* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Immune Response
Inflammation wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
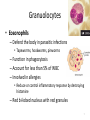
Atherosclerosis wikipedia , lookup
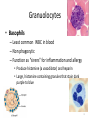
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Plasmodium falciparum wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
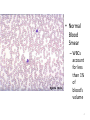
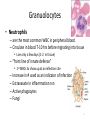
Immune Response Vocabulary • Immunology- the study of host defense mechanisms • Immunity- ability of the host to protect itself against foreign organisms. Resistance to disease. • Antigen (Ag)- is a foreign substance that can elicit specific immune response (IR) when is immunogenic • Antibody (Ab)- protein produced by the body’s immune system when it detects harmful substances called antigens • White blood cells (leukocytes)- chief function is to protect the body against microorganisms causing disease and fight infection when it occurs. They are bigger than red blood cells. 2 Leukocytes (White Blood Cells (WBC)) • Protect the body against microorganisms, toxins, & tumor cells. • • • remove dead cells & debris from body Complete cells with all organelles Stained & further identified by • • • • size shape of the nucleus presence/absence of granules colors taken up by their granules 3 • Normal Blood Smear – WBCs account for less than 1% of blood’s volume 4 White Blood Cells (WBC) • 5 Major types of WBC – Neutrophils – Eosonophils – Basophils – Lymphocytes (T and B Cells) – Monocytes • Divided into two categories – Granuolocytes and Agranuolocytes 5 Granuolocytes • Neutrophils – are the most common WBC in peripheral blood. – Circulate in blood 7-10 hrs before migrating into tissue • Live only a few days (1-2 in tissue) – “front line of innate defense” • 1st WBCs to show up at an infection site – – – – Increase in # used as an indicator of infection Extravasate in inflammation rxn Active phagocytes Fungi 6 Granuolocytes • Eosonophils – Defend the body in parasitic infections • Tapeworms, hookworms, pinworms – Function in phagocytosis – Account for less than 5% of WBC – Involved in allergies • Reduce or control inflammatory response by destroying histamine – Red bi-lobed nucleus with red granules 7 Granuolocytes • Basophils – Least common WBC in blood – Non phagocytic – Function as “sirens” for inflammation and allergy • Produce histamine (a vasodilator) and heparin • Large, histamine containing granules that stain dark purple to blue 8