* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download electric current
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
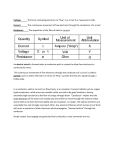
1-3 Electric Current and Magnetic Fields Electric Current • Electric Charge - all protons and electrons have an electric charge. • The flow of electric charges produce an electric current. • Ampere (A or amps) - unit used to measure the amount of charge that flows in a given time • An electric current produces a magnetic field (p. 31) • The field produced effects compasses just as a magnet does Moving Charge and Magnetism • All magnetism is caused by the movement of charges. • The movement of charges is also responsible for electric current. Electric Circuits • Electric currents need a circuit in order to flow . • A circuit is a closed path for the current to travel through. • All electrical devices contain circuits • All circuits have the same basic features • A source of electrical energy (power source) • Ex. Battery • A device that is run by electrical energy • Ex. Light Bulb • Conducting wires and a switch • See p. 31 Conductors and Insulators • Electric current does not flow through every material • Conductors allow electricity to flow freely • Ex. Copper, silver, iron, aluminum • Conductors have loosely bound electrons in their atoms, that allows the electrons to to flow through the material-->forms a current • Insulators do not allow electricity to flow freely • Ex. Rubber, wood, glass, plastic • Electrons are bound tightly to their atoms and do not flow easily. • Conducting copper wire is covered by a plastic coating so that it can be handled safely while currents flow through it. Electrical Resistance • A resistor uses electrical energy as it interferes with the flow of charge • Many times the energy is transferred into another form • Ex. Light bulb --> electrical energy to light and heat energy • Best example: Walking through a crowd. Stand up, let’s try it. Superconductors • A material that has NO electrical resistance • This would allow an electrical current to flow with out losing any energy • Computers could be the size of a watch and be just as effective and powerful as a typical desktop computer.