* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PS 2 - Purdyphysicalscience
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
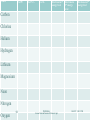
Vocabulary Atom, isotope, element, proton, atomic number, neutron, nucleus, electron, atomic mass 1 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM PS 2- Properties of Atoms Learning Goals (indicators) Compare the subatomic particle (protons, neutrons, electrons) of an atom with regard to mass, location, and charge, and explain how these particles affect the properties of an atom (including identity, mass, volume, reactivity) Illustrate the fact that the atoms of elements exist as stable or unstable isotopes Explain the trends of the periodic table based on the elements’ valence electrons and atomic numbers Use the atomic number and the mass number to calculate the number of protons, neutrons, and/or electrons for a given isotope of an element Predict the charge that a representative element will acquire according to the arrangement of electrons in its outer energy level Compare fission and fusion (including the basic processes and the fact both fission and fusion convert a fraction of the mass of interacting particles into energy and release a great amount of energy) Explain use of nuclear applications5/4/2017 (including PERSONAL 1:29:31 PM 2 the consequences that the \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt medical technologies, nuclear power plants, and nuclear weapons) can have. Element of the Week Every week you will look up information about an assigned element – due every THURSDAY EOW sheet Websites: www.chemicalelements.com www.webelements.com NO EXCUSES! Affects your grade 3 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Let’s see what you know 4 On your notes… PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Let’s see what your group knows There are 6 posters You will start at your normal lab table You will keep the marker that is there When you move to the next table you will hand the marker to someone else in your group You MUST put something down on the paper You can cross through a wrong answer You will have 2-3 minutes When you get back to your poster bring it to the white board and post it up with the magnet 5 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Questions you will answer throughout the unit What are atoms? What are some properties of atoms? What are atoms composed of? Where are the particles located? What is an isotope? What is the function of an isotope? How do isotopes impact our world? How does oxygen differ from aluminum? Draw the structure of an oxygen atom. What is the structure of atoms? How does the structure of the atoms determine the function of that atom? Why do atoms behave the way they do? What did you learn? 7 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Why study atoms? CT scans Funny and funnier Sodium Chemical reactions 8 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Day1 –periodic table intro You need your periodic table You need red, green, blue, and yellow 9 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Intro to Period Table Navigation If she can do it… This is your new best friend! You will use this on the EOC What does periodic mean? Repeating – table repeats every eight elements Summed Up!- COMPASS- Periodic Table 10 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM The Key Atomic number Letters are the symbol of the element- notice the capitals and lower cases The name is the word Average atomic mass 11 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt C 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM The symbols for some elements don’t always obviously match their names Write a few examples from the table 12 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Atomic Number All the protons in the nucleus of an atom Elements are listed by increasing atomic number Identifies the element Flip over and find the elements that have an atomic number of 2, 8, 14 13 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Atomic Mass All the protons AND neutrons in the nucleus of an atom This is an average of all the element’s isotopes Flip over and find the elements that have an atomic mass of 14.01, 32.07, 35.45 14 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM How to find… Neutrons 15 Electrons PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt Protons 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM To yourself… Find the atomic number, atomic mass, group number and period number for… Platinum Zirconium Barium Fluorine THUMBS?????? 16 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Where to find… Metals nonmetals (yellow) 17 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt metalloids (blue) 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Liquids, solids and gases at room temperature Liquids Solids Gases Exceptions: Aluminum and Mercury 18 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Atomic Structure Worksheet Thumbs? Finish for homework 19 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Video -flip to your definitions and add anything that you didn’t have the first time 20 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Reading P 283-285 P 317-320 P 323-325 21 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Questions P 292 #1, 3, 4 P 329 set one 22 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Day 2 23 History of the atom PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM History is important Timeline of cell phones Timeline of cars Atom History rap Atom History song WHY IS IT IMPORTANT TO KNOW HISTORY? 24 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Who are they? 25 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Where are the girls? 