* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Neuroinflammatory Reflex
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Behçet's disease wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Inflammation wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
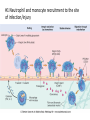
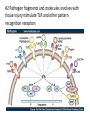
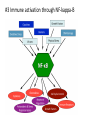
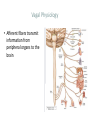
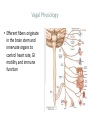
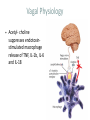
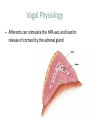
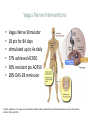
Neuroinflammatory Reflex I M P L I C AT I O N S O N R H E U M AT I C D I S E A S E Immunology Neuroscience #1 Neutrophil and monocyte recruitment to the site of infection/injury #2 Pathogen fragments and molecules involves with tissue injury stimulate TLR and other pattern recognition receptors #3 Immune activation through NF-kappa-B #4 Recruitment of adaptive immune cells #5 Resolution of inflammation via resolving and lipoxins Principles • Bi-direction communication between the periphery and the CNS • Reflex like circuits exist to quickly respond to inflammatory events Vagal Physiology • Afferent fibers transmit information from peripheral organs to the brain Vagal Physiology • Efferent fibers originate in the brain stem and innervate organs to control heart rate, GI motility and immune function Vagal Physiology • Efferent vagus nerve communicates with the splenic nerve to suppress excessive proinflammatory cytokine responses and inflammation Vagal Physiology • Acetyl- choline suppresses endotoxinstimulated macrophage release of TNF, IL-1b, IL-6 and IL-18 Vagal Physiology • Afferents can stimulate the HPA axis and lead to release of cortisol by the adrenal gland 13 14 Pavlov Immunol Res (2015) 63:38–57 Vagus Nerve Interventions • • • • • • Vagus Nerve Stimulator 18 pts for 84 days stimulated up to 4x daily 57% achieved ACR50 30% resistant pts ACR50 28% DAS-28 remission Frieda A. Koopman, et al. Vagus nerve stimulation inhibits cytokine production and attenuates disease severity in rheumatoid arthritis. PNAS, July 2016 Biologics • Generally ~50% of the patients have clinically relevant improvement (ACR20)1 1. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2013 Aug 14 Vagus Nerve Interventions • • • • Transcutaneous TENS device Improves heart rate variability 20% in 15minutes Has not been studied in rheumatologic disease Inexpensive and safe Jennifer A. Clancy, et al. Non-invasive Vagus Nerve Stimulation in Healthy Humans Reduces Sympathetic Nerve Activity. Brain Stimulation, 2014; DOI: 10.1016/j.brs.2014.07.031 Vagus Nerve Interventions • Mid tech: • Cryo helmets • PEMF stimulators • • • • • • • • • Low Tech: Deep breathing Facial ice bathes Cold showers Gargling Valsalva Laughing Singing Gagging Endogenous Opioids and Immune Function Low Dose Naltrexone • Monocytes isolated from RA/SLE patients have low levels of beta endorphin • Lower levels of beta endorphin are inversely correlated with inflammatory markers • Levels are 1/4 -1/8 of a normal healthy population • WHY? 1. Wiedermann CJ, Sacerdote P, Mur E, Kinigadner U, Wicker T, Panerai AE, et al.Decreased immunoreactive beta-endorphin in mononuclear leucocytes frompatients with rheumatic diseases. Clin Exp Immunol 1992;87:178–82. 2. Panerai AE, Vecchiet J, Panzeri P, Meroni P, Scarone S, Pizzigallo E, et al. Peripheral blood mononuclear cell beta-endorphin concentration is decreased in chronic fatigue syndrome and fibromyalgia but not in depression, preliminary report. Clin J Pain 2002;18:270–3 Low Dose Naltrexone • “The bio equivalent of an orgasm a day”- me • Modulated opioid growth factor (OGF) production and OGF receptors • Immunomodulating rather then suppressive 22 LDN • Increasing beta endorphins and OGF sensitivity decreases: • IL1, TNFa production • TLR4 activity • Auto reactive T cell proliferation • Glial activation • Mitochondrial apoptosis LDN • Principles of prescribing • 1.5mg caps PO HS x 7 nights, then 2 PO HS (3.0mg) x 7 nights, then 3 PO HS (4.5), then best tolerated dose thereafter • Use up to 6mg total dose depending on body weight • In pediatric patients >18months: 0.1mg/kg dosage • Avoid in pregnancy/early lactation • Avoid concurrent narcotic prescriptions** • **maybe