* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Islam
Islamofascism wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
History of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
Islamic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Satanic Verses wikipedia , lookup
Muhammad and the Bible wikipedia , lookup
Islamic Golden Age wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Mormonism wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Somalia wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
Sources of sharia wikipedia , lookup
Islamic–Jewish relations wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Islamic socialism wikipedia , lookup
Morality in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islamic ethics wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Nooruddeen Durkee wikipedia , lookup
Origin of Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Islamic culture wikipedia , lookup
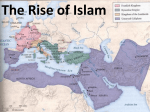
The Origins & Expansion of Islam Film: Islam: Empire of Faith Viewing Questions: Links to Parts One/Two & Three – Did you learn anything new about Islam from the film? – Did it challenge any of your preconceptions about Islam, its history, or followers? – Does the film (or do the filmmakers) have a bias? If so, what is it? – If the film is biased, do you trust the information it provides? Take notes on these questions as you view the film Pre-Islamic Arabia Isolated by desert – modern Arabian map No internal rivers or waterways Dominated by southern Arabian city-states (where there is enough rain) Development of trade routes – Camel caravans, north/south along Red Sea – Shipping to east Africa, Persia, India Fragmented politically and socially Depiction of camel-herder Iglum’s life Trade routes from southern to northern Arabia Bottom shows herder driving a camel Top shows herder with servants or family members at banquet – his own funeral banquet? Stele was carved from alabaster rock It was created to show devotion to the dead herder – the script curses anyone who destroys the stele Crossroads and Conflict Arabia – many religions over time – caught between empires Threatened by Christians in Ethiopia & Byzantium S. Arabian kings converted to Judaism in 400s CE Ruled by Ethiopians – forced conversion Then ruled by Persians – toleration Decline of s. Arabian kingdoms opened up space for Bedouins, Mecca, and Islam Rise of Mecca Center for trade – resting place for camel caravans Place of pre-Islamic worship – site of Ka’ba – worship of stone idols Expansionist tribe Quraysh took over around 500 CE Changing religious beliefs: Stone carving from Felix Arabia, Yemen Kingdom, 1st-3rd centuries CE Evolution of meaning and use: Pre-Islam: Probably first worshipped as stone incarnation of a deity – similar to Ka’ba Then transformed into a representation of a worshipper (added carved face) Or revered as ancestor who should be remembered The Great Mosque of Mecca – Ka’ba in back Muhammad & Allah Muhammad born in 570 CE Camel trader – used to travel and different cultures Revelations – 610 CE – angel Gabriel – known to Jews and Christians Words came from Allah, “the one true god” Arabs knew Allah as one of their preIslamic polytheistic gods Religious Connections Muhammad drew on other monotheistic religions Jews – Mosaic code of ethics and behavior Christians – Judgment Day for all people Zoroastrianism – struggle on earth between good and evil Muhammad said Jews and Christians were “People of the Book”: same god, but book and ideas mistranslated over time Muhammad was last Prophet, the Messenger of God, and would preach pure word from God Qur’an & Arabic Muhammad was illiterate He recited scripture to secretaries who wrote it out: became the Qur’an (or Koran) Religion became known as Islam (Arabic for “submission” to will of God) Qur’anic text became means for standardization of Arabic language Qur’an and Arabic became interconnected Hijrah to Medina By 619, Muhammad had limited # of followers in Mecca Invited to Medina (Mecca’s rival city) Polytheist tribes converted, but not Jews Muhammad added to Qur’an: Abraham, not Moses, was principle prophet and father of Arabs Jews and Christians had corrupted religion Abraham built Ka’ba shrine in Mecca Building Islam: The Five Pillars Muhammad had to build a community of believers Islam provided stability in land of fragmentation He built pure Islamic community, an umma, in Medina, then defeated Mecca in battle (seen as divine message) Five Pillars were basis for everyday life: – Shahadah (one god & messenger) – Salat (saying prayers 5 times daily while facing Mecca) – Zakat (giving alms to poor) – Sawm (fasting during Ramadan) – Hajj (pilgrimage to Mecca once during lifetime) Videos: Link #1, Link #2 Muhammad’s Death… Raised certain questions: – Not so much about religious leadership b/c Islam was based on individual worship – But questions of political leadership of the umma (community of believers) w/o Muhammad – Islam had grown in land of fractured politics (tribal), so difficult to remain united Caliphate Solution to instability after M’s death Father-in-law Abu Bakr took over leadership of umma, uniting religion and politics – assumed title of caliph Combination of Islamic church and state called a caliphate Contract between leader and followers Expansionist: believed in converting nonbelievers and imperial growth (632-732 CE) Jihad Belief in Islam as universal religion, applies to everyone Obligation of Muslims to convert nonbelievers and expand Islamic rule laid out in Qur’an Expansionist beliefs led to imperial conquests and growth Led to conflicts with Byzantine and Persian empires Shari’ah Law Based on pre-Islamic Arabian social order Religiously-based rules and obligations for Muslims Ways to regulate everyday life to make it easier for Muslims to follow will of God Rules to help create the umma – uniform laws that united Muslims throughout caliphate Protection for the weak Respect for women (divorce, property) But unequal power in society & relationships Tolerance Expansion of empire = what to do about nonbelievers? Qur’an outlawed forced conversion Qur’an accepted ‘People of the Book’ Nonbelievers taxed = helped support caliphate Tolerance for other religions, particularly Judaism, was widespread during caliphate Creation and Problems of Empire Islamic armies, led by Umar, took over parts of Byzantine Empire (Egypt, Syria, Lebanon) Egypt & North Africa Persia Questions arose: How to rule such a huge empire? Emirs governed locally, didn’t always follow caliphs directions Problems of Succession Question of political rule: Who will succeed last ruler? How? Issues of legitimacy in land of divisions (tribes, families, empire, power) Splits in Caliphate b/c of problems of succession Umar died; Uthman appointed caliph over Ali Uthman gave titles to family members Lasting Divisions Followers of Uthman (Umayyad family) and Ali battled and split Islamic umma Umayyads claimed caliphate (political power, dynastic succession)– led empire for centuries Umayyads also formed Sunni sect – majority sect, believed they were pure followers of The Prophet Shi’ites were followers of Ali – minority sect Islamic Expansion: Boundaries of Caliphate, 630-750 CE End of th 8 -Century Expansion Caliphate had expanded into Spain and India Internal divisions weakened power Shi’ites and Abbasid clan united to take over caliphate from Umayyads Defeat of Arab-Berbers in France in 732 CE halted advance Islamic Architecture Some early Islamic architects were Greeks – adapted Greek/Roman architecture to new needs and cultures Mosque: Islamic temple of worship – No depictions of God or people – No seats – Geometric and Arabic designs – Minarets – towers to call people to prayer Dome of the Rock Islamic temple in Jerusalem Built on rock platform, former site of Judaism’s main temple, Solomon’s Temple Also site of Temple Mount in Christian beliefs Dome of the Rock sacred to Muslims because it was the site of Muhammad’s Miraaj or ‘Night Journey’ to Jerusalem (Qur’an 17:1). Interior, Dome of the Rock Sacred rock on which Abraham sacrificed his son Isaac and from which Muhammad took flight on his horse to heaven Grand Mosque of Kairouan, Tunisia Interior, Grand Mosque of Kairouan, Tunisia Famous Mosques – Dome of the Rock, Jerusalem, Israel – Great Mosque of Kairouan, Tunisia – Mezquita (Mosque) de Cordoba, Cordoba Spain Links Islamic Art Link Names and dates of caliphs Video, 'Empire of Faith,' Parts 1 & 2 Video, ‘Story of God,’ Part 2