* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Proteasome-ubiquitin pathway in pathology
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Tay–Sachs disease wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Fetal origins hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
DiGeorge syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Down syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
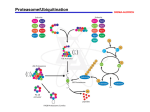
Proteasome-ubiquitin pathway in pathology • Nikolajs Sjakste, Faculty of Medicine, University of Latvia • Genetic and Environmental Influence of Bronchial Asthma in Taiwan, Latvia and Lithuania, • Tainan, 02.11.12 Proteasomes How the proteasome acts “E3-diseases” • • • • • • • There is only one E1 enzyme About 10 E2 enzymes 1000 E3 enzymes E3 enzymes are divided in 3 classes RING U-box HECT-domain E3 ligases What happens if a E3 enzyme gene of the proteasome-ubiquitin system gene is completely deleted? • Subtelomeric region of Chromosome 15 harbours UBE3A gene which encodes Ubiquitin-protein ligase E3A (UBE3A) Inheritance of the deletion from the mother on chromosome 15 produces Angelman syndrome • AS is characterized by intellectual and developmental delay, speech impediment, sleep disturbance, unstable jerky gait, seizures, hand flapping movements, frequent laughter/smiling and usually a happy demeanour. AS is a classic example of genetic imprinting caused by deletion or inactivation of critical genes on the maternally inherited chromosome 15. • Angelman syndrome can also be the result of mutation of a single gene. This gene (Ube3a) part of the ubiquitin pathway) is present on both the maternal and paternal chromosomes, but differs in the pattern of methylation (Imprinting). The paternal silencing of the Ube3a gene occurs in a brain region-specific manner; the maternal allele is active almost exclusively in the hippocampus and cerebellum. The most common genetic defect leading to Angelman syndrome is an ~4Mb (mega base) maternal deletion in chromosomal region 15q11-13 causing an absence of Ube3a expression in the maternally imprinted brain regions. Ube3a codes for an E6-AP ubiquitin ligase, which chooses its substrates very selectively and the four identified E6-AP substrates have shed little light on the possible molecular mechanisms underlying the human Angelman syndrome mental retardation state. E3 neurodevelopmental diseases Disease UPS component affected Function Angelman syndrome UBE3A E3 ligase Williams-Beuren syndrome TRIM50 E3 ligase Intellectual disability not otherwise specified CUL4B E3 ligase HUWE1 E3 ligase. Suppresses N-Myc-DLl3 cascade, stops proliferation enables neuronal differentiation A girl with Williams syndrome, illustrating typical facial features: broad forehead, short palpebral fissures, low nasal bridge, anteverted nostrils, long filtrum, full cheeks, and relatively large and often downturned mouth E3 neurodevelopmental diseases 2 Autism spectrum disorders Johanson-Blizzard syndrome UBE3A E3 ligase PARK2 E3 ligase RFWD2 E3 ligase FBXO40 Constitutes one of the four subunits of the ubiquitin protein ligase complex called SCFs (SKP1-cullin-F-box), E3 ligase UBR1 Johanson-Blizzard syndrome • Ectodermal displasia: • • • • • • Abnormal development of the pancreas Nose Scalp Mental retardaton Hearing loss Growth failure E3 neurodegenerative diseases Parkinson disease Parkin (PARK2) E3-ligase Machado-Joseph disease ATXN3 Ataxin-3 interacts with ubiquitinated proteins, can bind the proteasome, when the gene harbors an expanded repeat length, can interfere with the degradation substrates. Associates with the ubiquitin- and proteasome-binding factors Rad23 and valosin-containing protein (VCP/p97). proteins. E3 in inherited cancer syndromes • Von Hippel-Lindau syndrome • Adenomatous polyposis coli Von Hippel-Lindau syndrome pVHL is an E3 ligase Deubiqitination diseases Disease UPS component affected Function Ataxia USP-14 Ubiquitin carboxylterminal hydrolase 14 Parkinson disease UCH-L1 (PARK5) Ubiquitin carboxyterminal hydrolase L1 Immunoproteasomes • IFN-gamma induces the synthesis of three active site−containing beta-subunits as well as the synthesis of the proteasome maturation protein (POMP). • The immunosubunits 1i, 2i and 5i are preferentially incorporated into the 20S core after de novo synthesis to form the immunoproteasome. • In addition, IFN-gamma induces synthesis of PA28. Three PA28 and four P28 subunits form heptameric rings that can bind to the two outer alpha-rings of the 20S constitutive proteasome as well as the 20S immunoproteasome and activate the enzyme complex by opening the central gate. Immunoproteasomes “Immunoproteasome” diseases • Nakajo-Nishimura syndrome • JMP syndrome • CANDLE syndrome Nakajo-Nishimura syndrome • • • • an autoinflammatory disorder pernio-like rashes progressive partial lipodystrophy homozygous mutation c.224C > T in exon 2 the PSMB8 gene, which encodes the β5i subunit of immunoproteasome is responsible for development of the disease JMP syndrome • Recessive autoinflammatory syndrome characterized by joint contractures, muscle atrophy, microcytic anemia, and panniculitisinduced lipodystrophy (JMP) • Caused by homozygous missense mutation c.224C>T (p.Thr75Met) in the PSMB8 CANDLE syndrome • Chronic atypical neutrophilic dermatosis with lipodystrophy and elevated temperature is an autoinflammatory syndrome recently described in children. CANDLE syndrome is caused by mutations in PSMB8 • One patient was homozygous for a novel nonsense mutation in PSMB8 (c.405C>A), suggesting a protein truncation; • 4 patients were homozygous and 2 were heterozygous for a previously reported