26 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Read Read pages 317-320 27 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Early ideas about the atom Questions are in your notes 28 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Make a time line If you are in green, yellow, black you will be reading first 29 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Use your time line to expand information and design a poster Design a poster illustrating ONE of the models that were proposed since 1800s Explain how each model reflects the new knowledge that scientists gained through their experiments 30 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Democritus 31 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM John Dalton history John Dalton's Atomic Theory 1808 Each element is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. All atoms of a given element are identical. Atoms of different elements have different properties, including mass and chemical reactivity. Atoms are not changed by chemical reactions, but merely rearranged into different compounds. Compounds are formed when atoms of more than one element combine. A compound is defined by the number, type (element), and PERSONAL 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM proportion 32 of the constituent atoms. \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt Marie and Pierre Curie 33 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Thomson 34 Cathode ray tube PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Rutherford 35 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Niels Bohr 36 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Current model 37 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Day 3 38 Atomic structure PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM What do you know? What are atoms composed of? Where are the particles located? What are the charges of each particle? What is the mass of each particle? What is the volume of each particle? Why do atoms behave the way the do? 39 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Think about these What are the differences? What do they behave like they do? Imagine it! Sugar Cream Ice Disclaimer: yes you can add fruit and other things to change the flavor Review Periodic Table The chemical symbol is an abbreviation of the element’s name 42 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Atoms are the smallest unit of matter All matter is made up of atoms (atomic theory) Atoms are composed of three smaller (subatomic) particles called protons, neutrons, and electrons 43 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Find the electrons!! 44 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Element Builder Graphic Organizer -you are going to summarize what you learned from the gizmo in this graphic organizer 46 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Atoms Neutrally charged because P+ = EMade of smaller particles of matter The number of protons determines the identity Atoms of same element have the same number of protons but neutrons may vary Atoms may lose or gain electrons yet still remain the same element Atoms break down into subatomic particles (electrons, neutrons, protons) Neutrons (N±) Found in the center of nucleus and is very tiny Neutral charge with a AMU = 1 Atomic Mass = N± + P+ (avg. of all isotopes) Do not change during chemical reaction Isotopes – Neutrons change Atoms of same element can have a different number of N± Protons (P+) Charge is positive AMU = 1 Found in the center of the nucleus Gives the nucleus its positive charge Proton number never changes All elements are placed by increasing atomic numbers on the periodic table (IDs the element) Protons (positive) are equal to Electrons (negative) so all elements are neutral Protons do not change during a chemical reaction Electrons (E -) Charge is negative AMU = 0 Found in the energy cloud at no exact location Within the cloud there is more energy farther from the nucleus 1st 2e-, 2nd 8e-, 3rd 8eElectrons = Protons Responsible for an atoms chemistry Electrons can be transferred (gain or lose electrons) but are still the same atom Can be shared during a chemical reaction, Last energy level Echange during the chemical reaction Volume of an atom is the electron cloud Forms ions Think of an Atom as a Magnet The nucleus has a net charge that is positive Protons (+) + Electrons (-) attract Electrons (-) + Electrons (-) repel Atoms are neutrally charged because Protons = Electrons Particle Interaction Protons will repel each other Electrons will repel each other Protons and Electrons attract each other What is the charge of the nucleus? What is the charge of the electron cloud? 52 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM What are particles responsible for and what happens in a chemical reaction Neutrons: Protons Responsible for isotopes Is not affected by a chemical reaction Responsible for identification Is not affected by a chemical reaction Electrons Responsible for volume PERSONAL 53 Is affected by a chemical reaction \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Let’s Draw It You need red, blue, and yellow colored pencils Be precise because I do not have extra copies When you are finished put it in the box 54 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Video 55 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Day 4 56 Atomic structure PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Draw an atom of Oxygen Put the protons, neutrons, and electrons in the right spots 57 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Draw that Atom Practice Draw Na 58 Bohr's model shows electrons moving around the nucleus in fixed orbits PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt Bohr’s model 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Build It! Build an Atom You need a board and the three container with blue, red and yellow marbles… You have 20 minutes to do the front- when the timer rings sit down quickly to get instructions for the next activity Build the atoms then fill in the chart based on WHAT YOU SEE! 59 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Day 5 Atomic structure Atomic Number 61 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Carbon-12 62 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Atomic Number The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom It is a whole number Always the same for a given element and will never change Can be found on periodic table The number of protons gives an atom identity 63 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Organize