* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lymphatic System and Immunity
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
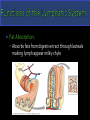
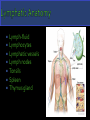
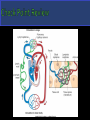
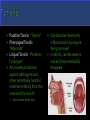
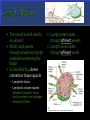
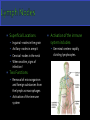
Fluid Balance, Fat Absorption, Defense Fluid Balance: 30L of fluid exits capillaries only 27L will return to vascular system 3L enters the lymphatic capillaries as lymph Water, plasma, hormones, enzymes & waste Fat Absorption: Absorbs fats from digestive tract through lacteals making lymph appear milky-chyle Defense: Destroy microorganisms and foreign substances. Lymphocytes act as part of the immune system & microorganisms are filtered by lymph nodes and by blood in the spleen Lymph-fluid Lymphocytes Lymphatic vessels Lymph nodes Tonsils Spleen Thymus gland Does not circulate fluid to and from tissues Carries fluid from tissue capillaries to circulatory system Lymphatic Capillaries are closed ended vessels made of simple squamous epithelium More permeable than blood capillaries Found in most all tissues of the body except CNS, bone marrow, epidermis and cartilage Lymphatic capillaries join together to form lymph vessels with a beaded appearance due to overlapping valves Lymph moves from small vessels to larger vessels Empty into blood in two locations Right lymphatic duct empties into the right subclavian vein ¼ of body Thoracic duct empties into the left subclavian vein ¾ of Three factors that assist Transport of lymph Contraction of skeletal muscle during activity Contraction of smooth muscle in lymph vessels Respiration pressure changes Lymphatic Organs: Tonsils, Lymph nodes, spleen & Thymus When blood and lymph filters through organs, fiber network traps microorganisms and other material Fine reticular fiber network that holds lymphocytes in place and traps microorganisms Lymphatic Tissues: Lymphocytes and other cells Lymphocytes originate in red bone marrow & carried to lymphatic organs by blood Lymphocytes divide and increase in number when in the presence of a foreign material causing an immune response Palatine Tonsils- “Tonsils” Pharyngeal Tonsils“Adenoids” Lingual Tonsils- “Posterior to tongue” All provide protection against pathogens and other potentially harmful material entering from the nose and the mouth. Soar throat when sick Can become chronically infected and may require being removed. In adults, can decrease in size and may eventually disappear. The size of a small seed to an almond Most lymph passes through at least one lymph node before entering the blood Surrounded by a dense connective tissue capsule Lymphatic tissue Lymphatic sinuses-spaces between lymphatic tissue which contains macrophages network of fibers Lymph enters nodes through afferent vessels Lymph leaves nodes through efferent vessel Superficial Locations: Inguinal –nodes in the groin Activation of the immune system includes: Axillary- nodes in armpit Germinal centers-rapidly Cervical- nodes in the neck When swollen, signs of infection! Two Functions: Removal of microorganism and foreign substances from the lymph as macrophages Activation of the immune system dividing lymphocytes. Two Specialized types of lymph tissues Major functions of the spleen: White pulp: Lymphatic tissue Filters blood instead of lymph surrounding arteries Red pulp: Consists of fibrous network filled with RBC’s & macrophages associated with veins Destroys old RBCs Removes foreign substances in the blood through phagocytosis The spleen serves as a reservoir for blood that can be released in case of emergencies A second function of the spleen is to filter red and white blood cells from the blood. A third job of the spleen is to store platelets Most important role of the spleen is to bring blood into contact with the spleen’s lymphocytes Finally, the spleen manufactures red blood cells for the fetuses Bi-lobed triangular gland Located in the mediastinum Increases in size until 1 years old, then remains the same After 60 years, decreases in size By 40 year, most of thymus is replaced with adipose tissue Functions as a site for the production and maturation of lymphocytes Lymphocytes do not respond to foreign substances while in the thymus After maturation, lymphocytes enter blood and travel to other lymphatic tissues.