* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download topic 12 Notes revised
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
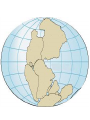
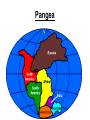
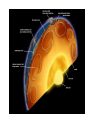
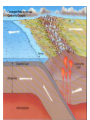
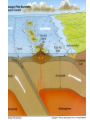
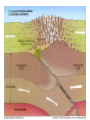
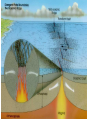
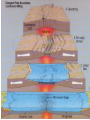
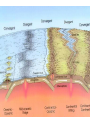
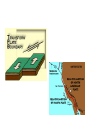
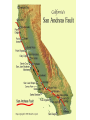
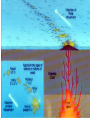
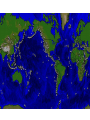
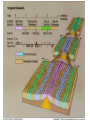
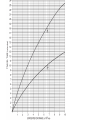
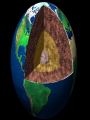
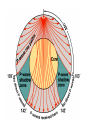
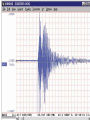
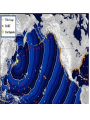
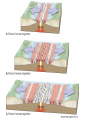
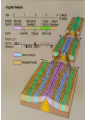
Topic 12 The Dynamic Crust Principle of Original Horizontality: • The assumption that sedimentary rocks form in horizontal layers. Drawing: • Then how do you explain this? Evidence of Crustal Change • Folding, faulting, tilting of rock strata (layers) • Drawings: • Displaced rocks and fossils • Volcanoes/ Earthquakes “Continental Drift”- Alfred Wegener Theory: the continents are sliding across the Earths’ surface. Evidence: • Shape of the continents. • Warm water fossils in Greenland. • Similar rocks and fossils • Similar mountain ranges • Pangea- “All lands” Pangea Pillow Lavas Plate Tectonics Theory: • Earth’s crust is made up of a variety of plates that are moving. • • • • • • Divergent Sea floor spreading Alfred Wegener Plate tectonics Volcano Convergent • • • • • • Mid ocean ridge Transform Boundary Mantle Convection Currents Trench Subduction Mid Ocean Ridge • Underwater mountain range that wraps around the Earth Evidence of Sea Floor Spreading 1. Age of rocks 2. Temperature of Rocks 3. Basalt Pillow lavas (igneous extrusive) 4. Paleomagnetism Drawing: Crustal plates move due to convection currents in the Earth’s mantle (asthenosphere)!!! Plate Boundaries Oceanic Crust • Thinner • More dense • basaltic Vs. Continental Crust • Thicker • Less dense • granitic Convergent Boundaries 1. Oceanic – Continental Drawing Features • E-quakes • Volcanoes • Trenches • Mountains Examples: • South America • Cascades 2. Oceanic – Oceanic Drawing Features • E-quakes • Volcanoes • Trenches • Mountains Examples: • Japan • Aleutian Islands (Alaska) 3. Continental – Continental Drawing Features • E-quakes • Mountains • Volcanoes (extinct) Examples: • Himalayas Divergent Boundaries: 1. Mid Ocean Ridges 2. Rift Zones Transform Boundary: • Boundary where plates slide by each other. Drawing: Example: • San Andreas Fault “Hot Spots” • Regions of volcanic (magmatic) activity usually away from plate edges. Example: • Hawaii Earthquakes, volcanoes and mountains are usually associated with plate boundaries. BONUS: • What is the relationship between the distance a planet is from the Sun and the gravitational force between the planet and the Sun? Earthquakes • The shock wave produced by the sudden movement of rocks in the Earth’s crust. Seismograph- instrument used to detect and record earthquake waves. Focus- point below the surface where the earthquake originates. Epicenter- point at the Earth’s surface directly above the focus. Seismic Waves Primary Waves Secondary Waves • “P-Waves” • Compressional waves • “S-Waves” • Transverse waves. • Faster • Travel through liquids and solids • Slower • Travel through solids only! The difference between the P & S wave arrival times can be used to calculate the distance from the epicenter. To find the epicenter, one must find the distance from at least 3 seismic stations. Earth’s Interior: • See diagram p. 10 in the Earth Science Reference Tables. Evidence: • Seismic Data • Meteor Composition • Earths Magnetic Field • Moon Composition Earthquake Damage Depends on… • Magnitude of the earthquake • Distance from the epicenter • Building structure • Type of surface Richter Scale vs. Mercalli Scale Brain teaser • A seismic station is located 5,200 km away from the epicenter of an earthquake. What will be the difference in the arrival time between the P and S waves at this station? Earthquake Emergency Planning Individual- “Drop, Cover and Hold” • Drop down under strong object (desk, table) • Cover your eyes • Hold onto the strong object you are under. • Earthquake drills • Have emergency supplies on hand. Do not try to run out of buildings!!! Earthquake Emergency Planning Community • Proper planning of building sites • Proper building construction • Retrofitting older buildings to make them safer Tsunami • Large wavelength ocean wave produced by disruption of the ocean floor. Volcanoes • A mountain composed of igneous extrusive rock. Violent Eruptions vs. Non-Violent Eruptions Mt. St. Helens Hawaii BONUS: • What was the name of the scientist who developed the Theory of Continental Drift? BONUS: • The epicenter of an earthquake is 4800 km away from a seismic station. What is the difference in arrival time of the P and S waves at that station? In Loving Memory of Ebony 2006-2012