* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Objectives and strategy
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Perfect competition wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Sales process engineering wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
Bayesian inference in marketing wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Affiliate marketing wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Ambush marketing wikipedia , lookup
Sports marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
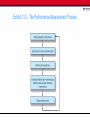
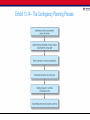
Chapter 13 Measuring and Delivering Marketing Performance 2 Chapter Overview 1. Profitability Analysis 2. Questions Used to Measure Marketing Performance 3. The Contingency Planning Process Exhibit 13.2 - The Performance Measurement Process Profitability Analysis • Analysts determine costs associated with specific marketing activities • Limitations • Objectives can best be measured in nonfinancial terms • Profit is a short-term measure • Profits can be affected by factors over which management has no control Profitability Analysis – Full costing: Analysts assign both direct, or variable, and indirect costs to the unit of analysis • Indirect costs: Fixed joint costs that cannot be linked directly to a single unit of analysis • Direct costing: Use of contribution accounting Customer Satisfaction • Understanding and measuring the criteria used by customers • Using face-to-face approaches Examples of Questions a Strategic Monitoring System Should Be Able to Answer 1. What changes in the environment have negatively affected the current strategy? 2. What changes have major competitors made in their objectives and strategies? 3. What changes have occurred in the industry in such attributes as capacity, entry barriers, and substitute products? 4. What new opportunities or threats have derived from changes i n the environment, competitors’ strategies, or the nature of the i ndustry? 5. What changes have occurred in the industry’s key success fact ors? 6. To what extent is the firm’s current strategy consistent with the preceding changes? Decisions for Strategic Monitoring Systems • Identifying key variables • Tracking and monitoring • Strategy reassessment Identifying Key Variables • Concerned with: – External forces – Effects of certain actions taken by the firm to implement the strategy Tracking and Monitoring • Use strategic plan as an early-warning system • Monitor industry sales regularly • Examine relevancy, accuracy, and cost of obtaining needed measures Strategy Reassessment • Takes place at periodic intervals • Quarterly • Annually • Setting triggers to signal the need to reassess viability of the firm’s strategy Questions Used to Measure Marketing Performance • Who needs what information? – Sales analysis • • • • • • Geographical areas Product, package size, and grade Customer Channel intermediary Method of sale Order size SEO and SEM Analysis • Search engine optimization (SEO): Set of techniques that ensure a company’s web pages are ranked highly when consumers use search engine for information • Search engine marketing (SEM): Buying keywords for which consumers are likely to search Questions Used to Measure Marketing Performance • When and how often is it needed? – Key criteria • Timeliness • Store payroll expense • In what media and in what format(s) should it be provided? – Advances in information technology made possible the measurement and reporting Questions Used to Measure Marketing Performance • Does your system of marketing metrics measure up? – Developing a set of marketing metrics as part of an overall performance measurement system is: • Getting the metrics aligned with the strategy • What contingencies should be planned for? – Strategies and action plans are based on assumptions about the future Exhibit 13.14 - The Contingency Planning Process Global Marketing Monitoring • Measuring the performance is difficult because of the number of countries involved: – Each presenting a unique set of opportunities and threats • Use of electronic data interchange and the Internet should: – Simplify performance evaluation across countries The Marketing Audit • Control and planning mechanism to review total marketing efforts • Conducted across all products and business units • Covers the SBU’s: – Objectives and strategy – Plan of action for each product-market entry • Provides an assessment of each SBU’s overall competitive position Types of Audits • Marketing environment: Requires an analysis of the firm’s present and future environment – Identifies significant trends • Objectives and strategy: Calls for an assessment of the internal factors Types of Audits • Planning and control system: Evaluates adequacy of the systems and the firm’s new development procedures • Organization: Deals with firm’s overall structure – Organization of marketing department – Extent of synergy between the various marketing units Types of Audits • Marketing productivity: Evaluates the profitability of the company’s: – Individual products – Markets – Key accounts • Marketing functions: Examines the marketing-mix elements Types of Audits • Ethical: Evaluates the extent to which the company engages in ethical and socially responsible marketing • Product manager: Determines whether product managers are channeling their efforts in the best ways possible