogen ions? Nov 912:31 PM 4 Atomic Physics.notebook December 04, 2013 Thomson's Atomic Model Thomson performed a series of experiments that led him to conclude that the greenish cathode rays were really beams of negatively charged particles (electrons). Thomson thus developed an atomic model that was different from the previous Dalton Solid Sphere model. Instead of the atom being a simple solid sphere. Thomson said that the atom was a sea of positive charge filled with these negatively charged electrons. Nov 912:31 PM 5 Atomic Physics.notebook December 04, 2013 Homework Practice Problems pg 756, 758 Mass Spectrometer pg 759 Check and Reflect pg 760 # 110 Nov 912:31 PM 6 Atomic Physics.notebook December 04, 2013 Millikan's Oil Drop Experiment Robert Millikan designed an experiment that would measure the elementary charge. • He sprayed oil through an atomizer into a chamber was bordered by a positively charged plate and a negatively charged plate. • He observed the way the oil drops interacted with the charges that were present on the plates. • The easiest oil drops to analyze are those that are suspended or are traveling at a constant velocity. Fe = Fm Fnet = Fe + Fg Nov 912:31 PM 7 Atomic Physics.notebook December 04, 2013 Example 3 An oil drop with a mass of 8.0 x 1015 kg is introduced between two parallel plates set 5.0 mm apart with a potential difference of 1.225 kV across the plates. If the oil drop is suspended between the plates, what is the charge on the oil drop? Nov 912:31 PM 8 Atomic Physics.notebook December 04, 2013 Homework Practice Problems pg 763, 764 Check and Reflect pg 767 # 17 Nov 912:31 PM 9