* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AP150 HEART IMAGES--post
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
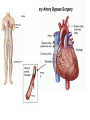
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
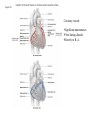
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
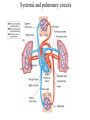
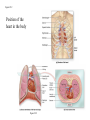
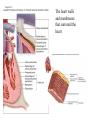
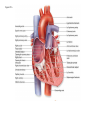
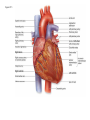
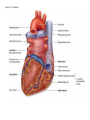
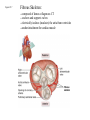
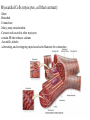
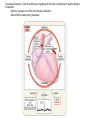
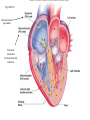
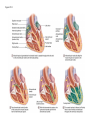
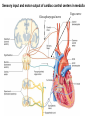
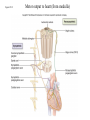
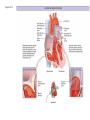
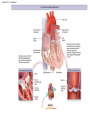
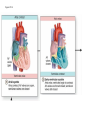
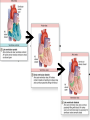
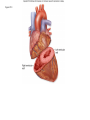
Systemic and pulmonary circuits Figure 22.2 Position of the heart in the body Figure 22.2 Figure 22.3 The heart walls and membranes that surround the heart Figure 22.6 Figure 22.5 Figure 22.5 continued Figure 22.7 Fibrous Skeleton: --composed of dense collagenous CT -- anchors and supports valves --electrically isolates (insulates) the atria from ventricles --anchor/attachment for cardiac muscle Myocardial Cells (myocytes, cell that contract): -Short -Branched -Uninucleate -Many, many mitochondria -Connect end-on-end to other myocytes -contain SR that releases calcium --has mild t-tubules --alternating, and overlapping myosin and actin filaments for contraction Figure 22.10 CARDIAC MUSCLE CELLS • Branched • joined by intercalated discs – desmosomes: tightly bind cells & transfer of tension – gap junction: electrical synapses that directly transfer electrical activity/AP from one cell to the next • Contractile/myocardial Cells (myocytes) => contract and conduct AP’s • Conductile/autorhythmic cells => produce and conduct action potentials Conceptual Overview: Electrical Stimulus originating at SA node is distributed to heart leading to contraction. --Blood is pumped out of the heart during contraction --Blood fills the heart during relaxation Fig. pf 20.13 Intrinsic/natural pacemaker Electrical connection between atria and ventricles Figure 22.11 Nervous System regulation of heart • Heart is regulated by medulla oblongata (cardiac control center) • Medulla receives sensory input through vagus nerve (CN X) and glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX). – Baroreceptors in aorta (aortic sinus) and common carrotid artery (carotid sinus) • Some receptors in heart • Medulla sends motor output through the: – Vagus nerve—parasympathetic division of ANS – Sympathetic nerves (cardiac plexus)—sympathetic division of ANS Sensory input and motor output of cardiac control centers in medulla Glossopharyngeal nerve Vagus nerve Figure 22.12 Motor output to heart (from medulla) PD Figure 22.13 Figure 22.13 continued Figure 22.14 Figure 22.14 Figure 22.8 Figure 22.9 Coronary vessels: •Significant anastomoses •Flow during diastole •Directly to R. A. Table 22.1 Table 22.2 Table 22.3