* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Status of Indian and global developments in Genetically Modified
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified food wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified organism containment and escape wikipedia , lookup
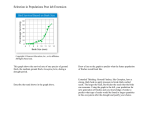
Status of Indian and global developments in Genetically Modified crops Jeetendra Solanki Biotech Consortium India Limited, New Delhi INTRODUCTION Classical plant breeding is limited to the introduction of required characters into plant by genetic crossing during sexual reproduction To feed the ever increasing population more and more food has to be produced from less and less land water and other natural resources It is obvious that emphasis has to be laid on new technologies that can improve crop yield against adverse conditions of biotic and abiotic stresses and improve the quality contd The earlier part of plant biotechnology era has been the development of tissue culture protocols of several commercially important crops The “gene revolution” as compared to green revolution is poised to benefit both poor and rich farmers equally and has an immense potential in transforming global agriculture. In India, significant efforts have been made to significantly for developing several programmes in Biotechnology WHAT IS A TRANSGENIC CROP – A transgenic crop is a crop which contains a gene or genes of a different species artificially inserted in its genome,which may come from an unrelated plant or from a completed different species. Why make transgenic crops? z Due to limitations of conventional breeding for attaining the desirable traits use of recombinant DNA technology has been taken advantage of and development of transgenics started CELL: SMALLEST UNIT OF LIFE NUCLEUS: BRAIN OF THE CELL CHROMOSOMES: STRUCTURE CONTAINING THE GENETIC INFORMATION GENES: SMALLER PIECES OF GENETIC INFORMATION DNA: BUILDING BLOCK OF THE GENE, DOUBLE HELIX STRUCTURE Organization of DNA in the cell Biotechnology is an Extension of Traditional Plant Breeding TRADITIONAL PLANT BREEDING DNA is a strand of genes, much like a strand of pearls. Traditional plant breeding combines many genes at once. Many genes are transferred Desired Gene X Donor Plant Commercial Plant Variety New Plant Variety PLANT BIOTECHNOLOGY Using plant biotechnology, you can add a single gene to the strand. Desired Gene A single gene is transferred Desired Gene + Donor Commercial Plant Variety Improved Commercial Plant Variety Development of GM Crop/ Trasgenics Identify gene(s) giving a desired trait Make copies of the gene Transfer to plant tissue Regenerate plants Lab analysis and safety testing Development of a variety Field tests Approval by Government agencies Commercialization Monitoring of efficacy and safety 7-8 years Methods of producing transgenic plant Advantages of transgenic crops over breeding Breeding Transgenic crops Exchange of genes within a species No barrier Gene of interest with flanking sequence transferred Only Gene of Interest Simple Technology Intensive Technology History of Safety New Technology Time needed for Safety History Transgenic Crops: Development Objectives z Integrated pest management z Herbicide tolerance z Nutritional enhancements z Product quality improvement z Increase in yield z Stress tolerance z Plant based pharmaceuticals GLOBAL SCENARIO 2006: Crops approved for commercial use z z z z z z First crop