* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit Topic: Colonial America
Foundations of mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Georg Cantor's first set theory article wikipedia , lookup
List of important publications in mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Collatz conjecture wikipedia , lookup
Series (mathematics) wikipedia , lookup
Proofs of Fermat's little theorem wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Real number wikipedia , lookup
History of algebra wikipedia , lookup
Elementary mathematics wikipedia , lookup
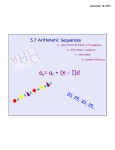
Unit Topic: Sequences & Series Content: Mathematics (Algebra 2) Grade: HS Duration: 3 weeks Big Idea: High school students should enter high school with a strong background in rational numbers and numerical operations and expand this to real numbers. Solving quadratic equations produces a working knowledge of complex numbers. This becomes the foundation for algebra and working with algebraic symbols. They understand large and small numbers and their representations, powers and roots. They compare and contrast properties of numbers and number systems and develop strategies to estimate the results of operations on real numbers. Students will use and understand the limitations of, graphing calculators and computer spreadsheets appropriately as learning tools. Program of Studies: Core Content for Assessment: Enduring Knowledge – Understandings MA-11-1.3.1 Students will solve real-world problems to specified accuracy levels by simplifying real number expressions involving addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, absolute value, integer exponents, roots (square, cube), and factorials. DOK - 2 Students will understand that numbers, ways of representing numbers, relationships among numbers and number systems are means of representing realworld quantities. Grade Skills and Concepts Number Operations Students will determine a specific term of a sequence given an explicit formula describe and extend arithmetic and geometric sequences determine an explicit rule for the nth term of an arithmetic sequence apply sequences and arithmetic and geometric series to solve realistic problems Patterns, Relations and Functions Students will see the patterns in arithmetic and geometric sequences using recursion see patterns in other sequences (e.g., quadratic, cubic) relate the patterns in arithmetic sequences to linear functions relate the patterns in geometric sequences to exponential functions Variables, Expressions and Operations Students will use symbolic expressions, including iterative and recursive forms, to represent relationships among various contexts Unit Topic: Sequences & Series 1 MA-11-1.3.2 Students will: describe and extend arithmetic and geometric sequences; determine a specific term of a sequence given an explicit formula; determine an explicit rule for the nth term of an arithmetic sequence; and apply sequences to solve real-world problems. DOK - 3 MA-11-1.3.2a Students will write an explicit rule for the nth term of a geometric sequence. MA-11-1.3.2b Students will recognize and solve problems that can be modeled using a finite geometric series, such as home mortgage problems and other compound interest problems. Content: Mathematics (Algebra 2) Grade: HS Duration: 2 weeks Big Idea: High school students should enter high school with a strong background in rational numbers and numerical operations and expand this to real numbers. Solving quadratic equations produces a working knowledge of complex numbers. This becomes the foundation for algebra and working with algebraic symbols. They understand large and small numbers and their representations, powers and roots. They compare and contrast properties of numbers and number systems and develop strategies to estimate the results of operations on real numbers. Students will use and understand the limitations of, graphing calculators and computer spreadsheets appropriately as learning tools. What students will Know Arithmetic Sequence & Series Geometric Sequence & Series Explicit Recursive Critical Vocabulary Sequence Ratio Finite Infinite What students will Do Determine if a sequence is arithmetic or geometric. Find various terms of a sequence. What students will Understand Difference between arithmetic and geometric. Real world applications of sequences and series. Write an explicit rule for the nth term of a sequence. Find the sum of a series. Resources: Kentucky CCT Coach Book (Grade 11) Internet resources (e.g. KDE – Diagnostic Assessments, Released Items, bsapp.com) 2 Essential Questions What is the difference between a sequence and a series? What is the difference between arithmetic and geometric? What are the real world meanings of each? Assessments Find terms of a sequence and the sum of a series. Write an explicit rule for the nth term of a sequence. Solve real world problem using a finite geometric series, such as home mortgage and other compound interest problems.