It! 64 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Atomic Number The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom, which makes it a whole number Atomic number is always the same for a given element Can be found on the periodic table! Protons (P+) Charge is positive AMU = 1 Found in the nucleus Gives the nucleus its positive charge Proton number never changes All elements are placed by increasing atomic numbers on the periodic table (IDs the element) Protons (positive) are equal to Electrons (negative) so all elements are neutral Protons do not change during a chemical reaction Electrons (E -) Charge is negative AMU = 0 Found in the energy cloud at no exact location Within the cloud there is more energy farther from the nucleus Electrons = Protons Responsible for an atoms chemistry Electrons can be transferred (gain or lose) or shared during a chemical reaction Think of an Atom as a Magnet The nucleus has a net charge that is positive Protons (+) + Electrons (-) attract Electrons (-) + Electrons (-) repel Atoms are neutrally charged because Protons = Electrons Let Draw! Atomic number activity 3 circles- first one is for the nucleus Red=protons (not green) Yellow= electrons (not red) 69 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Create a model You will work at your lab table, but EVERYONE is doing this Green, Yellow teams: Carbon Black, Red teams: Nitrogen White, Orange: Oxygen You will decide what color your protons, neutrons and electrons will be and put it on your lab sheet I will demonstrate step #12 70 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Video 71 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Day 6 72 Atomic mass PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM The nucleus How did they find it Atomic Mass The total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom Mass number is not on periodic table Atomic mass is the weighted averages of masses of naturally occurring isotopes It is usually a decimal 74 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Look at the differences! 75 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM You use the name or symbol of the element followed by the mass number boron-10 and boron-11 Or B-10 and B-11 76 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM OR 77 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM 78 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt Draw me!! 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Organize It!! 79 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Atomic Mass All Protons and Neutrons are found in the Nucleus of an Atom It is a weighted average of the masses of the naturally occurring isotopes Can be found on the periodic table It is an average and not usually a whole number Nucleus Nucleus is found in the center of an atom with the electrons moving in patterns around the nucleus Center of the atom which contains the P + and the N ± which are tightly bound Has a positive charge which is equal to the number of protons Particles inside the nucleus do not change in a chemical reaction Proton Found in the Nucleus Has a positive charge, Which gives the nucleus a positive charge Number of protons for an element never changes Atomic mass unit is equal to 1 Makes up part of the atomic mass of an element The number of protons determine the identity of an atom (an element) Neutron Found in nucleus Has no charge, it is neutral Has a AMU = 1 Makes up the other part of the atomic mass of an element Forms isotopes Isotopes An Isotope is an atom of the same element with the same atomic number but a different atomic mass. Isotopes are two or more atoms of the same element having the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons Let’s Draw It and Mass It!! Atomic mass activity- 15-20 min Atomic mass lab- 15-20 min Finish at home 85 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Video 86 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Day 7 Electrons-bohr models and Lewis dot structures You may need a calculator and a blank scratch sheet of paper 87 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Firework flame test Real electrons Review Protons? Neutrons? Electrons? 89 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Electron Cloud There are different “energy levels” The exact location of an electron cannot be pinpointed Scientists use the concept of probability to predict where an electron may be located It is drawn so it looks like electrons don’t move, but remember the drawings are a represenation 90 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Where are the electrons placed on a diagram? Each energy level (circle) has a maximum number of electrons that can fit there 2 in the first circle 8 in the second 8 in the third When drawing a representation you start on the first circle and fill it up then move out to the next circle and continue until you have put the correct number of dots 91 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Where are the electrons placed on a diagram? Examples- C, Cl, He, H, Li, Mg, Ne, N, O, P, Na, S 92 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Element # of P+ # of N+/- # of E- Electrons in 1st Electrons in energy level 2nd energy level Electrons in 3rd energy level Carbon Chlorine Helium Hydrogen Lithium Magnesium Neon Nitrogen Oxygen 93 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Coin Toss Probability If you flip a coin what are the total possible outcomes you could have? Heads or tails (2) For each flip what is the probability of getting a head? Tail? To find this you divided the possible outcome by the total possibilities 1/2 94 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Dice Probability Dice have how many sides (total possible outcomes) How many 1? 2? 