* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Marketing task
Pricing science wikipedia , lookup
Yield management wikipedia , lookup
Perfect competition wikipedia , lookup
Market segmentation wikipedia , lookup
Visual merchandising wikipedia , lookup
Revenue management wikipedia , lookup
Consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Bayesian inference in marketing wikipedia , lookup
Sales process engineering wikipedia , lookup
Affiliate marketing wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Price discrimination wikipedia , lookup
Customer experience wikipedia , lookup
Social media marketing wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
Customer relationship management wikipedia , lookup
Ambush marketing wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Sports marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Customer engagement wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Customer satisfaction wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Services marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
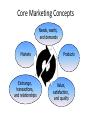
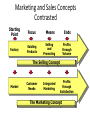
Principles of Marketing The digital revolution has placed a whole new set of capabilities in the hands of consumers and businesses. Now the marketers are to consider what customers have today that they didn’t have yesterday: • A substantial increase in buying power. • A greater variety of available goods and services • A great amount of information about practically anything • A greater ease in interacting and placing and receiving orders • An ability to compare notes on products and services Principles of Marketing Companies have a new set of capabilities also: • Wide geographical reach to inform and promote their businesses and products • Companies can collect fuller and richer information about markets, customers, prospects and competitors. • Companies can facilitate and speed up internal communication among their employees • Two-way communications with customers and prospects, and more efficient transactions • Companies are now able to send ads, coupons, samples and information to customers • Companies can customize offerings and services to individual customers Principles of Marketing • Companies can improve purchasing, recruiting, training and internal and external communications. • Companies can substantially improve logistics and operations for cost savings while improving accuracy and service quality Industrial age was characterized by mass production and mass consumption, stores overstuffed with inventory, ads everywhere and rampant discounting, The information age promises to lead to more accurate levels of production, more targeted communications, and more relevant pricing. Principles of Marketing So, the principle of marketing can be phrased as “meeting the needs profitably” What is Marketing? - A set of processes for creating, communicating, and delivering value to customers and for managing customer relationships in ways that benefit the organization and its stakeholder. - It is the art and science of choosing target markets and building profitable relationships with them. Ten types of entities can be marketed by the marketers • • • • • Goods Services Experience Properties Information •Places •Events •Persons •Organizations •Ideas Marketing tasks based on demand states Negative demand like vaccination, dental works, gall bladder operation, etc. Marketing task is to analyze the dislikes and may modify product i.e. redesign, lower price and more positive promotion to change beliefs and attitudes. No demand target consumers may be unaware of or uninterested in the products like foreign language course, new farming method etc. Marketing task is to connect the benefits of the products with peoples natural needs and interests. Latent demand consumers share a strong need that can not be satisfied by any existing products. e.g. more fuelefficient cars, safe neighborhood, side-effect free anticancer agents. Marketing task is to measure the size of potential market & develop goods & services to meet the demand. Marketing tasks based on demand states Declining demand every organization, sooner or later, faces declining demand for one or more of its products. e.g. Paracetamol+caffeine when marketized, paracetamol found declinind demand. Marketing task is to motivate consumers the benefit of the previous one or redesign the product so that it become acceptable again. Irregular demand that is seasonal demand. e.g. museums are under visited on weekdays and over crowded on weekends. Marketing task is to alter the pattern of demand through flexible pricing, promotion and other incentives. Full demand organizations face full demand when they are pleased with their volume of business. Marketing task is to maintain this demand, improve its quality and continually measure consumer satisfaction Marketing tasks based on demand states Overfull demand some organization faces this type of demand. e.g. Disney theater. Marketing task is to demarketize, like raising price and reducing promotion and services. Unwholesome demand cigarettes, alcohol, hard drugs, etc. Marketing task is to get people who wants to give it up and help them such a way like fear messages, price hike and reduced availability. Importance of customer satisfaction • It is important to consistently deliver product and service that create values for customers. • Brand equity and customer loyalty are built in this way. • This can be explained in terms of theory of uncertainty. Customer-Driven Marketing Strategy Selecting customers to serve • the company must first decide who it will serve, i.e. market segmentation is done and then selecting which market it will go after. • Targeting to serve all the customers means not serve any customers well. • Marketing management is customer management and demand management. Choosing a value proposition • A company’s value proposition is the set of benefits or values it promises to deliver to satisfy their needs. • Such value propositions