introduced was Flavr Savr tomato in USA in 1995 So far 20 crops approved for commercial cultivation in different countries Only four crops being marketed commercially I.e., corn, cotton, soybean and canola Commercial production initiated for papaya, squash, rice and alfalfa in USA and other countries, Others are approved but not yet being marketed Major characteristics are insect resistance, herbicide tolerance, virus resistance and improved product quality Major countries include USA, Canada, Japan, China, India, Brazil, EU, Argentina, South Africa GLOBAL SCENARIO 2006: Area Under Cultivation Area under cultivation: 102 million hectares No. of countries: 22 No. of farmers: over 10 million Global area of transgenic crops from 1996 to 2006 (million hectares) GLOBAL SCENARIO 2006: Crops Under Research z 63 countries involved at various stages z 57 plants identified for development z Second generation of traits include modifications such as nutritional enhancement, disease tolerance, stress tolerance and production of pharmaceuticals STATUS OF GM CROPS IN INDIA: Crops approved for commercial use z z z z z Only one crop approved i.e. Bt cotton Three hybrids containing Cry1Ac gene approved in 2002 and one in 2004 Six hybrids approved for northern states in 2005 62 hybrids approved for Kharif 2006 Three new events approved I.e. i. Cry1Ac gene (event 1) by M/s J.K. Agri Seeds Ltd. ii. Fusion genes (cry 1Ab+cry 1Ac) 'GFM by M/s Nath Seeds iii. Stacked genes cry1Ac and cry1Ab by M/s MAHYCO Area under Bt cotton cultivation Bt Cotton Hybrids Approved in India Zone North Central & North Central Company Hybrid Ankur Seeds Ltd Ankur 2534 Bt J.K. Agri Genetics Seeds Ltd. JKCH 1947 Bt MAHYCO MRC – 6304 Bt, MRC 6029 Bt., MRC-6025 Bt. Nath Seeds Ltd. NCEH-6R Nuziveedu Seeds Ltd NCS 138 Bt. Rasi Seeds Ltd RCH – 134 Bt, RCH 308 Bt., RCH – 317 Bt, RCH 314 Bt. Ankur Seeds Ltd Ankur – 651 Bt MAHYCO MRC – 6301 Bt Ajeet Seeds Ltd. ACH-11-2 BG II Ankur Seeds Ltd Ankur – 09 Ganga Kaveri Seeds Pvt. Ltd. GK 205 Bt., GK 204 Bt. J.K.Agri Genetics Seeds Ltd. JK Varun Bt. Krishidhan Seeds Pvt. Ltd. KDCHH 9821 Bt., KDCHH-441 BG II MAHYCO MECH 12 Bt *, MRC 7301 BG II, MRC-7326 BG II, MRC-7347 BG II Nath Seeds Ltd. NCEH-2R Pravardhan Seeds Ltd. PRCH-102 Bt. Rasi Seeds RCH 377 Bt., RCH –144 Bt, RCH –118 Bt, RCH - 138 Bt Vikki Agrotech Pvt Ltd VCH 111 Bt Zone Central & South North/Central/ South South Company Hybrid Ajeet Seeds Ltd. ACH-33-1 Bt., ACH-155-1 Emergent Genetics Brahma Bt. Krishidhan Seeds Pvt. Ltd. KDCHH 9810 Bt., KDCHH 9632 Bt. MAHYCO MECH 162 Bt* , MECH 184 Bt* Nuziveedu Seeds Ltd. NCS – 207 Mallika, NCS – 145 Bunny Prabhat Seeds Ltd. NPH 2171 Bt. Rasi Seeds Ltd RCH 2 Bt Tulasi Seeds Pvt. Ltd. Tulasi 4 Bt., Tulasi 117 Bt. Vikram Seeds Pvt. Ltd. VICH 5 Bt., VICH 9 Bt. Nuziveedu Seeds Ltd NCS-913 Bt. Ganga Kaveri GK-209 Bt., GK-207 Bt. JK Agri Genetics Ltd. JK Durga Bt, JKCH-99 Bt MAHYCO MRC – 6322 Bt, MRC – 6918 Bt, MRC-7351 BG II, MRC 7201 BG II Nath Seeds Ltd. NCEH-3 R Prabhat Seeds Ltd. PCH-2270 Bt. Rasi Seeds Ltd RCH – 20 Bt, RCH – 368 Bt, RCH 111 BG I, RCH-371 BG I, RCHB-708 BG I Crops Under Research Crops Under Development and Field Trials z z z 11 crops under various stages of contained field trials Include brinjal, cotton, cabbage, corn, groundnut, pigeon pea, castor, tomato, rice, okra and cauliflower Traits include insect resistance, herbicide tolerance, virus resistance, nutritional enhancement, salt tolerance, fungal resistance