* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electrcity UA
Survey
Document related concepts
History of subatomic physics wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Electron mobility wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Field (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Anti-gravity wikipedia , lookup
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Casimir effect wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
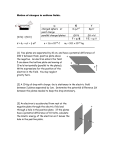
5/5/2017 P30 Unit B UA pt. A – Electricity Name: ______ Date: ______ Show all work, including starting equations, units and proper sig-digs, to receive full marks. 1. In a classroom demo, the dome of a Van de Graaff generator was initially charged negatively. A stream of closely spaced neutral soap bubbles was blown toward the dome of the generator. Much to the surprise of the students, the following observations were made: 1. The bubbles were initially attracted to the dome until the first bubble hit the dome. 2. The first bubble hit the dome and splattered 3. All the other bubbles stopped in mid-air before repelling from the dome of the generator and from each other. Using the concepts of electrostatic forces and charge distribution, explain: Why the soap bubbles were initially attracted to the top of the generator. (2 marks) Why, after the first bubble splattered, the other bubbles were repelled away from one another. (2 marks) A diagram or diagrams may be used to help you communicate your idea. 2. A single neutral 2.00 g pithball is touched by a charged rubber rod which had a charge of 2.3 x 10-8 C. The pithball then comes into contact with another pithball of equal size and shape. If the two pithballs are hung by two pieces of 3.00 cm thread from a single point (as shown) forming an angle of 15.0˚, what is the charge remaining on the original charged rod? (1.46 x 10-8 C) (4 marks) Putnam Industries 5/5/2017 Use the diagram to the righ to answer the next question: 3. A proton, electron and alpha particle are arranged as shown above. Using your data table and the diagram given, determine the magnitude and direction of the electric force acting on the proton due to the alpha particle and the electron. (5.9 x 10-18 N 74° S of W) (6 marks) 4. Draw a diagram showing the field lines in each of the following situations. (You can cut and paste the diagrams into your unit assignment!) (1 mark for each diagram) Putnam Industries 5/5/2017 Use the diagram to the right to answer the next question. 5. In the early 1800’s Michael Faraday performed an experiment used to investigate electric fields. This is now called Faraday’s Ice Pail Experiment. In the experiment, a hollow conducting ice pail is placed on an insulated plate. One electroscope is attached to the outside of the pail and one is attached to the inside of the pail. A positively charged rod is brought into the pail. Predict which electroscope will show a deflection when the rod is brought into the pail and justify your response using the principles learned in class (HINT: page 557-558 of your Pearson) (3 marks) 6. A negative charged particle that has a mass of 2.8 x 10-16 kg accelerates upwards at 2.8 m/s2 in the electric field between two horizontal plates that have a separation of 0.15 m. The potential difference across the plates is 4.2 x 102 V. Taking into consideration the force of gravity, find a) The magnitude and direction of the electric force on the particle. (3.5 x 10-15 N up) (3 marks) b) The magnitude of the particle’s charge. (1.3 x 10-18 C) (3 marks) 7. An electron, travelling horizontally at a speed of 5.45 x 106 m/s, enters a parallel plate capacitor with an electric field of 125 N/C between the plates. The separation between the plates is 6.20 mm. Ignoring gravitational effects, if the electron passes from the top plate to the bottom plate, how far will it have traveled into the capacitor? (0.130 m) (3 marks) Putnam Industries 5/5/2017 8. Find the net electrical force exerted onto an object (q1 = +2.00 C) due to another object (q2 = - 4.00 C) and an object on the opposite side (q3 = + 3.00 C) if q1 is 5.0cm away from each other charge. 9. Charge C (q = - 2.00 C) is 5.0 cm due west of charge B (q = + 8.00 C) and 6.0 cm due north of charge A (q = - 6.00 C). Determine the electrical force exerted onto charge C. If charge C has a mass of 1.62 x 10-2 mg, at what rate will it accerlerate? 10. An insulated hollow metal sphere with a diameter of 14.0 cm has a charge of 2.0 C added to it. Determine the electric field 6.0 cm from the surface of the sphere. 11. Determine the gravitational field strength and the electrical field strength 4.00 nm from an electron. 12. What is the magnitude of the electric field when a charge of 4.00 x 10-12 C experiences a force of 5.00 x 10-8 N after being placed inside this field? Putnam Industries 5/5/2017 13. A + 8.00 C enters midway into the electric field (100 N/C) created by two oppositely charged horizontal plates (positive on top) placed 24.0cm apart. If the charge (m = 25.0 mg) enters with a horizontal velocity of 15.0 m/s right, find: a) The vertical velocity of the charge 0.100 s after it enters the electric field. b) The horizontal distance that the charge travels before it strikes the negative plate. 14. An electron is placed (starting at rest) at the vertical negative plate across an electric field from a vertical positive plate. When released, the electron moves horizontally across the field and strikes the positive plate with a velocity of 4.00 x 106 m/s. c) Determine the potential difference between the two plates. Putnam Industries 5/5/2017 d) If the distance between the two plates is 3.00 cm, find the electric field strength. e) Determine the acceleration of the electron within the electric field. 15. A current of 3.60 mA flows through a circuit. How many electrons flow past a given point in the circuit in 1.20 minutes? 16. A 60.0 W light bulb is 20.0 % efficient (20.0% of energy is actually converted to light). The remaining energy goes into thermal energy. Determine the number of joules the light bulb converts to light each minute and the number of joules of thermal energy produced each minute. Putnam Industries 5/5/2017 17. An electroscope is charged by induction by grounding briefly while using a positively charged rod. Which of the following statements is true? a) Some positive charge moves from the ground to the electroscope b) Some positive charge moves from the electroscope to the ground c) The electroscope becomes positively charged d) The electroscope becomes negatively charged 18. If an electron is suspended midway between two horizontal electric plates that are separated by a distance of 55 cm, what velocity will it hit the positive plate with when the plates (E = 250 N/C) are turned on? 19. What potential difference exists when an alpha particle reaches a speed of 5.0 m/s as it hits the negative plate in a uniform electric field? 20. What is the electrostatic force exerted on an electron through a 9.0 N/C field? Putnam Industries 5/5/2017 21. What is the electrostatic force exerted on an electron when it experiences a potential difference of 12.0 V at a distance of 6 cm from a charged plate? 22. What is the kinetic energy gained by an alpha particle accelerated from rest through a potential difference of 3.00 x 105 V? What is this energy in electron volts? 23. Two horizontal electrical plates are placed 25 cm apart, with the positive plate on top. When turned on, the plates exert a potential difference of 15.0 V. a) When an electron is positioned halfway between the plates and the plates are turned on, what is the electrostatic force it experiences? b) What is the net force it experiences? c) What is the acceleration it experiences? Putnam Industries