3? There are 3 sides that have a one To find the probability of getting a 1 on a roll you divide 3 by 6 to get ½ or 50% What does this mean? 95 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Electron Probability How does this apply to electrons? Nobody knows the exact location of an electron at any given time Probability is used to predict where is might be or where it spends most of the time 96 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Roll It! 97 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Flaming Elements Light is given off from these chemicals in different colors What happens is that the electrons of the elements are heated and “excited” They “jump” to a higher energy level As they “fall” back down the result is color 98 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Flame Test Pull your hair back – I will light the flame Be careful with the flame from the sterno Write the symbols of the elements down on your paper. Find the name of the element on the periodic table and write that down 99 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM READ/LISTEN TO DIRECTIONS Carefully take a Q-tip and dip it in the alcohol cup Then dip into ONE of the elements Place it in the fire and watch what color it burns and make a note on your paper Some of them burn orange, but you have to look carefully past the orange- DO Na last!!!!!! 100 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Exit Slip In the space provided in your notes… Explain what you learned about electrons, Bohr models, and Lewis dot structure Let me know if you are confused 101 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Day 8 You need your periodic table You need the following colored pencils: Red Yellow Blue Green 2 others What102 are differences between… PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Period Table Navigation If she can do it… This is your new best friend! You will use this on the EOC What does periodic mean? Repeating – table repeats every eight elements Summed Up!- COMPASS- Periodic Table 104 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM The Key Atomic number Letters are the symbol of the element- notice the capitals and lower cases The name is the word Average atomic mass 105 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt C 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Atomic Number All the protons in the nucleus of an atom Elements are listed by increasing atomic number Identifies the element Flip over and find the elements that have an atomic number of 2, 8, 14 106 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Element Notation -label Carbon-12 107 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Atomic Mass All the protons AND neutrons in the nucleus of an atom This is an average of all the element’s isotopes Flip over and find the elements that have an atomic mass of 14.01, 32.07, 35.45 108 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Isotope An Isotope is a different version of the same element that has a different mass and different number of neutrons 109 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Isotope notation 110 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM How to find… Neutrons 111 Electrons PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt Protons 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM COMPASS-Periods and Groups 112 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Period (horizontal) Tells you the number of energy levels There are 7 TREND: As you move left to right the number of energy levels stays the same- As you move top to bottom they increase by one 113 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM The Periodic Table of Elements 114 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Group/Family (Vertical) Elements in the same groups have the same: Valence electrons Dot diagrams Oxidation #’s Similar chemistry (chemical behavior) 115 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM The Periodic Table of Elements 116 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM To yourself… Find the atomic number, atomic mass, group number and period number for… Platinum Zirconium Barium Fluorine THUMBS?????? 117 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Oxidation States (Number) The number of electrons that an element will lose, gain or share to become stable Choose any colored pencil… 118 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM The Periodic Table of Elements 119 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Valence Electrons Electrons in the last (outer) energy level TREND: From left to right across periods 1-3 atoms of all these elements contain one more valence electron that the atoms of the previous elements- From top to bottom within a group the elements contain the same number of valence electrons Choose another colored pencil… 120 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM The Periodic Table of Elements 121 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM Stability of Atoms Stable = happy Stable= full outer shell Stable= maximum amount of valence electrons 122 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:31 PM The valence electrons are involved in bonding. 1 8 7 2 6 3 Is Neon happy? 123 4 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Lewis Dot Structure (dot diagrams) Shows the pattern of valence electrons 124 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Atomic Diagram (Bohr model) 125 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM The Periodic Table of Elements 126 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Diatomics Elements that are so reactive they covalently bond to themselves to form a molecule Br.I.N.Cl.H.O.F You need a RED colored pencil 127 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM The Periodic Table of Elements 128 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Stair step line Divides chart into left and right (metals and nonmetals) 129 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM The Periodic Table of Elements 130 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Where to find… Metals nonmetals (yellow) 131 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt metalloids (blue) 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Liquids, solids and gases at room temperature Liquids Solids Gases Exceptions: Aluminum and Mercury 132 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM The Periodic Table of Elements 133 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Polyatomic ions A group of covalently