* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 4 Lesson 1 Plate Tectonics
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Geological history of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Supercontinent wikipedia , lookup
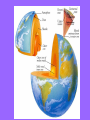
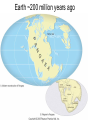
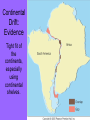
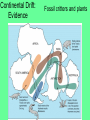
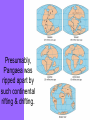
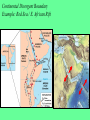
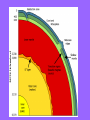
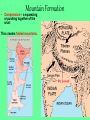
Chapter 4 Lesson 1 Plate Tectonics What Are Earth’s Layers Earth’s Layers • Core- central part – Inner Core – solid metals – Outer Core – liquid metals • Mantle – thick layer of solid and molten rock that surrounds the core • Lower – solid rock • Upper – 2 parts • Lithosphere – solidupper mantle & crust • Asthenosphere – upper mantle – melted rock • Crust – Thin layer of solid rock that makes up the outermost layer. – Where we live • Atmosphere – – All gases that surround the Earth • Hydrosphere – All of Earth’s liquid and solid water (lakes, oceans, rivers, glaciers) – Covers 70% of the Earth Landforms – a physical feature of the Earth’s surface Earth ~200 million years ago The Continental Drift Hypothesis Geologist – person that studies rocks Thought of by Alfred Wegener in 1915. Continents "drifted" to their present positions. Supercontinent Pangaea started to break up about 200 million years ago. Continental Drift: Evidence Geographic fit of South America and Africa Fossils match across oceans Rock types and structures match across oceans Ancient glacial features Continental Drift: Evidence Tight fit of the continents, especially using continental shelves. Continental Drift: Evidence Fossil critters and plants Continental Drift: Evidence Correlation of mountains with nearly identical rocks and structures Continental Drift: Evidence Glacial features of the same age restore to a tight polar distribution. Presumably, Pangaea was ripped apart by such continental rifting & drifting. What causes the continents to move? Plate Tectonics •Theory to explain how forces deep within Earth can cause seafloors to spread and continents to move. Tectonic Plates Continental Divergent Boundary Example: Red Sea / E. African Rift • Magma – hot melted rock • Tension – push or a stretch on the plates • Seafloor Spreading – caused by magma pushing on the plates Mid Ocean Ridges - underwater mountain ranges Subduction – when one tectonic plate can sink under another platecrust gets recycled back into the mantle • Mountain Formation Compression – a squeezing or pushing together of the crust This creates folded mountains. Fault – deep cracks in the Earth’s crust where rocks move in the opposite direction • Fault Block Mountain – Caused by tension when one block of rock moves down – Sierra Nevada Mountains