* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Instructor`s Copy - Let It Grow, Let It Grow, Let It Grow
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Verbascum thapsus wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
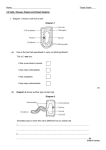
Instructor’s Copy Lab Worksheet – Let It Grow, Let It Grow, Let It Grow Purpose: To observe the differences between the five major plant groups and relate their adaptations to their environment. Materials: microscope samples of the 5 plant groups Examine each plant and answer the questions that follow. Even though algae is technically a plant-like protist, it is included in this lab for comparison. Algae, whether you are talking about single-celled Chlamydomonas (which grow in ponds) or giant marine kelp which can grow up to 60 m in length are a major part of aquatic food chains. I. Algae (view under microscope) A. How “thick” is this plant? 2-3 cells thick B. Would O2 exchange be difficult? no C. Through which process does the above occur? diffusion D. Why don’t these plants need true stems? Water supports them II. Mosses A. How tall are these plants? 2-3 cm B. What tissue do these lack to keep them from growing tall? (look in book) vascular tissue C. Draw a picture of the moss, and label the nonvascular stem, the nonvascular leaves, and the rhizoids. Picture depends on type of moss used. Nonvascular leaf Nonvascular stem Rhizoid D. Does the moss have roots? No If not, what do they have? rhizoids What function do these serve? They help anchor plant. E. Look at a leaf under the dissecting microscope. How thick are the leaves? Thin Why do you think moisture must be present for these to survive? To keep them from drying out. IV. Ferns A. Put a drop of water on the leaf. Describe what happens. Balls up a little; not as much as angiosperms. B. Must moisture be present for them to survive? yes Does the fern have roots? Yes What purpose do they serve? To help obtain moisture and nutrients and to anchor the plants. C. Examine the underside of the leaf. Note the dark spots. Refer to your book and name these structures and explain their function. These are spores – they are the reproductive structures of the plant. D. Label the frond, rhizome and roots. Spore Frond Rhizome Roots V. Gymnosperms A. Examine the pine cone, What does it shelter? seeds B. The needles are actually specialized leaves. C. How tall do pine trees grow (based on your knowledge)? Cedar may be small all the way up to very tall pine trees. What tissue(s) allows this to occur? Vascular tissue allows plants to grow tall. VI. Angiosperms A. In what structure are seeds produced? Angiosperms produce seeds in flowers. How is this adaptation useful for life on land? Flowers attract bees, birds and other pollinators that help fertilize the plants. B. Examine the leaf of the cactus. How many cells thick do you think the leaf is? Many How is this adaptation useful for life on land? The cells help with water storage. Examine the carrot. What part is eaten? The root Examine the root hairs. What purpose do they serve? They increase surface area for water absorption.