bonded elements that act as a single element. They have their own oxidation numbers Sulfate Phosphate Nitrate Carbonate PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt Hydroxide Ammonium Chlorate Sulfite 135 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Group or Family Name 1 Alkali Metals 2 Alkaline Earth Metals 13 Boron Group 14 Carbon Group 15 Nitrogen Group 16 Oxygen Group 17 Halogens 18 Noble Gases 136 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM The most reactive element (and metal) is Francium The most reactive nonmetal is Fluorine 137 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Atomic Structure Worksheet and “quiz” Thumbs? Finish for homework 138 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Video -flip to your definitions and add anything that you didn’t have the first time 139 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Day 9 140 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Carbon isotope use in anthropology Isotopes Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons and different mass numbers Ex. isotopes of hydrogen. 142 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM How are isotopes represented? You use the name or symbol of the element followed by the mass number boron-10 and boron-11 Or B-10 and B-11 143 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM OR 144 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM 145 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt Draw me!! 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Video 146 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM 147 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Practice Give the number of protons and neutrons that are found in each of the following Isotope Protons Neutrons P-31 Au-200 C-14 I-127 Ra-226 U-235 148 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Practice Write the symbol for atoms which have… 30 protons and 35 neutrons 82 protons and 125 neutrons 1 proton and 1 neutron 149 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Isotopes Graphic Organizer Element with a different number of neutrons will have a different atomic mass Two or more atoms of the same element having the same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons (different masses) 150 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Symbols for Isotopes Mass number 12 C 6 Symbol Symbol C – 12 Atomic number 151 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt Mass Number 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Hydrogen • Protium 1 H 1 • Deuterium 2 H 1 • Tridium 152 3 H 1 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Carbon C - 12 C - 14 (Carbon Dating) 153 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Uranium U-235 235 U 92 U -238 238 U 92 Radioactive 154 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Venn Diagram Isotope? Atomic number? Mass number? 155 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Questions There are 6 sets of atoms described. Are they… the same atom Different atoms Isotopes 156 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Let’s Draw Hydrogen Isotopes You will be give red, green and orangish stickers RED=PROTONS GREEN=NEUTRONS ORANGISH=ELECTRONS On each sticker place the correct representation for Protons (p+), neutrons (n+/-) and electrons (e-) Label the nucleus and the energy level Write the names and both notations for ALL three isotopes of hydrogen (from your notes) Place the correct amount of stickers in the proper location 157 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Isotope Homework You will have 15-25 minutes to do this Finish at home 158 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Isotope Penny lab-20 min 1982- The year of the PURDY Mass the penny and add 10- this is your coinium mass number Find protons, electrons and neutrons for the isotopes Draw two Bohr models and answer the questions 159 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Video Be prepared for a brief quiz at the end 160 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Day 10 161 Radioactive isotopes PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Testing food Radioactive isotopes-Japan Radiation found in food Read p 396-399 What is radioactivity? How does an radioactive nucleus become stable? What are the 3 kinds of nuclear decay? What happens in each of them? What are some ways that we use/see nuclear reactions for energy? What is nuclear waste? What is half-life? Where is nuclear waste stored now? What is the machine called that can detect a radioactive tracer? Who is 163 Marie Curie? PERSONAL 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt Isotope Review What are they? Examples? Drawing? Questions?????? 164 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM History Marie Curie 165 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Uses video 166 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Organize It Two types of isotopes… 167 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Stable Isotopes TO BE STABLE There must be enough neutrons to block the repulsive forces of the protons P+ 168 P+ PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Unstable Isotopes Too many or too few Neutrons compared to protons Does not occur naturally or exist for long Will give off particles and radiation to become a stable nucleus 169 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Radioactive Means that particles give off radiation 170 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Undergoes nuclear decay Nuclear decay occurs naturally in some elements Definition A nuclear reaction that involves emission of energy or particle from the nucleus Results in a more stable environment 171 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Emits radiation Describes the particles and/or energy that are emitted during nuclear decay Alpha, Beta, Gamma Rays What can they go through? 