* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The big data challenges of connectomics
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
The Measure of a Man (Star Trek: The Next Generation) wikipedia , lookup
Data (Star Trek) wikipedia , lookup
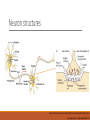
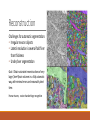
The big data challenges of connectomics JEFF W LICHTMAN, HANSPETER PFISTER NIR SHAVLT PRESENTED BY YUJIE LI, OCT 21TH,2015 Connectomics • The study of the structural and functional connections among brain cells. • Product is the “connectome,” a detailed map of those connections. • Significant to understanding of the healthy and diseased brain. • “I am my connectome” -- Sebastian Seung Neuron structures http://science.kennesaw.edu/~jdirnber/Bio2108/Lecture/LecPhysio/PhysioNervous.html http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK21535/ How many neurons in a human brain? 100 billion neurons How many neurons in a Drosophila? 100,000 neurons. ~ 107 synapses A video to appreciate the challenge faced with connectomics Brainbow Technique A Voyage Into the Brain http://ngm.nationalgeographic.com/2014/02/brain/voyage-video Acquisition Analytical problems stand between the acquired image and having access to the data in a useful form • Alignment • Reconstruction • Feature detection • Graph generation Alignment sections collected on a belt may rotate. Reconstruction Challenges for automatic segmentation: • Irregular neuron objects • Lateral resolution is several-fold finer than thickness • Under/over segmentation Goal : Obtain saturated reconstructions of very large (1mm3)brain volumes in a fully automatic way, with minimal errors and reasonably short time. Human tracers, cursive handwritings recognition Feature detection Subcellular features: mitochondria, synaptic vesicles etc… Difficult to find cell boundaries Irregular shape Reduce error and analysis time Graph generation •Data turned in to a form that represents the wiring diagram. •Data reduction step • How much of original data to retain? • How to store the graph? • Skip Oct-trees. Common theme: Dehumanizing the pipeline An irony is that humans are especially good at these tasks…. If we know how our brain wires, would be easier to develop tools to automate these processes. Big data challenges of connectomics • Data size • Data rate • Computational complexity • Parallel computing • Compute system • A heterogeneous hierarchical approach • Data management and sharing Data size 1mm3 rat cortex image = 2 million gigabytes = 2 petabytes A complete rat cortex 500mm3 = 1,000 petabytes (Walmart database manages a few petabytes of data) A complete human cortex ~1000 larger than rodents = 1,000 * 1000 petabytes = 1 zetabyte (All information recorded globally today) Data rate - Imaging task distributed to different labs - Complete connectome of a human cortex is the goal! - Maybe start with substructures. Data management and sharing - Assumed we obtained the data, do we store it? ◦ Yes, image and graph. - How to move from microscope to the computer system? Transfer bandwidth ◦ Placing computer near the microscope. ◦ 500 standard 4-core 3.6 GHz processors would suffice. $1 million. - Where to store? ◦ Disk or tapes. - How to share? ◦ Internet Current achievable data rates: 300 megabites/second ◦ Central sharing sites ◦ Reconstructed layout graph is easier to deal with. Computational complexity The goal of many big data system is more than to simply allow storage and access to large amounts of data. Rather, it is to discover correlations within data. ◦ Sampling ◦ Parallel computing ◦ Image segmentations and feature extraction are embarrassingly parallel. A heterogenerous hierarchical approach Combines bottom-up information from the image data with top-down information from the assembled layout graph, to dynamically decide on the appropriate computation level of intensity to be applied to a given sub-volume. 1) Initially apply the lowest cost computations to small volume. 2) The sub-graphs will be tested for consistency. 3) If discrepancies are found, more expensive computation used. 4) The process will continue hierarchically, growing the volume of merged segments. Prospects - The field needs a significant investment to advance. - Commercial values in connectomics ◦ Treating brain diseases ◦ Appling lessons learnt to making computer smarter - Challenges beyond the horizon: still big data problem Comments No address on the EM technical limitations: • Samples post-mortem, not in vivo • Physical damage during section, potential distortion. • Lack functional information No comparison with the current popular approaches to the problem • Two photon, confocal, brightfiled images • Neuron-labelling approaches (physical dye, genetic approach) Big data is not only about handling the super large dataset. • It is also about finding a smart way to fuse data from different modalities and different sources to obtain a comprehensive understanding