* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 6 - The Quantum Atomic Model SCH4U – Structure and Properties of
Quantum tunnelling wikipedia , lookup
Future Circular Collider wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Bremsstrahlung wikipedia , lookup
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
Dirac equation wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear structure wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Old quantum theory wikipedia , lookup
Atomic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
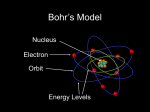
SCH4U – Structure and Properties of Matter 582715435 Date: ________________________ The Quantum Atomic Model Niels Bohr Bohr saw atomic spectra as evidence that the energy of electrons in an atom is “___________________” (limited to only certain __________________________) Bohr introduced the first “_________________ model” the atom by concluding that electrons in an atom are confided to discrete “___________________________” The energies that electrons can possess are determined by the allowable _______________________ in the atom In unenergized atoms, electrons would be found in their lowest possible energy levels, known as their “_______________________________” Bohr’s Model of the Atom All electrons have their __________________ at a certain distance from the nucleus Electrons exist in an orbit, but not in __________________ the levels Explained the line spectrum of ____________________ Page 1 of 6 SCH4U – Structure and Properties of Matter 582715435 Bohr’s Explanation of Atomic Spectra When energized, electrons can be “_________________” to higher energy levels Electron promotion requires that the electron gain the _______________ amount of energy required to make the ________________ from one allowable level to another The amount of energy required for a transition is equal to the energy ____________ between the two levels involved Bohr concluded that the “missing frequencies” of light in a dark line spectrum correspond to the specific _________________________ that will excite an electron from one lower level to another higher level The frequency of light = the ____________________ in _______________ (ΔE) between the two levels “_________________” electrons will eventually return to lower energy levels by _____________________ This energy is released as a photon of light of a specific frequency (_____________) The frequency of light emitted corresponds to the energy difference (ΔE) between the two energy levels involved in the electron transition Page 2 of 6 SCH4U – Structure and Properties of Matter 582715435 These frequencies of light would be visible as the distinct bands of light in the bright line spectrum Atomic spectra show these distinct bands of light because electrons cannot exist _____________________________________ and transitions between levels are _________________________ Bohr developed a _______________________ model of the hydrogen atom based on these ideas He developed an equation that allowed him to determine the energy of an electron in any energy level, n Knowing the energy of an electron in any energy level allowed Bohr to determine the ________________________ between any two levels Using Planck’s equation, Bohr was able to develop an equation that would allow him to _____________________________ of light in the hydrogen spectrum Bohr’s model not only successfully predicted the colours of light produced by hydrogen atoms in the visible region (________________ series) but also those that are produced in the infra-red region (_______________ series) and the ultra-violet region (______________ series) Page 3 of 6 SCH4U – Structure and Properties of Matter 582715435 Louis de Broglie de Broglie reasoned that if light has both _______________ and _______________ properties, then maybe particles also have _________ properties He considered the two equations defining energy: Using this equation, de Broglie was able to determine the wavelength of any moving particle given its _______________________ and ______________________ Applying this idea to the atom, de Broglie proposed that an electron behaves like a ____________________________ bound to the nucleus To explain the _____________________ of an electron de Broglie proposed that the ___________________ of the electron must fit the circumference of its orbit exactly, resulting in only a defined number of _____________________________________ Werner Heisenberg Heisenberg (1927) showed that due to the dual nature of matter, it is impossible to know simultaneously with exact precision, the ____________ and ______________ of a particle This became known as the “Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle” Applying this to the structure of the atom, it is impossible to know with any degree of certainty ________________ or ______________ an electron moves in an atom The act of determining the where an electron is disturbs the electron According to Heisenberg’s calculations, the uncertainty in the position of an electron in an atom is about the size of the atom itself! Page 4 of 6 SCH4U – Structure and Properties of Matter 582715435 Erwin Schrödinger Schrödinger used conventional wave equations to develop a __________________ __________________________________________________________________ The solutions to this equation provides us with what is called the electron’s “_______ _________________” (Ψ) which defines the ______________ of finding an electron in any given location around the nucleus This ________________________ of finding an electron is called an ____________ These equations assigned an electron a set of three _________________________ that defined an electron’s energy level, sublevel and orbital Max Born Used Schrödinger’s equations to develop _________________________ that could produce a plot of __________________________ which define a _______________ ____________________ in space around the nucleus where there is a 90% probability of finding an electron represents the electron’s ______________ Wolfgang Pauli Pauli proposed a fourth quantum number with _____ possible values to resolve inconsistencies between observed spectra and the developing theory of quantum mechanics The fourth quantum number relates to a property of the electron called _________ which is responsible for an electron’s weak _______________________ He formulated the “Pauli Exclusion Principle”, which stated that no two electrons could exist in the _______________________________ Page 5 of 6 SCH4U – Structure and Properties of Matter 582715435 Paul Dirac Dirac developed a new version of the wave equation that included the fourth quantum number for ______________________ An electron can have one of two possible spins (“______” or “_________”), resulting in two opposing magnetic fields Electrons with opposite ________ would have opposite _______________________ which would minimize ___________________ allowing these electrons to share the same region in space or _______________ Page 6 of 6