* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Wave-Particle Duality - the Principle of Complementarity The
Path integral formulation wikipedia , lookup
Delayed choice quantum eraser wikipedia , lookup
Ensemble interpretation wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Tight binding wikipedia , lookup
Coherent states wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Wheeler's delayed choice experiment wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization group wikipedia , lookup
Probability amplitude wikipedia , lookup
Quantum state wikipedia , lookup
Interpretations of quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Canonical quantization wikipedia , lookup
EPR paradox wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Wave function wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
Copenhagen interpretation wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
Particle in a box wikipedia , lookup
Hidden variable theory wikipedia , lookup
Bohr–Einstein debates wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
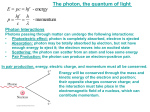
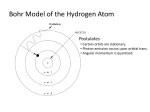
Wave-Particle Duality - the Principle of Complementarity We have phenomena such as diffraction and interference that show that light is a wave, and phenomena such as the photoelectric effect that show that it is a particle. Which is it? This question has no answer; we must accept the dual wave-particle nature of light. The principle of complementarity states that both the wave and particle aspects of light are fundamental to its nature. Indeed, waves and particles are just our interpretations of how light behaves. 1 The photon, the quantum of light Energy: E pc hf hf h Momentum: p c Wave Nature of Matter Just as light sometimes behaves as a particle, matter sometimes behaves like a wave. (Idea of the symmetry in nature - de Broglie 1927) The wavelength of a particle of matter (De Broglie wavelength) is: • This wavelength is extraordinarily small. • The wave nature of matter becomes more important for very light particles such as the electron. • Electron wavelengths can easily be on the order of 10-10 m; electrons can be diffracted by crystals just as X-rays can. 2 Example1: What is the de Broglie wavelength of a 0.20kg ball moving with speed 15m/s? h h 6.6 1034 J s 2.2 1034 m p mv 0.20kg 15m / s) Example2: Determine the wavelength of an electron that has been accelerated through a potential difference of 100 V. V 100V m 9.11 10 31 kg 1 2 e 1.60 10 19 C ? mv eV v 2 2eV ; m h mv h 2eVm 1.2 10 10 m Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) image 3 De Broglie’s Hypothesis Applied to Atoms The correspondence principle applies here as well – when the differences between quantum levels are small compared to the energies, they should be imperceptible. De Broglie’s hypothesis is the one associating a wavelength with the momentum of a particle. He proposed that only those orbits where the wave would be a circular standing wave will occur. This yields the same relation that Bohr had proposed. In addition, it makes more reasonable the fact that the electrons do not radiate, as one would otherwise expect from an accelerating charge. quantization: de Broglie’s wavelength: Bohr’s quantization: 2rn n h mv nh mvrn 2 These are circular standing waves for n = 2, 3, and 5. About Quantum Mechanics Quantum mechanics incorporates wave-particle duality, and successfully explains energy states in complex atoms and molecules, the relative brightness of spectral lines, and many other phenomena. It is widely accepted as being the fundamental theory underlying all physical processes. Quantum mechanics is essential to understanding atoms and molecules, but can also have effects on larger scales. Classical physics v<<c xpx Classical relativistic physics xpx v~c Quantum nonrelativistic physics xpx v<<c Quantum relativistic physics xpx v~c 5 The Wave Function and Its Interpretation Question: An electromagnetic wave has oscillating electric and magnetic fields. What is oscillating in a matter wave? Answer: This role is played by the wave function, Ψ. The square of the absolute value of the wave function at any point is proportional to the number of electrons expected to be found there. For a single electron, the wave function is the probability of finding the electron at that point. In the classical mechanics we use Newton’s equations of motion to describe particles positions and velocities, in the classical electrodynamics we use Maxwell’s equations to describe the electric and magnetic fields. In quantum mechanics we use Schrödinger equation to describe the function: Ψ= Ψ(x,y,z;t). 6 The Wave Function and the Double-Slit Experiment The interference pattern is observed after many electrons have gone through the slits. If we send the electrons through one at a time, we cannot predict the path any single electron will take, but we can predict the overall distribution. Philosophic Implications - Probability versus Determinism The world of Newtonian mechanics is a deterministic one. If you know the forces on an object and its initial velocity, you can predict where it will go. Quantum mechanics is very different – you can predict what masses of electrons will do, but have no idea what any individual one will. 7 The Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle Quantum mechanics tells us there are limits to measurement – not because of the limits of our instruments, but inherently. This is due to the wave-particle duality, and to interaction between the observing equipment and the object being observed. xpx h 2 x - the uncertaint y in the position p x - the uncertaint y in the momentum Similar: yp y zpz The Heisenberg uncertainty principle tells us that the position and momentum cannot simultaneously be measured with precision. 8 Two examples Example 1: An electron moves in a straight line with a constant speed v=1.10x106 m/s which has been measured to a precision of 0.10%. What is the maximum precision with which its position could be simultaneously measured? v 10 3 v p mv 1.06 10 34 J s 7 x 1 . 1 10 m 31 3 6 p mv 9.11 10 kg 10 1.10 10 m / s Example 2: What is the uncertainty in position, imposed by the uncertainty principle, on 150–g baseball thrown at (93 ± 2) mph = (42 ± 1) m/s? 1.06 10 34 J s x 7 10 34 m p mv 0.150kg1m / s 9 The uncertainty principle for energy and time Et This says that if an energy state only lasts for a limited time, its energy will be uncertain. It also says that conservation of energy can be violated if the time is short enough. Example: The Z boson typically decays very quickly. Its average energy is 91.19 GeV, but its short lifetime shows up as an intrinsic width of 2.49 GeV (rest energy uncertainty). What is the lifetime of this particle? h t E 2E 4.14 10 15 eV s 55 t 2 . 65 10 s 9 2 2.49 10 eV 10 Example: Imagine trying to see an electron with a powerful microscope. At least one photon must scatter off the electron and enter the microscope, but in doing so it will transfer some of its momentum to the electron. The uncertainty in the momentum of the electron is taken to be the momentum of the photon: p h In addition, the position can only be measured to about one wavelength of the photon: x Combining, we find the combination of uncertainties: x c c hc E hf t xpx h Et h 11