* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The ovaries produce oestrogen and progesterone and 1 egg each
Hypothyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (menopause) wikipedia , lookup
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Growth hormone therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Progesterone (medication) wikipedia , lookup
Progesterone wikipedia , lookup
Pituitary apoplexy wikipedia , lookup
Polycystic ovary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Kallmann syndrome wikipedia , lookup
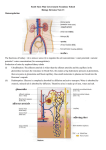
Menstrual Hormones & Fertility BLOOD TEST & HORMONES FSH < 6mlU/ml excellent; 6-8 good; 9-10 fair; 11-13 poor reserve. High levels = poss PCOS, menopause. Oestradiol 25-75pg/ml LH < 7mlU/ml Prolactin < 24ng/ml Progesterone >15ng/ml Thyroid (TSH) 1.7ulU/ml Testosterone 6-86ng/dl: >50 elevated. Luteinizing Hormone (LH): Released by the pituitary, stimulates ovulation, the formation of the corpus luteum and the production of progesterone by the ovaries. Tested days 1-3, high levels may indicate PCOS or menopause. Prolactin: Secreted by the pituitary, controls milk production and stimulates progesterone. Tends to be higher in the LH phase. It is tested if PCOS is suspected. High levels may cause ovulation problems or low progesterone which may cause difficulty maintaining pregnancy. Thyroid (TSH): Produced by the pituitary, controls thyroid function, important for metabolic processes and body systems. A high TSH level + low thyroxine (T4) level usually points to under active thyroid, a factor in infertility. If TSH levels are normal + low T4, there is a poss pituitary problem. Androgens (Testosterone): Level checked at beginning of cycle to eliminate possibility of PCOS. If the pituitary produces high levels of LH, it prevents ovulation and causes the ovaries to secrete high levels of male hormone. Progesterone: Checked at day 21 (7-10 days after ovulation in a 28 day cycle, or 7 days pre-period), when the follicle releases it’s egg, it becomes the corpus leuteum and progesterone is produced. It indicates if ovulation has occurred, or if there is Luteal phase defect (LPD) which may cause pregnancy difficulty. The ovaries produce oestrogen and progesterone and 1 egg each month. There are two phases: (i) (ii) Follicular phase associated with oestrogen production stimulates development on the egg until release (Ovulation). Luteal Phase associated with progesterone stimulates endometrium (womb lining) growth to sustain a fertilised egg. Medical Acupuncture Clinic – www.med-acu.com Menstrual Hormones & Fertility FOLLICULAR PHASE: Begins the 1st day of menstrual bleeding. The egg (ovum) begins development. It contains half the genetic material required, the other half is provided by the sperm, for the foetus. At the start of the follicular phase, the hypothalamus (regulates the Pituitary gland) in the brain releases gonadotrophin –releasing hormone (GnRH), this stimulates the pituitary to release follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), which stimulates the eggs to develop in the ovary. Up to 20 eggs may respond and develop within sacs called follicles, which provide nourishment for growth. As the eggs develop, the ovaries release oestrogen. This causes the pituitary to reduce FSH so that only sufficient is available to stimulate growth of 1 egg, the others deteriorate. Oestrogen also stimulates the uterus lining (endometrium) to thicken for fertilised egg implantation. The primary follicle contains the developing egg. The oestrogen level continues to increase until it triggers the pituitary to release a surge of Luteinizing hormone (LH) which stimulates ovulation (the follicle ruptures and releases the egg and follicular fluid on the ovary surface). LUTEAL PHASE: The ruptured follicle continues to receive pulses of LH, turning it into a small cyst, the corpus luteum, which produces progesterone. PROGESTERONE: (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) Thickens the endometrium, developing glandular structures and blood vessels to supply a developing embryo. Shuts down FSH & LH production. Raises basal body temperature (BBT) by half a degree, warming & infusing the uterus. Cervical mucus secretion / texture improves & cervix moves lower in the vagina. Medical Acupuncture Clinic – www.med-acu.com Menstrual Hormones & Fertility THE EGG: Surrounded by a protective shell (zona pellucida) which is further surrounded by a mass of sticky cells (cumulus oophorous) which allow finger-like projections at the end of the Fallopian tubes to move the egg into the tube. The tubes are lined with cilia (small hairs), & together with muscular contractions - provided fertilization occurs - these direct the egg into the uterus which takes approx 6 days. If the egg while in the fallopian tube is not fertilized, it disintegrates and is absorbed. Fertilization needs to occur within 24 hrs of ovulation. FERTILIZATION: Most healthy sperm can live in the female reproductive tract for several days. Therefore intercourse up to 3 days pre-ovulation may still result in fertilization. Upon penetration of the egg nucleus by the sperm the genetic material of both fuse to form the required 46 chromosomes for development. Cell division begins. Hormonal Imbalance & Fertility OESTROGEN DEFICIENCY Generally in older