* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 3: Ancient Indian Civilizations
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islamic Golden Age wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Islamic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Sources of sharia wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
Satanic Verses wikipedia , lookup
Husayn ibn Ali wikipedia , lookup
Islamic ethics wikipedia , lookup
Usul Fiqh in Ja'fari school wikipedia , lookup
Islamic socialism wikipedia , lookup
Islamic missionary activity wikipedia , lookup
Imamah (Shia) wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Bangladesh wikipedia , lookup
Morality in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Historicity of Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Islamic culture wikipedia , lookup
Succession to Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Twelver Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and other religions wikipedia , lookup
Abbasid Caliphate wikipedia , lookup
History of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
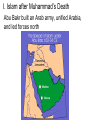
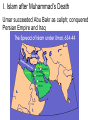
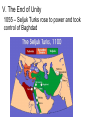
The Strait of Gibraltar Rock of Gibraltar or Jabal Tariq "Mountain of Tariq" Chapter 9 - The Islamic World Section 2: The Spread of Islam Section 2: The Spread of Islam Main Idea After Muhammad’s death, Islam spread beyond the Arabian Peninsula, shaping a major empire within 100 years. While the empire eventually broke into smaller parts, Islam continued to spread. Objectives • How did Islam evolve after Muhammad’s death? • What were key events of the Umayyad dynasty? • What changes occurred under the Abbasid dynasty? • What led to the end of the caliphate’s unity? I. Islam after Muhammad’s Death AD 632 - Muhammad died without naming a successor; Abu Bakr chosen as caliph Muhammad and Abu Bakr visit poor Bedouins who have no food to share until the Prophet makes their ewe give milk I. Islam after Muhammad’s Death Abu Bakr built an Arab army, unified Arabia, and led forces north I. Islam after Muhammad’s Death Umar succeeded Abu Bakr as caliph; conquered Persian Empire and Iraq I. Islam after Muhammad’s Death Arabs attacked the Byzantine Empire and failed; took Syria, Jerusalem, and Egypt II. Internal conflict and Division Uthman became next caliph, supported by Umayyad clan; was soon murdered II. Internal conflict and Division Disagreement over caliph split Muslims; Ali chosen as caliph and war broke out between Ali’s forces and Umayyads Alī ibn Abī Ṭālib (c.598-661) was the cousin and son-inlaw of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and ruled over the Islamic Caliphate from 656 to 661 II. Internal conflict and Division Ali was assassinated; Umayyads took control and Mu‘awiyah became caliph Mu’awiyah: First caliph of the Umayyad Dynasty II. Internal conflict and Division Most Muslims accepted Mu‘awiyah as caliph – Known as the Sunni, or “followers of the Sunna” II. Internal conflict and Division Ali’s followers believed only his descendants should be caliphs; the Shia – “party of Ali” II. Internal conflict and Division Split became permanent when Umayyads killed Ali’s son, Husayn Mausoleum of Imam Husayn, Kerbala, Iraq II. Internal conflict and Division A third group emerged - the Sufi, Muslim mystics who lived simple lives centered on God Whirling Dervishes The Sufi Whirling Dervishes of Istanbul - YouTube III. The Umayyad Dynasty Muslim rule spread under the Umayyad caliphs III. The Umayyad Dynasty Achievements: Arabic official language Common currency First work of Islamic architecture - Dome of the Rock in Jerusalem The winged steed Buraq, carries Muhammad to the "farthest mosque" Muhammad meets Gabriel on his night journey IV. The Abbasid Dynasty 740s – the Abbasids, led by descendants of Muhammad’s uncle, wipe out Umayyads IV. The Abbasid Dynasty Abbasids move capital to Baghdad; end of Arab domination of Muslim world V. The End of Unity European Christian armies weaken Muslim rule: i.e. Spain and Crusades V. The End of Unity 1055 – Seljuk Turks rose to power and took control of Baghdad V. The End of Unity 1200 - Mamluks took control of Egypt and Syria V. The End of Unity 1258 - Mongols destroy Baghdad, kill Abbasid caliph – the end of the caliphate Now I Get It: Sunni vs. Shia by Katie Couric Yahoo Global News Anchor Katie Couric explains why there’s such bad blood between Sunni and Shia Muslims in Iraq. Sunni vs Shia Muslims Shiite Muslim worshippers, stained by their own blood from self inflicted wounds, during the festival of Ashura, where the faithful show their grief over the killing of Hussein at the Battle of Karbala in 680. Ashura is a major festival that commemorates the death of Husayn (also spelled Hussein), grandson of Muhammad. The event led to the final split between the Sunni and Shia sects of Islam.