172 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Half-Life The amount of time it takes for half of a sample to decay Why does this matter? Read the paragraph that explains the half-life of a radioactive substance on the nuclear medicine sheet. *Notes: a nuclide is a term for an atom that takes energy into account A Geiger counter detects radiation 173 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM To find half life… There is a formula y= ½t2 Graph data- hours on x axis and counts on y axis Select any point- determine a value for counts/min and for time Take your value for counts/min divide in half and then find the appropriate time Subtract the new time from the original and that is the half life 174 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Let’s practice On your Nuclear medicine sheet pick any date points on the graph or on the table… 175 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Dating Game Read instructions Important points… Remove heads up, replace with beans Put tails up and beans back in box Your graph should have two lines on your graph You have 30 minutes 176 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Homework Isotopes Worksheet 177 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Day 11 178 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Nuclear reactions Nuclear Reactions In the Middle Ages, individuals called alchemists spent a lot of time trying to make gold. Making an element is possible only if you can achieve a nuclear reaction, which has more energy than chemical reaction 180 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt Different because electrons are not involved 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Nuclear reactions involve either combining or splitting the nuclei of atoms. 181 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Nuclear Reactions There are two kinds of nuclear reaction: fusion and fission. The process of combining the nuclei (lightweight) of atoms to make different atoms is called fusion. 182 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Fusion Mass of products is less than the mass of the reactants and lost mass is converted to energy Usually occurs on sun Using this in nuclear power plants is still in the developmental stage Hydrogen bomb, also called a thermonuclear bomb, utilizes nuclear fusion 183 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM 184 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Draw It! Energy 185 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Fission Breaking up the nucleus of an atom (usually a large one) A large amount of energy is released Occurs in power plants and A bombs Chain reaction could occur- must be a certain amount of mass (critical mass) of fissionable material in close proximity for a chain reaction 186 to occur PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Fission (cont) the mass of the products is less than the mass of the reactants The lost mass is converted into energy (E=mc2) Ex U-235 splits into 2 or more parts 187 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM 188 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM 189 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM 190 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Nuclear Reactions Fission and fusion are nuclear reactions. Protons and neutrons—the two most important subatomic particles in the nucleus—participate in these reactions. 191 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Comparing Chemical and Nuclear Reactions 192 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Video Have Known Sin- Atomic Bombs Fission and Power Plants 193 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Compare Fission and Fusion 194 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Domino-Chain Reaction 195 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Energy from the Atom How is nuclear energy used? 196 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Day 12 197 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Using Nuclear Reactions 198 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Using Nuclear Reactions Nuclear medicine Carbon dating Nuclear power reactors Nuclear weapons 199 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Nuclear Medicine Radioactive isotopes can be used to detect problems in organ systems Ex. Benefits: Destroy target cells, such as cancer • Cells are most susceptible to radiation during cell division (cancer is rapidly dividing cells) Mapping substances through organs • Can show proper function or malfunction 200 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Nuclear Medicine Disadvantages Wastes must be stored in a special way until it is no longer radioactive Cancer cell treatment damages healthy tissue 201 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Using Nuclear Reactions The age of some fossils can be determined using radioisotopes such as carbon-14. It is possible to figure out the age of objects made from plants or animals that are between 50,000 and a few thousand years old using carbon dating. 202 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Nuclear Power Reactors Nuclear-power reactors Nuclear technology is used to produce electricity Energy from controlled nuclear fission is used to heat water to steam • Steam expands turns turbine which spins a huge magnet which creates electricity Difference in coal-powered and nuclear powered is the heating up of water 203 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Nuclear Power Reactors Benefits Lots of energy from not a lot of fuel No greenhouse gas emission Used anywhere (unlike wind, solar, etc…) Non-reliance on fuel 204 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Nuclear Power Reactors Disadvantages Need specialized technology to refine fuel Can cause thermal pollution Storing process is complicated Wastes are transported from where it is generated to where it is stored Can cause long-term reactive decay problems Three Mile Island Exposure of workers is sometimes fatal 205 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Nuclear Weapons Video 207 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM Works Cited http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Mende lejevs_periodiska_system_1871.png http://neolegacyandrew.blogspot.com/ 2008/08/baskin-robins-ice-cream.html 208 PERSONAL \\screen\Internal\TeacherII\Teacher II.ppt 5/4/2017 1:29:32 PM