* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Motion Along a Straight Line at Constant
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
State of matter wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Weightlessness wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Anti-gravity wikipedia , lookup
Field (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
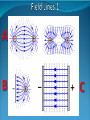
Book Reference : Pages 72-73 1. To recap what we can remember from Y11 about static electricity What can you remember about static electricity? What is it? How is it made? What kinds of charges are there? What part of the atom is involved? What do like charges do? What do unlike charges do? What is it? Is an excess electrical charge (either positive or negative) which cannot move, either because the material is an insulator or it is a conductor which is isolated from “Earth”. The charges cannot move and are therefore static How is it made? Some materials allow electrons to be easily removed from their atoms. For example when a dry cloth rubs a plastic rod. What part of the atom is involved? Only the electrons which have a negative charge are involved since they are the only particles which can be dislodged What kinds of charges are there? Positive and negative. Things become positively charged when there are electrons missing or negatively charged when there is an excess of electrons What do like charges do? Repel (Push away/apart) What do unlike charges do? Attract (Pull towards each other) NB Same rules as magnetic poles Name some good electrical conductors and electrical insulators [Jumper/Balloon Animation] Conductors Metals are good conductors & contain a “sea” of free electrons which are not bound to one particular atom & are free to move (conduct) Insulators Most non-metals are insulators and do not contain free electrons. The electrons are attached to individual atoms Note Carbon, (graphite) is an exception & is a non-metal which conducts electricity well A gold leaf electroscope is a simple device which allows electrical charges to be detected and compared [Electroscope Animation] Modern semiconductor integrated circuits (silicon chips) are very sensitive to damage by static electricity. Particularly CMOS (complimentary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) devices Antistatic Packaging and handling precautions must be taken to avoid damage When charged objects are brought together they exert an equal and opposite (non-contact) force on each other. Consider a small object, which is free to move, has a positive charge and is brought near a fixed object which also has a positive charge then the free object will be repelled and will move The path this free positive charge would take is called the field line or line of force A B C Experimentally we can plot the field lines for an electric field in a similar manner to a magnetic field. (We can use grains of semolina dusted on to the surface of an oil film which has had a field set up across it). Diagram A shows the field created by oppositely charged objects. The field lines are concentrated near the objects and our free positive test object would take a curved path to the negative charge Diagram B shows a point object with a positive charge near an oppositely charged plate. The field lines are at right angles to the plate Diagram C shows a oppositely charged plates. There is a uniform between them shown by the parallel lines. In keeping with gravitational and magnetic field lines, the shape, density, (closer together shows a stronger field) and direction of the field is significant