missense mutation (c.224C>T) Pathologies of “bad substrates” for proteasomes Polyglutamine (PolyQ) Diseases Disease Gene DRPLA ATN1 or (Dentatoru DRPLA bropallidolu ysian atrophy) Normal number of repeats Pathologic number of repeats between 6 and 35 copies of CAG between 49 and 88 copies Polyglutamine (PolyQ) Diseases 2 HD HD (Huntington's disease) between 10 and 35 copies of CAG more than 35 copies SBMA (Spinobulb ar muscular atrophy or Kennedy disease) between 9 and 36 copies of CAG between 38 and 62 copies AR Androgen receptor on the X chromosom e Models of Poly Q diseases Silica NPs • Aggregation-prone proteins • Amyloid formation • Insoluble aggregates Liddle syndrome • severe hypertension, hypokalemia, and metabolic alkalosis. • In contrast to hyperaldosteronism, which can result in similar symptoms, low aldosterone and renin levels • The gene responsible for Liddle syndrome was actually identified as a mutation in the beta subunit of the renal epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) . The site of the mutation is located in its binding site to Nedd4 (E3 ubiquitin ligase) . • Because Nedd4 cannot recognize the channel and target it for degradation,it accumulates. Thus, the mutation leads to excessive re-absorption of Na+ accompanied by water. Alzheimer’s disease • Mutated ubiquitin • Impaired proteasome function • More immunoproteasomes Ubiquitination sites on amino terminally processed tau. Ihara Y et al. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2012;2:a006361 ©2012 by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press Dysfunction of autophagic and endocytic pathways to lysosomes driven by relevant genes and other risk factors in Alzheimer disease (left side of the diagram) causes or promotes pathophysiology critical to the development and progression of Alzheimer disease... Ihara Y et al. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2012;2:a006361 ©2012 by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press Schematic illustrating the endocytic and the autophagic pathways to the lysosome. Ihara Y et al. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2012;2:a006361 ©2012 by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press Frontotemporal dementias • Ubiquitinylated TAR DNA-binding protein (TDP-43) accumulates • Ubiquilin 2 – involved in transport of ubiquinylated proteins to proteasome • FUS protein Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis • Ubiquitinylated TAR DNA-binding protein (TDP-43) accumulates Parkinson disease • Degradation of aplha-synuclein is a crucial question for Parkinson’s disease • Ubiquitin proteasomal system is defective in SN affected neurons • Autophagy-lysosomal pathway is also affected Parkinson disease (non-monogenic) • Dysfunction of the UPS • Reduced proteasome activity in the substantia nigra • Reduced expression of proteasomal subunits in the subsatntia nigra • Reduced proteasome activity and expression of UPS-related proteins in peripheral blood mononuclear cells • Altered proteasome function in toxin-based models of PD • Altered proteasome function in alpha -synuclein overexpressing rodents • Mutated PSMC1 subunit of ATPase in a rodent model SKP1A protein interacting E3 ligase is down-regulated in PD E2 Cullin Ub Early PD Late PD • Enahncement of autophagy by rapamycin (inhibitor of mTOR) is prospective for tratment of neurodeganerative diseases Autoimmune diseases • • • • • • Autonatibodies to proteasomes in Sjogren’ s syndrome SLE Rheumatoid arthritis Autoimmune myositis Result in decreased proteasomal activity Inflammatory response Inflammatory disease • Inflammatory arthritis. Proteasome inhibition improves the arhritis score. • Psoriasis. T-cell mediated disease, related to activation of NF-kappa. Proteasome inhibition reduces lesions. Asthma and allergy • Abnormal activation of of Type 2 helper cells. E3 ubiquitin ligase Itch maintains immune tolerance. Itch-deficient mice fail to block development of airway inflamamation. Cell proliferation and cancer Proteasomes regulate density of cardiac ion channels • Mutations in SCNA5 gene encoding Nav1.5 channel hindering its interactions with E3 (Nedd4-2) cause arrhythmias and conduction defects • Mutations in the gene hERG1 (K+ channel) resulting in its rapid decay cause the long QT syndrome Heart diseases Ub mRNA E2 mRNA Atrophy/ Unloading Hypertrophy Hypoxemia Heart failure Increased Increased Increased _ Increased Increased _ Heart diseases 2 Atrophy/ Unloading Hypertrophy Hypoxemia Heart failure E3 mRNA Atrogin 1 Decreased Increased Increased _ E3 mRNA MuRF1 Decreased Increased Increased _ Heart diseases 3 Atrophy/ Unloading Hypertrophy Hypoxemia Heart failure Proteasome proteolytic Activity Decreased Decreased Decreased PSMB4 mRNA Increased Increased Increased Heart diseases 4 Atrophy/ Unloading Deubiquitination enzymes Hypertrophy Hypoxemia Heart failure Increased Proteasome inhibitors • Cancer treatment • Antiinflammatory action Funding • Joint research project “Genetic studies of human diseases and longevity in Latvian population”, sub-project “Genome-wide scanning of proteasomal gene polymorphisms and their association with autoimmune diseases” - No 10.0010/09 • National Reserach Program 2010.10.-4/VPP4 „Creation of novel means and methods for prophylaxis, treatment and diagnostics, elaboration of biomedical Technologies for improvement of social health“ • ERAF project ESS2010/110 „Creation of a method for early diagnostics of autoimmune diseases” • Joint LV-LT-TW project “Proteasomal gene alleles as risk factors for bronchial asthma in Latvian, Lithuanian and Taiwanese populations” Ieguldījums Jūsu nākotnē