* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Adaptations of Greater Plantain
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Verbascum thapsus wikipedia , lookup
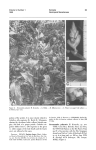
Adaptations of Greater Plantain (Plantago major) Description Leaves in a rosette formation that can be 15-20cm in diameter Each leaf is oval, between 5-20cm long and 4-9cm broad Acute apex and smooth margin Apex = the end of the leaf (tip) furthest away from centre of the plant Acute = pointed end with straight sides 5 – 9 clearly visible veins running parallel to each other along the length of the leaf The flowers are small, greenish- brown with purple stamens, produced in a dense like spike (5-15cm) on top of a stem approximately 15cm tall. Thick tough leaves. Growing environment It grow better than most other plants in compacted soils (e.g. beside paths, roadsides, pathways). It is also common in grasslands. It is wind pollinated, the seeds are held high above the ground on tall stems. Adaptations to environment; - Thick tough leaves are resistant to trampling - Parallel veins in leaf give added strength - Rosette shape allows plant to lie close to the ground protecting it from trampling and mowing - Tall stem of the flower allows seeds to be dispersed (travel further in the wind, avoid being sheltered by other plants) - Tall stem is tough and “springy”, when trodden on it will bounce back allowing seeds to remain in the correct position for dispersal