* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Revisiting moving electric charges
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Electron mobility wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
Casimir effect wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Field (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Electrostatics wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
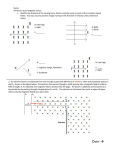
Revisiting moving electric charges A 20 μF parallel plate capacitor stores 300 μC of charge. The plates are 6 cm apart. An electron enters the region between the plates along the midpoint with a speed of 1 x 106 m/s as shown. What is the magnitude and direction of the force that acts on the electron (Neglect gravity). Sketch the path the electron follows on the diagram. (Neglect fringing). What direction is the electric field between the plates? down fringing It looks like this How can we neglect gravity?? – what is the weight of the electron? C = 20µF = 20 x 10-6 F Q= 300μC = 300 x 10-6 C Q C= V d = 6 cm electron m = 9.1 x 10-31 kg q = -1.6 x 10-19 C v = 1 x 106 m/s F=Eq F = 250 (1.6 x 10-19) F = 4.0 x 10-17 N 20 = 300 V V = 15 V V=Ed 15 = E (.06) E = 250 V/m down 4.0 x 10-17 N up We can cause this particle to pass through the region between the plates undeflected by introducing a magnetic field in that region. Determine the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field necessary for this to occur. What is the electric force? 4.0 x 10-17 N up What is the magnetic force necessary to cause the electron 4.0 x 10-17 N to pass through the field down undeflected? palm - down fingers - into thumb left page F= qvB (negative) -17 -19 6 4.0 x 10 = (1.6 x 10 )(1.0 x 10 )(B) B = 2.5 x 10-4 T into page direction?? RHRII This is the magnitude of the field palm - up thumb - left fingers - F= qvB F = (1.6 x 10-19)(1.0 x 107)(17x10-4) out of page 2.72 x 10-15 N We can cause this particle to pass through the tube undeflected by introducing an electric field in the region of the magnetic field. Determine the magnitude and direction of the electric field necessary for this to occur. F=Eq E = 1.7 x 104 N/C 2.72 x 10-15 = E (1.6 x 10-19) NEVER USE RHR TO DETERMINE THE DIRECTION OF AN ELECTRIC FIELD OR FORCE What direction does the electric down force need to be? Where would a positive plate have to be placed to force the electron beneath it down? Where would a negative plate have to be placed to force the electron above it down? What direction is the electric field from positive to between parallel plates negative (up) Electric field is up