* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 3: Ecosystems - micsapes
Ecosystem services wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
River ecosystem wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
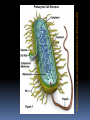
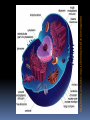
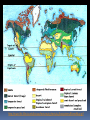
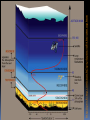
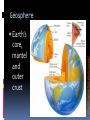
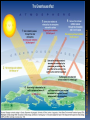
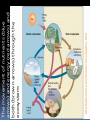
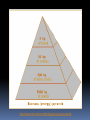
What are they and how do they work? CHAPTER 3: ECOSYSTEMS Cell Review Smallest functional unit of life Cell theory All living things are made of cells Single or multi-cellular Prokaryotic Eukaryotic http://www.cic-caracas.org/departments/science/Topic1.php http://www.uvm.edu/~inquiryb/webquest/fa06/mvogenbe/ Ecology Study of how organisms interact with one another and with their physical environment (matter and energy) Connections in Nature http://www.ux1.eiu.edu/~cfruf/bio3002/levels_ecology.htm Levels of Organization Species Set of individuals that can mate and produce fertile offspring Classification system KPCOFGS Genus species or Genus species Population Group of individuals of the same species hat live in the same place a the same time Variation – genetic diversity Habitat – where they live Community Biological community All the populations of different species that live in a particular place Ecosystem Community of different species interacting with one another and with their nonliving environment (soil, water, other forms of matter, and energy) No clear boundaries Not isolated Biomes Large regions of land with distinct climates and certain species Especially vegetation Aquatic Biomes Marine Freshwater (2%) http://www.life.illinois.edu/bio100/lectures/s97lects/04Ecosystems/BiomeMap.gif Biosphere The Global ecosystem in which all organisms exist and can interact wit one another Parts of the atmosphere hydrosphere and geosphere where life exists Atmosphere Thin spherical envelope of gases surrounding the earths surface Troposphere – greenhouse gases Stratosphere – ozone layer http://qwickstep.com/search/?q=5+layers+of+the+atmosphere Hydrosphere All the water on or near the earth’s surface Liquid, solid, gas forms 71% in Ocean Earth’s core, mantel and outer crust http://thegeosphere.pbworks.com/ Geosphere 3 Factors work together within the Spheres 4 SPHERES MAKE UP THE LIFE – SUPPORT SYSTEM Gravity Allows the planet to hold onto its atmosphere Enables movement and cycling of chemicals through air, water, soil and organisms Recycling of Matter within and between Ecosystems One way flow of high quality energy http://maps.grida.no/go/graphic/greenhouse-effect 2 components of an Ecosystem Abiotic Nonliving components water, air, nutrients, rocks, heat, solar energy Biotic Living and once living biological components Plants, animals, microbes Range of Tolerance Different species and their populations thrive under different physical and chemical conditions Limiting Factor Principle Too much or too little of any abiotic factor can limit or prevent growth of a population, even if all other factors are at or near the optimal range of tolerance Contributes to population control Examples? Trophic(feeding) levels Producers Autotrophs “Self – feeders” Photosynthesis 6CO2 + 6H2O = light = C6H12O6 + 6O2 Chemosynthesis Trophic(feeding) levels Consumers Heterotrophs “Other – feeders” Herbivores, Carnivores, Higher- level Carnivores, Omnivores, Decomposers, Detritivores Page 61 Science Focus MANY OF THE WORLD’S MOST IMPORTANT SPECIES ARE INVISIBLE TO US http://apesnature.homestead.com/chapter2.html The movement of nutrients (blue arrows) and energy (red arrows) and both (brown arrows) through the ecosystem Sequence of organisms, each of which serves as a source of food or energy for the next http://producersconsumers.wikispaces.com/11 Food Chains http://envirosci.net/111/niches/niches.htm Food Web Complex network of interconnected food chains Useable energy decreases Ecological efficiency % of usable chemical energy transferred from one tropic level to the next Typically 10% Pyramid of Energy Flow http://www.mlms.logan.k12.ut.us/~mlowe/speds2o2b.html http://www.tutorvista.com/biology/ecological-pyramids OWL PELLETS, FOOD WEBS, AND BIOMASS PYRAMIDS NUTRIENT CYCLING IN THE BIOSPHERE