women, from 35yrs there is a decline in oestrogen and subsequently ovulation. Oestrogen levels can also be reduced by: Excess of wheat fibre in the diet, low body weight - 15% below normal, poor diet, anorexia, lack of Vit.A, excess exercise, smoking, antibiotics, contraceptive pill long term, all may cause menstruation to become intermittent or stop. Symptoms: Irregular Periods, intercourse difficulty, vaginal dryness, hot flashes, night sweats, bladder infections, premature ageing. Treatment: Phyto-oestrogens – plant compounds resembling oestrogen but weaker. These attach to oestrogen receptors on body cells supplementing oestrogen. This helps reduce the heaviness & length of the menstrual flow, rebalance the oestrogen/progesterone ratio, lengthen the Luteal Phase and inhibit oestrogen dependent carcinogens that can cause breast cancer. They are also rich in immunity-enhancing flavonoids, vitamins, minerals, amino acids, essential fats and fibre. Food sources: Fruit, green veg, grains beans, pulses, alfalfa, oats, hops, cherries, etc. (Soya is a rich source but may have contraceptive properties – not recommended.) Herbalist – low dose natural oestrogen PABA – para-aminobenzoic acid, a component of Vit.B-complex, stimulates the pituitary to produce oestrogen. Medical Acupuncture Clinic – www.med-acu.com Menstrual Hormones & Fertility PROGESTERONE DEFICIENCY Progesterone production declines during Perimenopause, when ovulation also declines. Insufficiency can occur due to: Ovulation failure, or insufficient length of time of progesterone production in the Luteal Phase – it is also known as Luteal Phase Defect (LPD). Pregnancy is unlikely unless the Luteal Phase is longer than 10days. Initially, progesterone maintains pregnancy, so deficiency may cause miscarriage. It may also occur after pill use, miscarriage, or breastfeeding. It is more likely in polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Can be caused by faulty secretion of other reproductive hormones – FSH, LH, or Prolactin. It is linked to endometriosis and menstrual cycle difficulties. Symptoms: Include painful or lumpy breasts, menstrual cycle headaches, anxiety, irritability, sleeping problems, unexplained weight gain, PMS (premenstrual syndrome), bleeding between periods and reduced libido. Solutions: Prescribed medications, Vit.B6 & E, magnesium, evening primrose oil, Vitex Agnus Castus (herbal). Treatment: Reduce stress, exercise but not excessively, increase low body weight. OESTROGEN EXCESS: Environmental oestrogens (found in pesticides, plastics and PCBs – chemical pollutants in water, air and soil) are structurally similar to body oestrogen, with similar action, upset the oestrogen / progesterone balance. Diet: too much refined carbohydrate and saturated animal fat, high fat diet, obesity, lack of exercise and too little fibre contributes. Eat fresh fruit, esp apples and pears, veg, whole grains, oats and oat bran (NOT wheat bran – may irritate intestine lining). Organic is best. Symptoms: Puffiness, bloating, water retention, rapid weight gain, breast tenderness, heavy bleeding, mood swings, sleep problems, migraine, flushed face, reduced libido, foggy thinking, endometriosis, fibroids, gall bladder problems, poor blood sugar control, and hypothyroidism. Treatment: Low fat, high fibre, nutrient rich diet with phyto-oestrogens will improve hormonal balance. Veg like the cabbage family increase the rate the liver converts oestrogen to a water soluble form for excretion. Increased protein improves oestrogen metabolism in the liver, and Vit.B6 reduces the effects of oestrogen excess. Medical Acupuncture Clinic – www.med-acu.com Menstrual Hormones & Fertility ANDROGEN EXCESS (MALE HORMONE) Usually associated with PCOS (polycystic ovary) in women, also poor diet – excess sugar, refined foods and simple carbohydrates (sweets, jams, tinned fruit, chocolate, etc.), adrenal disorders, steroids, and obesity. Symptoms: acne, ovarian cysts, ovarian tumor, excess body hair, unstable blood-sugar levels, thinning head hair, mid-cycle pain, irregular periods. Treatment: High-fibre vegetarian diet low in saturated fats and high in phyto-oestrogens. Medical help. CORTISOL Produced in the adrenal glands over the kidneys, it also increases oestrogen, If deficient, some of the causes include long-term stress, and poor nutrition. Stress causes glucocorticoids (steroid) levels in blood to rise, this activates the hypothalamus to secrete corticotrophin-releasing hormone (CRH), which causes the pituitary gland to release adrinocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) into the blood, which enters the adrenal glands and causes release of cortisol. This is a negative feedback loop, the excess cortisol activates the brain’s glucocorticoid receptors and suppresses CRH production. In chronically stressed people, the loop no longer works resulting in excess CRH & cortisol levels, causing depression. Cortisol competes for receptor sites with progesterone, the progesterone becomes less active and causes oestrogen dominance over time. Symptoms: Unstable blood-sugar levels, chronic fatigue, candidiasis, PMS, libido loss, reduced immunity, low blood pressure, headaches, depression. Treatment: Reduce sugar, tobacco, caffeine, alcohol and eat a balanced diet. Use relaxation techniques. Medical Acupuncture Clinic – www.med-acu.com