differentiate one brand from another. What is Marketing? Customer-Driven Marketing Strategy cont…. Marketing management orientation there are five alternative concepts under which organizations design and carry out their marketing strategies. They are: • Production concept: - oldest orientation model lead to marketing myopia - consumers will favor products that are available and highly affordable - it loses the sight of real objective, i.e. customer satisfaction • Product concept: -product quality, performance, and innovative features - it also can lead to marketing myopia Customer-Driven Marketing Strategy cont…. • Selling concept: - it is typically practiced with unsought goods such as insurance, blood donation etc. - carries high risk, as it focuses on creating sales transaction rather long term customer relationship • Marketing concept: - instead of “make and sell” philosophy it is a customer centered “sense and respond” philosophy - the job is not to find the right customers for the product but to find right products for the customers Customer-Driven Marketing Strategy cont…. • Social marketing concept: -it tells that marketing strategy should deliver value to customers in a way that maintains or improves both the consumer’s and society’s well being. The Marketing Mix • The conventional view of the marketing mix consisted of four components: Product marketing efficiency depends on the best quality products. Price if the price is reasonable then marketing becomes easier. There are three types of price: Penetration Pricing – charging a low price, possibly not quite covering costs, to gain a position in the market. This is quite popular with new businesses trying to get a ‘toehold’. Creaming – the opposite to penetration pricing, this involves charging a deliberately high price to persuade people that the product is of high quality. Luxury car makers often use this strategy Cost plus Pricing – this is the most common form of pricing. Costs are totalled and a margin is added on for profit to make the total price. Place a place having available transport and good communication facilities Promotion Customers have to be made aware of the product. The two main considerations are target market and cost. A new business will not be able to afford to advertise on national television, for instance and would not wish to because its market will be local to start with. Leaflets, billboards, advertisements in local newspapers, Yellow Pages and ‘word of mouth’ would be more appropriate. The Marketing Mix • Generally acknowledged that this is too narrow today; now includes service, processes, technology. • Marketers today are focused on virtually all aspects of the firm’s operations that have the potential to affect the relationship with customers. Marketers and Markets • Marketers are focused on stimulating exchanges with customers who make up markets – B2C or B2B. • The market is comprised of people who play a series of roles: decision makers, consumers, purchasers, and influencers. • It is essential that marketers have a detailed understanding of consumers, their needs and wants. • Much happens before and after the sale to affect customer satisfaction Customer-Relationship Thinking • The customer-relationship view of marketing requires some new thinking: • It is very much a long-term strategy • Requires that management take the customer’s view • The value proposition must be defined very broadly • Different measures of success are needed The New View of Marketing • The marketing emphasis today is on keeping existing customers as well as getting new ones • Four principles guide marketing: – – – – retention: keeping them coming back referrals: encourage them to recommend us relationships: build an emotional connection recovery: solve problems as they arise The Purpose of a Business Is to Create and Retain the Right Customer Core Marketing Concepts Needs, wants, and demands Markets Exchange, transactions, and relationships Products Value, satisfaction, and quality Need, Wants, Demands • Need. A human need is a state of felt deprivation. Examples include the need for food, clothing, warmth and safety. • Wants. Wants are how people communicate their needs. A hungry person may want a hamburger, noodles, or cheese and bread. • Demands. When backed by buying power, wants become demands. Product A product is anything that can be offered to satisfy a need or a want. Value, Satisfaction, and Quality • Customer value is the difference between the benefits that the customer gains from owning and/or using a product and the costs of obtaining the product. • Customer satisfaction depends on a product’s perceived performance in delivering value relative to a buyer’s expectations. • Quality begins with customer needs and ends with customer satisfaction. Why Satisfaction May Not Lead To Customer Loyalty • Some customers never return to an area – but they can still recommend • Some customers shop for the best price differentiate your product • Some customers like to have different purchase experiences – like to stay or dine at different places Why Managers Should Be Concerned About Customer Loyalty • Customer loyalty leads to increased profit • Customer loyalty leads to increased partnership • Lower marketing and sales costs Exchange, Transactions, and Relationships • Exchange is the act of obtaining a desired object from someone by offering something in return. • A transaction is marketing’s unit of measurement and consists of a trade of values between two parties. • Relationship marketing builds relationships with valued customers, distributors, dealers, and suppliers by promising and consistently delivering high-quality products, good service, and fair prices. Markets A market is a set of actual and potential buyers who might transact with a seller. Marketing and Sales Concepts Contrasted Starting Point Focus Factory Existing Products Means Ends Profits through Volume Selling and Promoting The Selling Concept Market Customer Needs Integrated Marketing Profits through Satisfaction The Marketing Concept