* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Fundamentals of Genetics Power Point
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
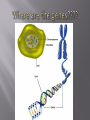
Chapter 9 Lab Bio Chapter 12 Honors Bio Brainstorm: - define genetics - define heredity Anticipatory Set: How important is it to be able to find your own answers to questions you may face? Does education and learning end with your high school or college years? How do you plan to develop the skills to become a life long learner? The study of how characteristics are transmitted from parent to offspring The transmission of characteristics from parent to offspring Chromosome: structure within nucleus, made of DNA Gene: unit of heredity found in DNA molecule (words) Allele: symbols (letter) used to represent genes ex: T=tall, t=short Dominant: trait/characteristic that are expressed – represented with capital letter Recessive: trait/characteristic that may not be expressed (always lower case) ex: t=short Homozygous/pure: both alleles are alike ex: TT or tt Heterozygous/hybrid: alleles differ ex: Tt Genotype: genetic make up ex: pure )homozygous) tall, hybrid (hetero.) tall Phenotype: what you see (physical appearance) ex: tall, short Cross: symbolic of reproduction ____ X _____ P: parent generation F1: first generation Do you think that we could make as many discoveries in science if we didn’t use animals? Explain….. ! Austrian Monk Studied garden pea plants (Pisum sativum) 1842 he entered the monastery in Austria 1851 enetered Univ. of Vienna to study science and mathematics (statistics) Observed 7 characteristics each in 2 contrasting traits: Long short stems Axial terminal (flower position) Green yellow (pod color) Inflated constricted (pod appearance) Smooth wrinkled (seed texture) Yellow green (seed color) Purple white (flower color) He controlled how pea plants were POLLINATED!!! SELF POLLINATION=pollen is transferred from anthers (male) of a flower to stigma (female) of same flower or flower on the same plant CROSS POLLINATION=involves flowers of 2 separate plants 1. remove anthers from a flower 2. manually transfer the anther of a flower on one plant to stigma of a flower on another plant P1 (cross) yellow x green Law of Dominance F1 ALL GREEN F1 (cross) green x green Law of Segregation F2 ¾ GREEN, ¼ YELLOW Mendel hypothesized that the trait appearing in the F1 generation was controlled by a DOMINANT FACTOR because it masked, or dominated, the other factor for a specific characteristic. RECESSIVE is the trait that did not appear in the F1 generation but reappeared in the F2 generation. A pair of factors (alleles) is segregated (or separated) during the formation of gametes Each reproductive cell (gamete) receives only one factor of each pair. Crossed two heterozygous green plants! He also crossed plants with 2 different characteristics Ex: flower color & seed color FACTORS FOR DIFFERENT CHARACTERISTICS ARE DISTRIBUTED TO GAMETES INDEPENDENTLY. Ex: Pure tall yellow x pure short green TTYY x ttyy A GENE is the segment of DNA on a chromosome that controls a particular trait. Chromosomes are in pairs i.e. Genes occur in pairs (each of several alternative forms of a gene is called an ALLELE MENDEL’S FACTORS ARE NOW KNOW AS ALLELES!!!!!! CAPITAL = Dominant alleles Lower case = recessive alleles Example: G = green color (dom.) g = Yellow pod color (rec.) When gametes combine in fertilization offspring receive ONE ALLELE for a given trait from EACH PARENT! Helps us predict the likely outcome of offspring!! 1. genotype: genetic make-up, consists of alleles Ex: P=purple, Pp = purple PP = purple White = pp p=white 2. Phenotype = appearance of an offspring (what you see) Ex: purple flowers, white flowers, hair color 3. Homozygous = when both alleles of a pair are alike Ex: tt, TT, PP, pp Homozygouse recessive = pp Homozygouse dominant = PP 4. Heterozygous = two alleles in a pair are different Ex: Pp or Tt Law of Dominance Law of Segregation Test Cross MENDEL’E RULES DO NOT APPLY TO: Incomplete dominance Multiple alleles Codominmanmce Polygenic inheritance Pleiotyropy Environmental influence Law of dominance Law of segregation Test cross Incomplete dominance Codominance Independent assortment Sex determination Sex linkage Multiple alleles