* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Key Revision Points for Cardiac Function Key points about the
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
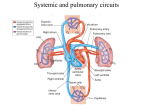
SAN is the heart’s pacemaker – intrinsic rhythm. Impulses spread through the atria causing contraction of both atria. Impulse picked up by AVN. Impulse spreads through septum in the bundle of His. Impulse then spreads through ventricles in Purkinje fibres causing ventricular contraction. SAN rate is altered by autonomic nervous system. Parasympathetic vagus nerve slows heart rate. Sympathetic nerve speeds up heart rate. Release of adrenaline increases heart rate prior to exercise. During exercise there is an increase in carbon dioxide levels. This causes an increase in the acidity of blood. This is detected by chemoreceptors. Impulses sent from medulla in the brain. Decreases vagus stimulation. Increases sympathetic impulses. Results in an increase in activity from SAN and an increase in heart rate. Heart rate increases. Stroke volume increases. This is due to Starling’s Law. Cardiac output increases. Remember: SV x HR = cardiac output Cardiac hypertrophy. Results in increase in stroke volume. RESTING heart rate decreases. RESTING cardiac output remains the same (no need for resting levels to change).